常量:
python中没有常量,只能通过名字特征来提示
例如:
全部大写,如 : OLDBOY_AGE=57
一.变量
变量
声明变量
#!/usr/bin/env python
age=18
gender1='male'
gender2='female'
变量作用:保存状态(程序的运行本质是一系列状态的变化,变量的目的就是用来保存状态,变量值的变化就构成了程序运行的不同结果。)
例如:CS枪战,一个人的生命可以表示为life=active表示存活,当满足某种条件后修改变量life=inactive表示死亡。
- 变量命名规则遵循标识符命名规则,详见第二篇
- name='lhf':'lhf'才是内存变量,name只是内存变量的引用
- 与c的区别在于变量赋值操作无返回值
- 链式赋值:y=x=a=1
- 多元赋值:x,y=1,2 x,y=y,x
- 增量赋值:x+=1
二.数据类型
2.1 什么是数据类型及数据类型分类
程序的本质就是驱使计算机去处理各种状态的变化,这些状态分为很多种
例如英雄联盟游戏,一个人物角色有名字,钱,等级,装备等特性,大家第一时间会想到这么表示
名字:德玛西亚------------>字符串
钱:10000 ------------>数字
等级:15 ------------>数字
装备:鞋子,日炎斗篷,兰顿之兆---->列表
(记录这些人物特性的是变量,这些特性的真实存在则是变量的值,存不同的特性需要用不同类型的值)
python中的数据类型
python使用对象模型来存储数据,每一个数据类型都有一个内置的类,每新建一个数据,实际就是在初始化生成一个对象,即所有数据都是对象
对象三个特性
- 身份:内存地址,可以用id()获取
- 类型:决定了该对象可以保存什么类型值,可执行何种操作,需遵循什么规则,可用type()获取
- 值:对象保存的真实数据
注:我们在定义数据类型,只需这样:x=1,内部生成1这一内存对象会自动触发,我们无需关心
这里的字符串、数字、列表等都是数据类型(用来描述某种状态或者特性)除此之外还有很多其他数据,处理不同的数据就需要定义不同的数据类型
| 标准类型 | 其他类型 |
| 数字 | 类型type |
| 字符串 | Null |
| 列表 | 文件 |
| 元组 | 集合 |
| 字典 | 函数/方法 |
| 类 | |
| 模块 |
2.2 标准数据类型:
2.2.1 数字
定义:a=1
特性:
1.只能存放一个值
2.一经定义,不可更改
3.直接访问
分类:整型,长整型,布尔,浮点,复数
2.2.1.1 整型:
Python的整型相当于C中的long型,Python中的整数可以用十进制,八进制,十六进制表示。
>>> 10 10 --------->默认十进制 >>> oct(10) '012' --------->八进制表示整数时,数值前面要加上一个前缀“0” >>> hex(10) '0xa' --------->十六进制表示整数时,数字前面要加上前缀0X或0x
python2.*与python3.*关于整型的区别
python2.*
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
python3.*整形长度无限制
2.2.1.2 长整型long:
python2.*:
跟C语言不同,Python的长整型没有指定位宽,也就是说Python没有限制长整型数值的大小,
但是实际上由于机器内存有限,所以我们使用的长整型数值不可能无限大。
在使用过程中,我们如何区分长整型和整型数值呢?
通常的做法是在数字尾部加上一个大写字母L或小写字母l以表示该整数是长整型的,例如:
a = 9223372036854775808L
注意,自从Python2起,如果发生溢出,Python会自动将整型数据转换为长整型,
所以如今在长整型数据后面不加字母L也不会导致严重后果了。
python3.*
长整型,整型统一归为整型
python2.7 >>> a=9223372036854775807 >>> a >>> a+=1 >>> a 9223372036854775808L python3.5 >>> a=9223372036854775807 >>> a >>> a+=1 >>> a 查看
''' # print(type(n)) # print(type(f)) # print(1.3e-3) # print(1.3e3) # print(bin(10)) #二进制 # print(oct(10)) #八进制 # # 0-9 a b c d e f # print(hex(10)) #16进制 ''' #数字类型的特点: # 1.只能存放一个值 # # 2.一经定义,不可更改,更改的是变量和值的对应关系 # # 3.直接访问 # x=10123123123 # print(id(x)) # x=11 # print(id(x)) # print(id(11)) #====================运行结果:===================== # D:Python36python.exe D:/py/train.py # 2368243792624 # 1640347008 # 1640347008 # Process finished with exit code 0 #================================================
2.2.1.3 布尔bool:
True 和False
1和0
2.2.1.4 浮点数float:
Python的浮点数就是数学中的小数,类似C语言中的double。
在运算中,整数与浮点数运算的结果是浮点数
浮点数也就是小数,之所以称为浮点数,是因为按照科学记数法表示时,
一个浮点数的小数点位置是可变的,比如,1.23*109和12.3*108是相等的。
浮点数可以用数学写法,如1.23,3.14,-9.01,等等。但是对于很大或很小的浮点数,
就必须用科学计数法表示,把10用e替代,1.23*109就是1.23e9,或者12.3e8,0.000012
可以写成1.2e-5,等等。
整数和浮点数在计算机内部存储的方式是不同的,整数运算永远是精确的而浮点数运算则可能会有
四舍五入的误差。
2.2.1.5 复数complex:
复数由实数部分和虚数部分组成,一般形式为x+yj,其中的x是复数的实数部分,y是复数的虚数部分,这里的x和y都是实数。
注意,虚数部分的字母j大小写都可以,
>>> 1.3 + 2.5j == 1.3 + 2.5J True
2.2.1.6 数字相关内建函数
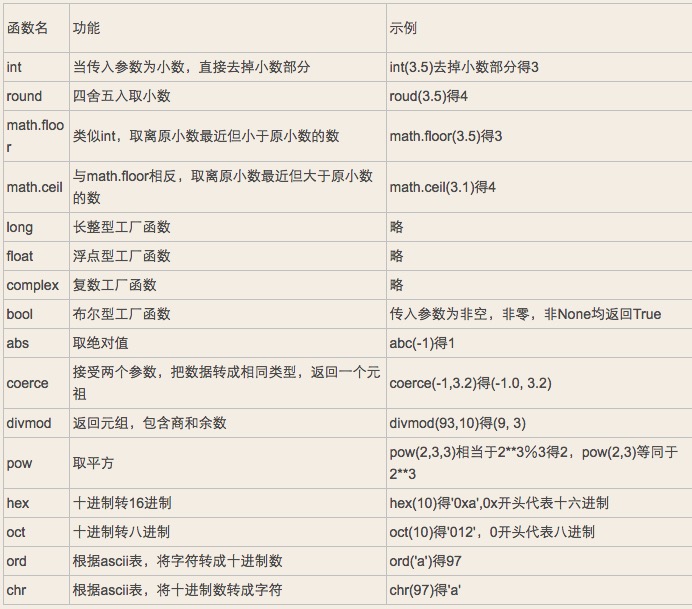
2.2.2 字符串
定义:它是一个有序的字符的集合,用于存储和表示基本的文本信息,‘’或“”或‘’‘ ’‘’中间包含的内容称之为字符串
特性:
1.只能存放一个值
2.不可变
3.按照从左到右的顺序定义字符集合,下标从0开始顺序访问,有序
补充:
1.字符串的单引号和双引号都无法取消特殊字符的含义,如果想让引号内所有字符均取消特殊意义,在引号前面加r,如name=r'l hf'
2.unicode字符串与r连用必需在r前面,如name=ur'l hf'
2.2.2.1 字符串创建
‘hello world’
2.2.2.2 字符串常用操作
移除空白
分割
长度
索引
切片
2.2.2.3 字符工厂函数str()

1 class str(object): 2 """ 3 str(object='') -> str 4 str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str 5 6 Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or 7 errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer 8 that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler. 9 Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined) 10 or repr(object). 11 encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding(). 12 errors defaults to 'strict'. 13 """ 14 def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 15 """ 16 首字母变大写 17 S.capitalize() -> str 18 19 Return a capitalized version of S, i.e. make the first character 20 have upper case and the rest lower case. 21 """ 22 return "" 23 24 def casefold(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 25 """ 26 S.casefold() -> str 27 28 Return a version of S suitable for caseless comparisons. 29 """ 30 return "" 31 32 def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 33 """ 34 原来字符居中,不够用空格补全 35 S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str 36 37 Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is 38 done using the specified fill character (default is a space) 39 """ 40 return "" 41 42 def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 43 """ 44 从一个范围内的统计某str出现次数 45 S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int 46 47 Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in 48 string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are 49 interpreted as in slice notation. 50 """ 51 return 0 52 53 def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 54 """ 55 encode(encoding='utf-8',errors='strict') 56 以encoding指定编码格式编码,如果出错默认报一个ValueError,除非errors指定的是 57 ignore或replace 58 59 S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes 60 61 Encode S using the codec registered for encoding. Default encoding 62 is 'utf-8'. errors may be given to set a different error 63 handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise 64 a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and 65 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with 66 codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors. 67 """ 68 return b"" 69 70 def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 71 """ 72 S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool 73 74 Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise. 75 With optional start, test S beginning at that position. 76 With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. 77 suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try. 78 """ 79 return False 80 81 def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 82 """ 83 将字符串中包含的 转换成tabsize个空格 84 S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str 85 86 Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces. 87 If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed. 88 """ 89 return "" 90 91 def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 92 """ 93 S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int 94 95 Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found, 96 such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional 97 arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. 98 99 Return -1 on failure. 100 """ 101 return 0 102 103 def format(self, *args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format 104 """ 105 格式化输出 106 三种形式: 107 形式一. 108 >>> print('{0}{1}{0}'.format('a','b')) 109 aba 110 111 形式二:(必须一一对应) 112 >>> print('{}{}{}'.format('a','b')) 113 Traceback (most recent call last): 114 File "<input>", line 1, in <module> 115 IndexError: tuple index out of range 116 >>> print('{}{}'.format('a','b')) 117 ab 118 119 形式三: 120 >>> print('{name} {age}'.format(age=12,name='lhf')) 121 lhf 12 122 123 S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str 124 125 Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs. 126 The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). 127 """ 128 pass 129 130 def format_map(self, mapping): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 131 """ 132 与format区别 133 '{name}'.format(**dict(name='alex')) 134 '{name}'.format_map(dict(name='alex')) 135 136 S.format_map(mapping) -> str 137 138 Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping. 139 The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). 140 """ 141 return "" 142 143 def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 144 """ 145 S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int 146 147 Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found. 148 """ 149 return 0 150 151 def isalnum(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 152 """ 153 至少一个字符,且都是字母或数字才返回True 154 155 S.isalnum() -> bool 156 157 Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric 158 and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. 159 """ 160 return False 161 162 def isalpha(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 163 """ 164 至少一个字符,且都是字母才返回True 165 S.isalpha() -> bool 166 167 Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic 168 and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. 169 """ 170 return False 171 172 def isdecimal(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 173 """ 174 S.isdecimal() -> bool 175 176 Return True if there are only decimal characters in S, 177 False otherwise. 178 """ 179 return False 180 181 def isdigit(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 182 """ 183 S.isdigit() -> bool 184 185 Return True if all characters in S are digits 186 and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. 187 """ 188 return False 189 190 def isidentifier(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 191 """ 192 字符串为关键字返回True 193 194 S.isidentifier() -> bool 195 196 Return True if S is a valid identifier according 197 to the language definition. 198 199 Use keyword.iskeyword() to test for reserved identifiers 200 such as "def" and "class". 201 """ 202 return False 203 204 def islower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 205 """ 206 至少一个字符,且都是小写字母才返回True 207 S.islower() -> bool 208 209 Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is 210 at least one cased character in S, False otherwise. 211 """ 212 return False 213 214 def isnumeric(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 215 """ 216 S.isnumeric() -> bool 217 218 Return True if there are only numeric characters in S, 219 False otherwise. 220 """ 221 return False 222 223 def isprintable(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 224 """ 225 S.isprintable() -> bool 226 227 Return True if all characters in S are considered 228 printable in repr() or S is empty, False otherwise. 229 """ 230 return False 231 232 def isspace(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 233 """ 234 至少一个字符,且都是空格才返回True 235 S.isspace() -> bool 236 237 Return True if all characters in S are whitespace 238 and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. 239 """ 240 return False 241 242 def istitle(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 243 """ 244 >>> a='Hello' 245 >>> a.istitle() 246 True 247 >>> a='HellP' 248 >>> a.istitle() 249 False 250 251 S.istitle() -> bool 252 253 Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one 254 character in S, i.e. upper- and titlecase characters may only 255 follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones. 256 Return False otherwise. 257 """ 258 return False 259 260 def isupper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 261 """ 262 S.isupper() -> bool 263 264 Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is 265 at least one cased character in S, False otherwise. 266 """ 267 return False 268 269 def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 270 """ 271 #对序列进行操作(分别使用' '与':'作为分隔符) 272 >>> seq1 = ['hello','good','boy','doiido'] 273 >>> print ' '.join(seq1) 274 hello good boy doiido 275 >>> print ':'.join(seq1) 276 hello:good:boy:doiido 277 278 279 #对字符串进行操作 280 281 >>> seq2 = "hello good boy doiido" 282 >>> print ':'.join(seq2) 283 h:e:l:l:o: :g:o:o:d: :b:o:y: :d:o:i:i:d:o 284 285 286 #对元组进行操作 287 288 >>> seq3 = ('hello','good','boy','doiido') 289 >>> print ':'.join(seq3) 290 hello:good:boy:doiido 291 292 293 #对字典进行操作 294 295 >>> seq4 = {'hello':1,'good':2,'boy':3,'doiido':4} 296 >>> print ':'.join(seq4) 297 boy:good:doiido:hello 298 299 300 #合并目录 301 302 >>> import os 303 >>> os.path.join('/hello/','good/boy/','doiido') 304 '/hello/good/boy/doiido' 305 306 307 S.join(iterable) -> str 308 309 Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the 310 iterable. The separator between elements is S. 311 """ 312 return "" 313 314 def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 315 """ 316 S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str 317 318 Return S left-justified in a Unicode string of length width. Padding is 319 done using the specified fill character (default is a space). 320 """ 321 return "" 322 323 def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 324 """ 325 S.lower() -> str 326 327 Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase. 328 """ 329 return "" 330 331 def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 332 """ 333 S.lstrip([chars]) -> str 334 335 Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed. 336 If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 337 """ 338 return "" 339 340 def maketrans(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 341 """ 342 Return a translation table usable for str.translate(). 343 344 If there is only one argument, it must be a dictionary mapping Unicode 345 ordinals (integers) or characters to Unicode ordinals, strings or None. 346 Character keys will be then converted to ordinals. 347 If there are two arguments, they must be strings of equal length, and 348 in the resulting dictionary, each character in x will be mapped to the 349 character at the same position in y. If there is a third argument, it 350 must be a string, whose characters will be mapped to None in the result. 351 """ 352 pass 353 354 def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 355 """ 356 以sep为分割,将S分成head,sep,tail三部分 357 358 S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) 359 360 Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it, 361 the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not 362 found, return S and two empty strings. 363 """ 364 pass 365 366 def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 367 """ 368 S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str 369 370 Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring 371 old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is 372 given, only the first count occurrences are replaced. 373 """ 374 return "" 375 376 def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 377 """ 378 S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int 379 380 Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found, 381 such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional 382 arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. 383 384 Return -1 on failure. 385 """ 386 return 0 387 388 def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 389 """ 390 S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int 391 392 Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found. 393 """ 394 return 0 395 396 def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 397 """ 398 S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str 399 400 Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is 401 done using the specified fill character (default is a space). 402 """ 403 return "" 404 405 def rpartition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 406 """ 407 S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) 408 409 Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return 410 the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the 411 separator is not found, return two empty strings and S. 412 """ 413 pass 414 415 def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 416 """ 417 S.rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings 418 419 Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the 420 delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and 421 working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit 422 splits are done. If sep is not specified, any whitespace string 423 is a separator. 424 """ 425 return [] 426 427 def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 428 """ 429 S.rstrip([chars]) -> str 430 431 Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed. 432 If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 433 """ 434 return "" 435 436 def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 437 """ 438 以sep为分割,将S切分成列表,与partition的区别在于切分结果不包含sep, 439 如果一个字符串中包含多个sep那么maxsplit为最多切分成几部分 440 >>> a='a,b c d e' 441 >>> a.split() 442 ['a,b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] 443 S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings 444 445 Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the 446 delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit 447 splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any 448 whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are 449 removed from the result. 450 """ 451 return [] 452 453 def splitlines(self, keepends=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 454 """ 455 Python splitlines() 按照行(' ', ' ', ')分隔, 456 返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表,如果参数 keepends 为 False,不包含换行符,如 果为 True,则保留换行符。 457 >>> x 458 'adsfasdf sadf asdf adf' 459 >>> x.splitlines() 460 ['adsfasdf', 'sadf', 'asdf', 'adf'] 461 >>> x.splitlines(True) 462 ['adsfasdf ', 'sadf ', 'asdf ', 'adf'] 463 464 S.splitlines([keepends]) -> list of strings 465 466 Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries. 467 Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends 468 is given and true. 469 """ 470 return [] 471 472 def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 473 """ 474 S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool 475 476 Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise. 477 With optional start, test S beginning at that position. 478 With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. 479 prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try. 480 """ 481 return False 482 483 def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 484 """ 485 S.strip([chars]) -> str 486 487 Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing 488 whitespace removed. 489 If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 490 """ 491 return "" 492 493 def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 494 """ 495 大小写反转 496 S.swapcase() -> str 497 498 Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase 499 and vice versa. 500 """ 501 return "" 502 503 def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 504 """ 505 S.title() -> str 506 507 Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case 508 characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case. 509 """ 510 return "" 511 512 def translate(self, table): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 513 """ 514 table=str.maketrans('alex','big SB') 515 516 a='hello abc' 517 print(a.translate(table)) 518 519 S.translate(table) -> str 520 521 Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped 522 through the given translation table. The table must implement 523 lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list, 524 mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If 525 this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched. 526 Characters mapped to None are deleted. 527 """ 528 return "" 529 530 def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 531 """ 532 S.upper() -> str 533 534 Return a copy of S converted to uppercase. 535 """ 536 return "" 537 538 def zfill(self, width): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 539 """ 540 原来字符右对齐,不够用0补齐 541 542 S.zfill(width) -> str 543 544 Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field 545 of the specified width. The string S is never truncated. 546 """ 547 return "" 548 549 def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 550 """ Return self+value. """ 551 pass 552 553 def __contains__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 554 """ Return key in self. """ 555 pass 556 557 def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 558 """ Return self==value. """ 559 pass 560 561 def __format__(self, format_spec): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 562 """ 563 S.__format__(format_spec) -> str 564 565 Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec. 566 """ 567 return "" 568 569 def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 570 """ Return getattr(self, name). """ 571 pass 572 573 def __getitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 574 """ Return self[key]. """ 575 pass 576 577 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 578 pass 579 580 def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 581 """ Return self>=value. """ 582 pass 583 584 def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 585 """ Return self>value. """ 586 pass 587 588 def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 589 """ Return hash(self). """ 590 pass 591 592 def __init__(self, value='', encoding=None, errors='strict'): # known special case of str.__init__ 593 """ 594 str(object='') -> str 595 str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str 596 597 Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or 598 errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer 599 that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler. 600 Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined) 601 or repr(object). 602 encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding(). 603 errors defaults to 'strict'. 604 # (copied from class doc) 605 """ 606 pass 607 608 def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 609 """ Implement iter(self). """ 610 pass 611 612 def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 613 """ Return len(self). """ 614 pass 615 616 def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 617 """ Return self<=value. """ 618 pass 619 620 def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 621 """ Return self<value. """ 622 pass 623 624 def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 625 """ Return self%value. """ 626 pass 627 628 def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 629 """ Return self*value.n """ 630 pass 631 632 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 633 def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 634 """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ 635 pass 636 637 def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 638 """ Return self!=value. """ 639 pass 640 641 def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 642 """ Return repr(self). """ 643 pass 644 645 def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 646 """ Return value%self. """ 647 pass 648 649 def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 650 """ Return self*value. """ 651 pass 652 653 def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 654 """ S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """ 655 pass 656 657 def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 658 """ Return str(self). """ 659 pass 660 661 字符串工厂函数 662 663 字符串工厂函数
2.2.2.4 常用举例
s.strip() s.split() s.find() #搜索,索引或-1 s.index() #搜索,但是报错 s.count() s.replace() s.startwith() s.endwith() s.isdigit() s[1:5:2]

# -*-coding:UTF-8-*- # 字符串: #补充 # x='a' #x=str('a') 字符串操作本质上都是调用str() # x.replace ===> str.replace() ''' #字符串类型:引号包含的都是字符串类型 #需要掌握的常用操作: msg='hello' 移除空白 msg.strip() 分割msg.split('|') 长度len(msg) 索引msg[3] msg[-1] 切片msg[0:5:2] #0 2 4 ''' # 字符串 # s='hello world' # s1="hello world" # s2="""hello world""" # s3='''hello world''' # print(type(s)) # print(type(s1)) # print(type(s2)) # print(type(s3)) ''' # x='*****egon********' # x=x.strip() #strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格)。 # print(x) # print(x.strip('*')) ''' #首字母大写 # x='hello' # print(x.capitalize()) ''' #所有字母大写 # x='hello' # print(x.upper()) ''' # #居中显示 # x='hello' # print(x.center(30,'#')) ''' #统计某个字符的长度,空格也算字符 # x='hel lo love' # print(x.count('l')) # print(x.count('l',0,4)) # 0 1 2 3 ''' # x='hello ' #开始的字符、末尾的字符分别是什么 # print(x.endswith(' ')) # print(x.startswith('h')) ''' # x='hello ' #find() 方法检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str , # print(x.find('e')) #如果指定 beg(开始) 和 end(结束) 范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内, # print(x.find('l')) #如果包含子字符串返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。 ''' # 格式化字符串 # msg='Name:{},age:{},sex:{}' # print(msg) #Name:{},age:{},sex:{} # print(msg.format('egon',18,'male')) # msg='Name:{0},age:{1},sex:{0}' # print(msg.format('aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa','bbbbbbbbbbbbbb')) # msg='Name:{x},age:{y},sex:{z}' # print(msg.format(y=18,x='egon',z='male')) ''' # x='hello world' # print(x[0]) # print(x[4]) # print(x[5]) # print(x[100]) #报错 # print(x[-1]) # print(x[-3]) # print(x[1:3]) # print(x[1:5:2]) #始 末 步长 ''' # x='hello' #方法检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str , # print(x.index('o')) #如果指定 beg(开始) 和 end(结束) 范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内, # print(x[4]) #该方法与 python find()方法一样,只不过如果str不在 string中会报一个异常。 # print(x[x.index('o')]) ''' # x='123' # print(x.isdigit()) #检测字符串是否只由数字组成。 # # age=input('age: ') # if age.isdigit(): # new_age=int(age) # print(new_age,type(new_age)) ''' # msg='hello alex' # print(msg.replace('x','X')) # print(msg.replace('alex','SB')) # print(msg.replace('l','A')) # print(msg.replace('l','A',1)) #替换一个 # print(msg.replace('l','A',2)) #替换两个 ''' # x='hello world alex SB' # x='root:x:0:0::/root:/bin/bash' # print(x.split(':')) # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,如果参数num 有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串 # 语法:str.split(str="", num=string.count(str)). # num是指切几次,切出几个 ''' # x='hello' # # print(x.upper()) #全部变成大写 # x='H' # print(x.isupper()) #是否是大写 # x='HELLO' # print(x.islower()) #是否是小写 # print(x.lower()) #全部变成小写 # x=' ' # print(x.isspace()) #是否全是空格 # msg='Hello' # msg='hEEEE' # print(msg.istitle()) #首字母大写/字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写。 # # x='hello' # print(x.title()) #首字母大写 # x='abc' # print(x.ljust(10,'*')) # print(x.rjust(10,'*')) # ljust() 方法返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至指定长度的新字符串。如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。 # 语法:str.ljust(width[, fillchar]) # rjust是右对齐 # x='Ab' # print(x.swapcase()) #对字符串的大小写字母进行转换。
2.2.3 列表
列表之间可以比较大小,从第一个元素开始比较,只要这个元素能够分出大小就结束
定义:[]内以逗号分隔,按照索引,存放各种数据类型,每个位置代表一个元素
特性:
1.可存放多个值
2.可修改指定索引位置对应的值,可变
3.按照从左到右的顺序定义列表元素,下标从0开始顺序访问,有序
2.2.3.1 列表创建
list_test=[’lhf‘,12,'ok']
或
list_test=list('abc')
或
list_test=list([’lhf‘,12,'ok'])
2.2.3.2 列表常用操作
索引
切片
追加
删除
长度
切片
循环
包含
2.2.4 元组
定义:与列表类似,只不过[]改成()
特性:
1.可存放多个值
2.不可变
3.按照从左到右的顺序定义元组元素,下标从0开始顺序访问,有序
2.2.4.1 元组创建
ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55)
或
ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
2.2.4.2 元组常用操作
索引
切片
循环
长度
包含
2.2.4.3 元组工厂函数tuple()
2.2.5 字典
定义:{key1:value1,key2:value2},key-value结构,key必须可hash
特性:
1.可存放多个值
2.可修改指定key对应的值,可变
3.无序
2.2.5.1 字典创建
person = {"name": "sb", 'age': 18}
或
person = dict(name='sb', age=18)
person = dict({"name": "sb", 'age': 18})
person = dict((['name','sb'],['age',18]))
{}.fromkeys(seq,100) #不指定100默认为None
注意:
>>> dic={}.fromkeys(['k1','k2'],[])
>>> dic
{'k1': [], 'k2': []}
>>> dic['k1'].append(1)
>>> dic
{'k1': [1], 'k2': [1]}
2.2.5.2 字典常用操作
索引
新增
删除
键、值、键值对
循环
长度
2.2.5.3 字典工厂函数dict()
2.2.6 集合
定义:由不同元素组成的集合,集合中是一组无序排列的可hash值,可以作为字典的key
特性:
1.集合的目的是将不同的值存放到一起,不同的集合间用来做关系运算,无需纠结于集合中单个值
2.2.6.1 集合创建
{1,2,3,1}
或
定义可变集合set
>>> set_test=set('hello')
>>> set_test
{'l', 'o', 'e', 'h'}
改为不可变集合frozenset
>>> f_set_test=frozenset(set_test)
>>> f_set_test
frozenset({'l', 'e', 'h', 'o'})
2.2.6.2 集合常用操作:关系运算
in
not in
==
!=
<,<=
>,>=
|,|=:合集
&.&=:交集
-,-=:差集
^,^=:对称差分
2.2.7 bytes类型
定义:存8bit整数,数据基于网络传输或内存变量存储到硬盘时需要转成bytes类型,字符串前置b代表为bytes类型
>>> x
'hello sb'
>>> x.encode('gb2312')
b'hello sb'
2.2.8 数据类型转换内置函数汇总
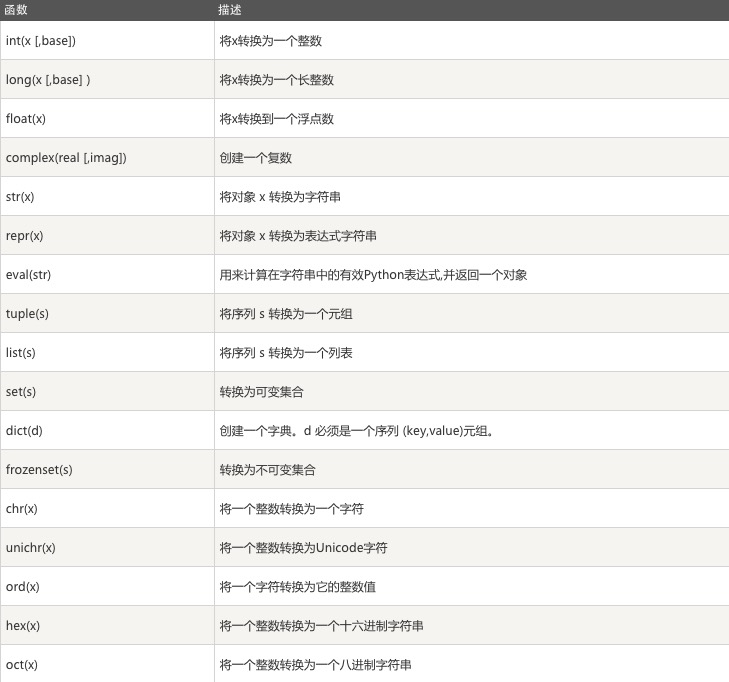
注:真对acsii表unichr在python2.7中比chr的范围更大,python3.*中chr内置了unichar
三 算数运算;逻辑运算;比较运算;关系运算;
四.标准数据类型特性总结
按存值个数区分
| 标量/原子类型 | 数字,字符串 |
| 容器类型 | 列表,元组,字典 |
按可变不可变区分
| 可变 | 列表,字典 |
| 不可变 | 数字,字符串,元组 |
按访问顺序区分
| 直接访问 | 数字 |
| 顺序访问(序列类型) | 字符串,列表,元组 |
| key值访问(映射类型) | 字典 |
