第四十一讲!分词器内部组成 内置分词器
课程大纲
1、什么是分词器
切分词语,normalization(提升recall召回率)
给你一段句子,然后将这段句子拆分成一个一个的单个的单词,同时对每个单词进行normalization(时态转换,单复数转换),分词器
recall,召回率:搜索的时候,增加能够搜索到的结果的数量
character filter:在一段文本进行分词之前,先进行预处理,比如说最常见的就是,过滤html标签(<span>hello<span> --> hello),& --> and(I&you --> I and you)
tokenizer:分词,hello you and me --> hello, you, and, me
token filter:lowercase,stop word,synonymom,dogs --> dog,liked --> like,Tom --> tom,a/the/an --> 干掉,mother --> mom,small --> little
一个分词器,很重要,将一段文本进行各种处理,最后处理好的结果才会拿去建立倒排索引
2、内置分词器的介绍
Set the shape to semi-transparent by calling set_trans(5)
standard analyzer:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set_trans, 5(默认的是standard)
simple analyzer:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set, trans
whitespace analyzer:Set, the, shape, to, semi-transparent, by, calling, set_trans(5)
language analyzer(特定的语言的分词器,比如说,english,英语分词器):set, shape, semi, transpar, call, set_tran, 5
第四十二讲!query string分词 以及 mapping
课程大纲
1、query string分词
query string必须以和index建立时相同的analyzer进行分词
query string对exact value和full text的区别对待
date:exact value
_all:full text
比如我们有一个document,其中有一个field,包含的value是:hello you and me,建立倒排索引
我们要搜索这个document对应的index,搜索文本是hell me,这个搜索文本就是query string
query string,默认情况下,es会使用它对应的field建立倒排索引时相同的分词器去进行分词,分词和normalization,只有这样,才能实现正确的搜索
我们建立倒排索引的时候,将dogs --> dog,结果你搜索的时候,还是一个dogs,那不就搜索不到了吗?所以搜索的时候,那个dogs也必须变成dog才行。才能搜索到。
知识点:不同类型的field,可能有的就是full text,有的就是exact value
post_date,date:exact value
_all:full text,分词,normalization
2、mapping引入案例遗留问题大揭秘
GET /_search?q=2017
搜索的是_all field,document所有的field都会拼接成一个大串,进行分词
2017-01-02 my second article this is my second article in this website 11400

_all,2017,自然会搜索到3个docuemnt
GET /_search?q=2017-01-01
_all,2017-01-01,query string会用跟建立倒排索引一样的分词器去进行分词
2017
01
01
GET /_search?q=post_date:2017-01-01
date,会作为exact value去建立索引
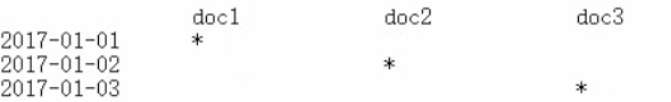
post_date:2017-01-01,2017-01-01,doc1一条document
GET /_search?q=post_date:2017,这个在这里不讲解,因为是es 5.2以后做的一个优化
3、测试分词器
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Text to analyze"
}
第四十三讲!mapping
课程大纲
(1)往es里面直接插入数据,es会自动建立索引,同时建立type以及对应的mapping
(2)mapping中就自动定义了每个field的数据类型
(3)不同的数据类型(比如说text和date),可能有的是exact value,有的是full text
(4)exact value,在建立倒排索引的时候,分词的时候,是将整个值一起作为一个关键词建立到倒排索引中的;full text,会经历各种各样的处理,分词,normaliztion(时态转换,同义词转换,大小写转换),才会建立到倒排索引中
(5)同时呢,exact value和full text类型的field就决定了,在一个搜索过来的时候,对exact value field或者是full text field进行搜索的行为也是不一样的,会跟建立倒排索引的行为保持一致;比如说exact value搜索的时候,就是直接按照整个值进行匹配,full text query string,也会进行分词和normalization再去倒排索引中去搜索
(6)可以用es的dynamic mapping,让其自动建立mapping,包括自动设置数据类型;也可以提前手动创建index和type的mapping,自己对各个field进行设置,包括数据类型,包括索引行为,包括分词器,等等
mapping,就是index的type的元数据,每个type都有一个自己的mapping,决定了数据类型,建立倒排索引的行为,还有进行搜索的行为
第四十四讲!44.初识搜索引擎_mapping的核心数据类型以及dynamic mapping
课程大纲
1、核心的数据类型
string
byte,short,integer,long
float,double
boolean
date
2、dynamic mapping
true or false --> boolean
123 --> long
123.45 --> double
2017-01-01 --> date
"hello world" --> string/text
3、查看mapping
GET /index/_mapping/type
第四十五讲!45.初识搜索引擎_手动建立和修改mapping以及定制string类型数据是否分词
课程大纲
1、如何建立索引
analyzed
not_analyzed
no
2、修改mapping
只能创建index时手动建立mapping,或者新增field mapping,但是不能update field mapping
PUT /website
{
"mappings": {
"article": {
"properties": {
"author_id": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"post_date": {
"type": "date"
},
"publisher_id": {
"type": "text",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT /website
{
"mappings": {
"article": {
"properties": {
"author_id": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "index_already_exists_exception",
"reason": "index [website/co1dgJ-uTYGBEEOOL8GsQQ] already exists",
"index_uuid": "co1dgJ-uTYGBEEOOL8GsQQ",
"index": "website"
}
],
"type": "index_already_exists_exception",
"reason": "index [website/co1dgJ-uTYGBEEOOL8GsQQ] already exists",
"index_uuid": "co1dgJ-uTYGBEEOOL8GsQQ",
"index": "website"
},
"status": 400
}
PUT /website/_mapping/article
{
"properties" : {
"new_field" : {
"type" : "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
"index":true /false
3、测试mapping
GET /website/_analyze
{
"field": "content",
"text": "my-dogs"
}
GET website/_analyze
{
"field": "new_field",
"text": "my dogs"
}
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "remote_transport_exception",
"reason": "[4onsTYV][127.0.0.1:9300][indices:admin/analyze[s]]"
}
],
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Can't process field [new_field], Analysis requests are only supported on tokenized fields"
},
"status": 400
}
第46讲!46.初识搜索引擎_mapping复杂数据类型以及object类型数据底层结构大揭秘
课程大纲
1、multivalue field
{ "tags": [ "tag1", "tag2" ]}
建立索引时与string是一样的,数据类型不能混
2、empty field
null,[],[null]
3、object field
PUT /company/employee/1
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age": 27,
"join_date": "2017-01-01"
}


address:object类型
{
"company": {
"mappings": {
"employee": {
"properties": {
"address": {
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"country": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"province": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"join_date": {
"type": "date"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
object数据结构
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age": 27,
"join_date": "2017-01-01"
}
{
"name": [jack],
"age": [27],
"join_date": [2017-01-01],
"address.country": [china],
"address.province": [guangdong],
"address.city": [guangzhou]
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
变为列式存储
{
"authors": [
{ "age": 26, "name": "Jack White"},
{ "age": 55, "name": "Tom Jones"},
{ "age": 39, "name": "Kitty Smith"}
]
}
{
"authors.age": [26, 55, 39],
"authors.name": [jack, white, tom, jones, kitty, smith]
}
第 47讲.初识搜索引擎_search api的基础语法介绍
课程大纲
1、search api的基本语法
GET /search
{}
GET /index1,index2/type1,type2/search
{}
GET /_search
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10
}
2、http协议中get是否可以带上request body
HTTP协议,一般不允许get请求带上request body,但是因为get更加适合描述查询数据的操作,因此还是这么用了
GET /_search?from=0&size=10
POST /_search
{
"from":0,
"size":10
}
碰巧,很多浏览器,或者是服务器,也都支持GET+request body模式
如果遇到不支持的场景,也可以用POST /_search
第48讲.初识搜索引擎_快速上机动手实战Query DSL搜索语法
课程大纲
1、一个例子让你明白什么是Query DSL
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2、Query DSL的基本语法
{
QUERY_NAME: {
ARGUMENT: VALUE,
ARGUMENT: VALUE,...
}
}
{
QUERY_NAME: {
FIELD_NAME: {
ARGUMENT: VALUE,
ARGUMENT: VALUE,...
}
}
}
示例:
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"test_field": "test"
}
}
}
3、如何组合多个搜索条件
搜索需求:title必须包含elasticsearch,content可以包含elasticsearch也可以不包含,author_id必须不为111
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "article",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "my hadoop article",
"content": "hadoop is very bad",
"author_id": 111
}
},
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "article",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "my elasticsearch article",
"content": "es is very bad",
"author_id": 110
}
},
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "article",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "my elasticsearch article",
"content": "es is very goods",
"author_id": 111
}
}
]
}
}
GET /website/article/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"title": "elasticsearch"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"content": "elasticsearch"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"author_id": 111
}
}
]
}
}
}
GET /test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "name": "tom" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "hired": true }},
{ "bool": {
"must": { "match": { "personality": "good" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "rude": true }}
}}
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
}
第49.初识搜索引擎_filter与query深入对比解密:相关度,性能
课程大纲
1、filter与query示例
PUT /company/employee/2
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "jiangsu",
"city": "nanjing"
},
"name": "tom",
"age": 30,
"join_date": "2016-01-01"
}
PUT /company/employee/3
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "shanxi",
"city": "xian"
},
"name": "marry",
"age": 35,
"join_date": "2015-01-01"
}
搜索请求:年龄必须大于等于30,同时join_date必须是2016-01-01
GET /company/employee/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"join_date": "2016-01-01"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30
}
}
}
}
}
}
2、filter与query对比大解密
filter,仅仅只是按照搜索条件过滤出需要的数据而已,不计算任何相关度分数,对相关度没有任何影响
query,会去计算每个document相对于搜索条件的相关度,并按照相关度进行排序
一般来说,如果你是在进行搜索,需要将最匹配搜索条件的数据先返回,那么用query;如果你只是要根据一些条件筛选出一部分数据,不关注其排序,那么用filter
除非是你的这些搜索条件,你希望越符合这些搜索条件的document越排在前面返回,那么这些搜索条件要放在query中;如果你不希望一些搜索条件来影响你的document排序,那么就放在filter中即可
3、filter与query性能
filter,不需要计算相关度分数,不需要按照相关度分数进行排序,同时还有内置的自动cache最常使用filter的数据
query,相反,要计算相关度分数,按照分数进行排序,而且无法cache结果
第50.初识搜索引擎_上机动手实战常用的各种query搜索语法
课程大纲
1、match all
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2、match
GET /_search
{
"query": { "match": { "title": "my elasticsearch article" }}
}
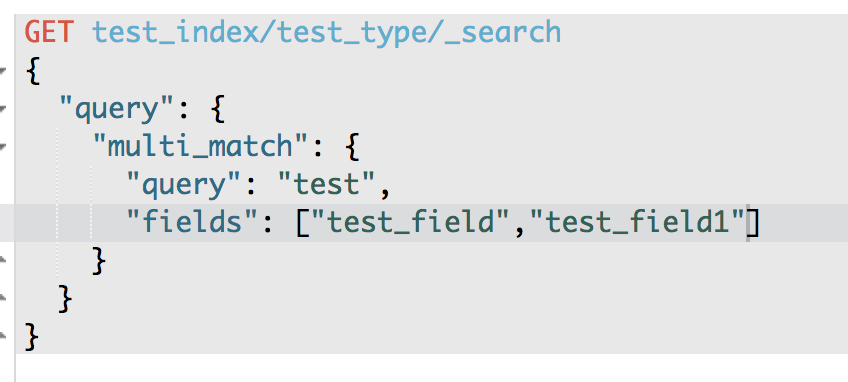
3、multi match
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "test",
"fields": ["test_field", "test_field1"]
}
}
}
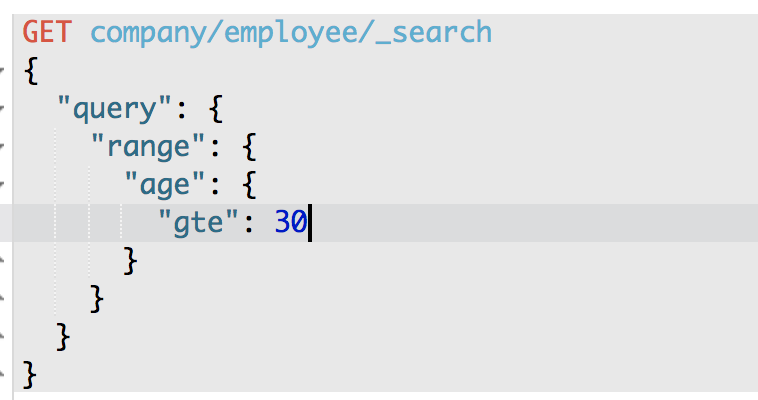
4、range query
GET /company/employee/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30
}
}
}
}
5、term query
match会将test 和 hello分为两个词进行查询 term不会分词 只查找test hello
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"test_field": "test hello"
}
}
}
6、terms query
GET /_search
{
"query": { "terms": { "tag": [ "search", "full_text", "nosql" ] }}
}
7、exist query(2.x中的查询,现在已经不提供了)