20.01 递归概述和注意事项
递归:方法定义中调用方法本身的现象
递归注意事项:
1.要有出口,否则就是死递归
2.次数不能太多,否则就内存溢出
3.构造方法不能递归使用
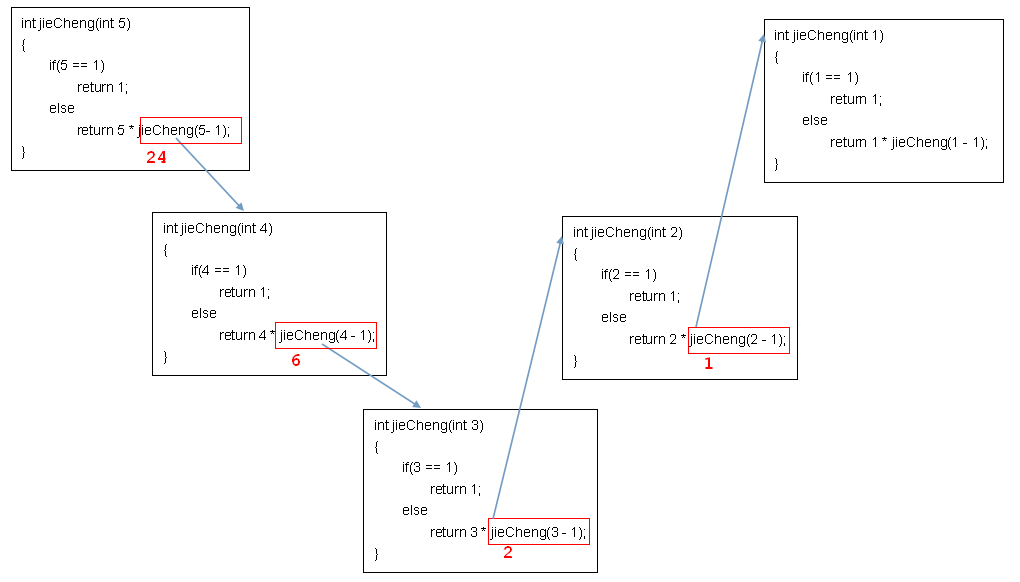
20.02 递归求阶乘的代码实现及内存图解
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 System.out.println(jieCheng(5)); 6 } 7 public static int jieCheng(int i) 8 { 9 if(i == 1) 10 return 1; 11 else 12 return i * jieCheng(i - 1); 13 } 14 }
20.03 不死神兔问题案例
有一对兔子,从出生后第3个月起每个月都生一对兔子,小兔子长到第三个月后每个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问第二十个月的兔子对数为多少?
第1个月:1 第2个月:1 第3个月:2
第4个月:3 第5个月:5 第6个月:8
...
由此可见兔子对象的数据是:1,1,2,3,5,8...
规则:A:从第三项开始,每一项是前两项之和
B:而且说明前两项是已知的
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 //方式1:数组实现 6 int[] arr = new int[20]; 7 arr[0] = 1; 8 arr[1] = 1; 9 for(int i = 2 ; i < arr.length; i++) 10 { 11 arr[i] = arr[i - 2] + arr[i - 1]; 12 } 13 System.out.println(arr[19]); 14 System.out.println("------"); 15 //方式2:变量的变化实现 16 int a = 1; 17 int b = 1; 18 for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++) 19 { 20 int temp = a; 21 a = b; 22 b = temp + b; 23 } 24 System.out.println(b); 25 System.out.println("------"); 26 //方式3 27 System.out.println(sum(20)); 28 } 29 //方式3:递归实现 30 public static int sum(int i) 31 { 32 if(i == 1 || i == 2) 33 return 1; 34 else 35 return sum(i - 1) + sum(i - 2); 36 } 37 }
20.04 递归输出指定目录下所有的java文件的绝对路径案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 File f = new File("E:\javaSE"); 6 getAllJavaFilePaths(f); 7 } 8 public static void getAllJavaFilePaths(File srcFolder) 9 { 10 // 获取该目录下所有的文件或者文件夹的File数组 11 File[] fileArray = srcFolder.listFiles(); 12 13 // 遍历该File数组,得到每一个File对象 14 for (File file : fileArray) 15 { 16 // 判断该File对象是否是文件夹 17 if (file.isDirectory()) 18 { 19 //如果是目录继续进入 20 getAllJavaFilePaths(file); 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 // 继续判断是否以.java结尾 25 if (file.getName().endsWith(".java")) 26 { 27 // 就输出该文件的绝对路径 28 System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }
20.05 递归删除带内容的目录案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 File f = new File("D:\demo"); 6 deleteFolder(f); 7 } 8 private static void deleteFolder(File srcFolder) 9 { 10 // 获取该目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的File数组 11 File[] fileArray = srcFolder.listFiles(); 12 if (fileArray != null) 13 { 14 // 遍历该File数组,得到每一个File对象 15 for (File file : fileArray) 16 { 17 // 判断该File对象是否是文件夹 18 if (file.isDirectory()) 19 { 20 deleteFolder(file); 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 file.delete(); 25 System.out.println("删除文件:"+file.getName()); 26 } 27 } 28 //删除文件夹 29 srcFolder.delete(); 30 System.out.println("删除文件夹:"+srcFolder.getName()); 31 } 32 } 33 }
20.06 IO流概述及分类
IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输
Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式
Java用于操作流的对象都在IO包中
20.07 IO流基类概述
按照数据流向:输入流[读入数据]、输出流[写出数据]
按照数据类型:
字节流字节输入流[InputStream]、字节输出流[OutputStream]
字符流字符输入流[Reader]、字符输出流[Writer]
注:由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名的后缀
InputStream:此抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。
OutputStream:此抽象类是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。
Reader:用于读取字符流的抽象类。
Writer:写入字符流的抽象类。
20.08 FileOutputStream的构造方法
FileOutputStream的构造方法
public FileOutputStream(File file)throws FileNotFoundException
创建一个向指定 File 对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。
public FileOutputStream(String name)throws FileNotFoundException
创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。
20.09 FileOutputStream写出数据
例:
1 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt"); 2 fos.write("hello,IO".getBytes()); 3 //释放资源,关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。 4 fos.close();
创建字节输出流对象了做了3件事情:
A:调用系统功能去创建文件
B:创建fos对象
C:把fos对象指向这个文件
字节输出流操作步骤:
A:创建字节输出流对象
B:写数据
C:释放资源
为什么一定要close()
A:让流对象变成垃圾,这样就可以被垃圾回收器回收了
B:通知系统去释放跟该文件相关的资源
20.10 FileOutputStream的三个write()方法
FileOutputStream 的方法:
1.public void write(int b)throws IOException
将指定字节写入此文件输出流。实现 OutputStream 的 write 方法。
2.public void write(byte[] b)throws IOException
将 b.length 个字节从指定 byte 数组写入此文件输出流中。
3.public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len)throws IOException
将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此文件输出流。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt"); 6 //写一个字节 7 fos.write(97); 8 byte[] bys = {97,98,99,100,101}; 9 //写一个字节数组 10 fos.write(bys); 11 //写一个字节数组的一部分,从1开始写3个 12 fos.write(bys,1,3); 13 //释放资源 14 fos.close(); 15 } 16 }
文件a.txt中的内容:aabcdebcd
20.11 FileOutputStream写出数据实现换行和追加写入
public FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append)throws FileNotFoundException
创建一个向具有指定 name 的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。如果第二个参数为 true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 //true表示每次将内容写到文件的末尾 6 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt",true); 7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 8 { 9 fos.write(("hello"+i).getBytes()); 10 //写入换行符,不同系统下的换行符是不一样的,Windows下为 11 fos.write(" ".getBytes()); 12 } 13 //释放资源 14 fos.close(); 15 } 16 }
20.12 FileOutputStream写出数据异常处理
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 FileOutputStream fos = null; 6 try 7 { 8 fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt"); 9 fos.write("hello".getBytes()); 10 } 11 catch (FileNotFoundException e) 12 { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 catch(IOException e) 16 { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 finally 20 { 21 //fos不是null才close() 22 if(fos != null) 23 { 24 //保证close一定会执行 25 try { 26 fos.close(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }
20.13 FileInputStream读取数据
FileInputStream的构造方法
1.public FileInputStream(File file)throws FileNotFoundException
通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的 File 对象 file 指定。
2.public FileInputStream(String name)throws FileNotFoundException
通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的路径名 name 指定。
FileInputStream的成员方法
1.public int read()throws IOException
从此输入流中读取一个数据字节。
2.public int read(byte[] b)throws IOException
从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"); 6 // //读一个字节,没有数据返回-1 7 // int by = fis.read(); 8 // System.out.println((char)by); 9 //循环读取 10 int ch = 0; 11 while((ch = fis.read()) != -1) 12 { 13 //此处如果读中文会出现乱码,因为一个汉字占用两个字节 14 System.out.print((char)ch); 15 } 16 fis.close(); 17 } 18 }
20.14 字节流复制文本文件案例(一次读一个字节)
数据源:从哪里来 a.txt--读取数据--FileInputStream
目的地:到哪里去 b.txt--写数据--FileOutputStream
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装数据源 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\a.txt"); 7 // 封装目的地 8 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\b.txt"); 9 10 int by = 0; 11 while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) 12 { 13 fos.write(by); 14 } 15 16 // 释放资源 17 fos.close(); 18 fis.close(); 19 } 20 }
20.15 计算机是如何识别把两个字节拼接为中文
例:
1 String s = "你好中国"; 2 byte[] bys = s.getBytes(); 3 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys));
运行结果:
[-60, -29, -70, -61, -42, -48, -71, -6]
上例中在GBK编码下将"你好中国"转为字节数组发现数组中的元素都是负数
在计算机中中文的存储分两个字节:
第一个字节肯定是负数。
第二个字节常见的是负数,可能有正数。但是没影响。
20.16 字节流复制图片案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\06.jpg"); 6 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\006.jpg"); 7 8 int by = 0; 9 while((by = fis.read()) != -1) 10 { 11 fos.write(by); 12 } 13 14 fis.close(); 15 fos.close(); 16 } 17 }
20.17 FileInputStream读取数据一次一个字节数组
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"); 6 7 //数组的长度一般是1024或者1024的整数倍 8 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 9 int len = 0;//定义一个变量用于接收读取的字节个数 10 while((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) 11 { 12 //将数组的一部分转成字符串,因为数组不一定每次都是读满的 13 //读多少数据就转多少数据 14 //不需要换行符 15 System.out.print(new String(bys, 0, len)); 16 17 } 18 //释放资源 19 fis.close(); 20 } 21 }
20.18 字节流复制文本文件案例(一次读一个字节数组)
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 //原数据 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"); 7 //目的数据 8 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\c.txt"); 9 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 10 int len = 0; 11 while((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) 12 { 13 fos.write(bys, 0, len); 14 } 15 //释放资源 16 fis.close(); 17 fos.close(); 18 } 19 }
20.19 字节流复制视频案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 //原数据 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\test.flv"); 7 //目的数据 8 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\aaa.flv"); 9 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 10 int len = 0; 11 while((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) 12 { 13 fos.write(bys, 0, len); 14 } 15 //释放资源 16 fis.close(); 17 fos.close(); 18 } 19 }
20.20 BufferedOutputStream写出数据
字节流一次读写一个数组的速度明显比一次读写一个字节的速度快很多,这是加入了数组这样的缓冲区效果,java本身在设计的时候,也考虑到了这样的设计思想(装饰设计模式),所以提供了字节缓冲区流
字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream
字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream构造方法:
1.public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的底层输出流。
2.public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out,int size)
创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将具有指定缓冲区大小的数据写入指定的底层输出流。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt"); 6 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 7 //写数据 8 bos.write("hello".getBytes()); 9 //关闭资源 10 bos.close(); 11 } 12 }
20.21 BufferedInputStream读取数据
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 BufferedInputStream bis1 = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt")); 6 //方式1:读一个字节 7 int by = 0; 8 while((by = bis1.read()) != -1) 9 { 10 System.out.print((char)by); 11 } 12 System.out.println("------"); 13 //方式2:读一个字节数组 14 BufferedInputStream bis2 = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt")); 15 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 16 int len = 0; 17 while((len = bis2.read(bys)) != -1) 18 { 19 System.out.println(new String(bys, 0, len)); 20 } 21 22 bis1.close(); 23 bis2.close(); 24 } 25 }
20.22 字节流四种方式复制MP4并测试效率
基本字节流一次读写一个字节 //耗时:103891毫秒
基本字节流一次读写一个字节数组 //耗时:1110毫秒
高效字节流一次读写一个字节 //耗时:1547毫秒
高效字节流一次读写一个字节数组 //耗时:953毫秒
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 6 // method1("C:\test.flv","D:\test1.flv"); 7 // method2("C:\test.flv","D:\test2.flv"); 8 // method3("C:\test.flv","D:\test3.flv"); 9 method4("C:\test.flv","D:\test4.flv"); 10 long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 11 System.out.println("耗时:"+(time2 - time1)+"毫秒"); 12 } 13 //基本字节流一次读写一个字节 14 //耗时:103891毫秒 15 public static void method1(String src,String dest) throws IOException 16 { 17 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); 18 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest); 19 20 int by = 0; 21 while((by = fis.read()) != -1) 22 { 23 fos.write(by); 24 } 25 26 fis.close(); 27 fos.close(); 28 } 29 //基本字节流一次读写一个字节数组 30 //耗时:1110毫秒 31 public static void method2(String src,String dest) throws IOException 32 { 33 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); 34 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest); 35 36 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 37 int len = 0; 38 while((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) 39 { 40 fos.write(bys,0,len); 41 } 42 43 fis.close(); 44 fos.close(); 45 } 46 //高效字节流一次读写一个字节 47 //耗时:1547毫秒 48 public static void method3(String src,String dest) throws IOException 49 { 50 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 51 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); 52 53 int by = 0; 54 while ((by = bis.read()) != -1) 55 { 56 bos.write(by); 57 } 58 59 bos.close(); 60 bis.close(); 61 } 62 //高效字节流一次读写一个字节数组 63 //耗时:953毫秒 64 public static void method4(String src,String dest) throws IOException 65 { 66 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 67 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); 68 69 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 70 int len = 0; 71 while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) 72 { 73 bos.write(bys, 0, len); 74 } 75 76 bos.close(); 77 bis.close(); 78 } 79 }