1、Python与用户交互
如何交互
name=input('请输入你的姓名;')
pwd=input('请输入你的密码:')
print(type(name))
print(type(pwd))
请输入你的姓名:nick
请输入你们的密码:123
<class 'str'>
<class 'str'> /#字符串类型
age=input('请输入你的年龄:')------->请输入你的年龄:18
print(age) ---------->18
age=int(age)
print(int(age)) ------------》<class 'int'>
age = age +1
print(age) ----------->19
无论我们输入的是数字类型,字符串类型,还是列表类型,input接收的值都是字符串类型
Python和Python2的交互(熟悉)
name= raw_input('请输入你的姓名:')
pwd= raw_input('请输入你的密码:')
print(type(name)) # 'str'
print(type(pwd)) # 'str'
python2当中的raw_input就是python3中的input。
x = input('username: ') 必须输入明确的数据类型,你输入什么类型则接收什么数据类型,输入'egon'而不是egon,否则会报错
2、格式化输出
1.1占位符:
* age=input('age:>>>') ------->age:>>>19
print('My age is'+age) ------->My age is 19
* age=input('age:>>>') ------->age:>>>19
print('My age is',age) ------->My age is 19
* name=input('name:>>>')
age= input('age:>>>')
height=input('heighter:>>>')
print('My name is %s, My age is %s, My height is %s')
------------>
name:>>> nick
age:>>> 16
height:>>> 170
My name is nick, My age is 17,My height is 170
* name=input('name:>>>')
age=input('age:>>>')
height=input('height:>>>')
print('My name is %s,My age is %s,My height is %s'%(name,age,height))
name:>>> nick
age:>>>12
height:>>>12
My name is nick,My age is 12,My height is 12
* print('My name is %s, My age is %s, My height is %s')
My name is %s, My age is %s, My height is %
* name=input('name:>>>')
name=int(input)
age=input('age:>>>')
age_int=int(age)
height=int(input(height:>>>))
print ('My name is %d ,My age is %d,My height is %d'%(name,age,height))
name:>>>1
age:>>>1
height:>>>1
My name is 1 ,My age is 1, My height is 1
format格式化(了解)
-
name='nick'
age =19
print("hello,{}.you are {}.".format (name,age))
hello ,nick . you are 19
-
name='nick'
age=19
print("hello,{1}.You are {0}-{0}.".format(age.name))
hello ,nick.You are 19-19
-
name='nick'
age=19
print("hello,{name}.You are {age}-{age}.".format(age=age,name=name))hello,nick,You are 19-19
f-string 格式化(掌握)
相比较占位符的方式,python3.6版本新增了f-String格式化的方式,比较简单易懂。推荐使用 大小写F,f适用 :.2f"代表显示小数点后2位
* name='nick'
age=19
print(f"hello,{name}. You are {age}.")
hello, nick.You are 19.
* age=19
print(f'{age*2}')
38
* salary=6.6666
print(f'{salary:.2f}')
6.67
基本运算符
1、算术运算符:
-
print(1+2)---->3
-
x=10
y=10
z=x+y
print(z)----->20
-
有零有整除,得到一个浮点型
print(10/3)------->3.33333333
-
地板除,只取整数部分
print(10//3)-----> 3
print(10//4)----->2
-
%:取余数
print(10%3)-----> 1
-
**:取幂
print(10**3)-----> 1000
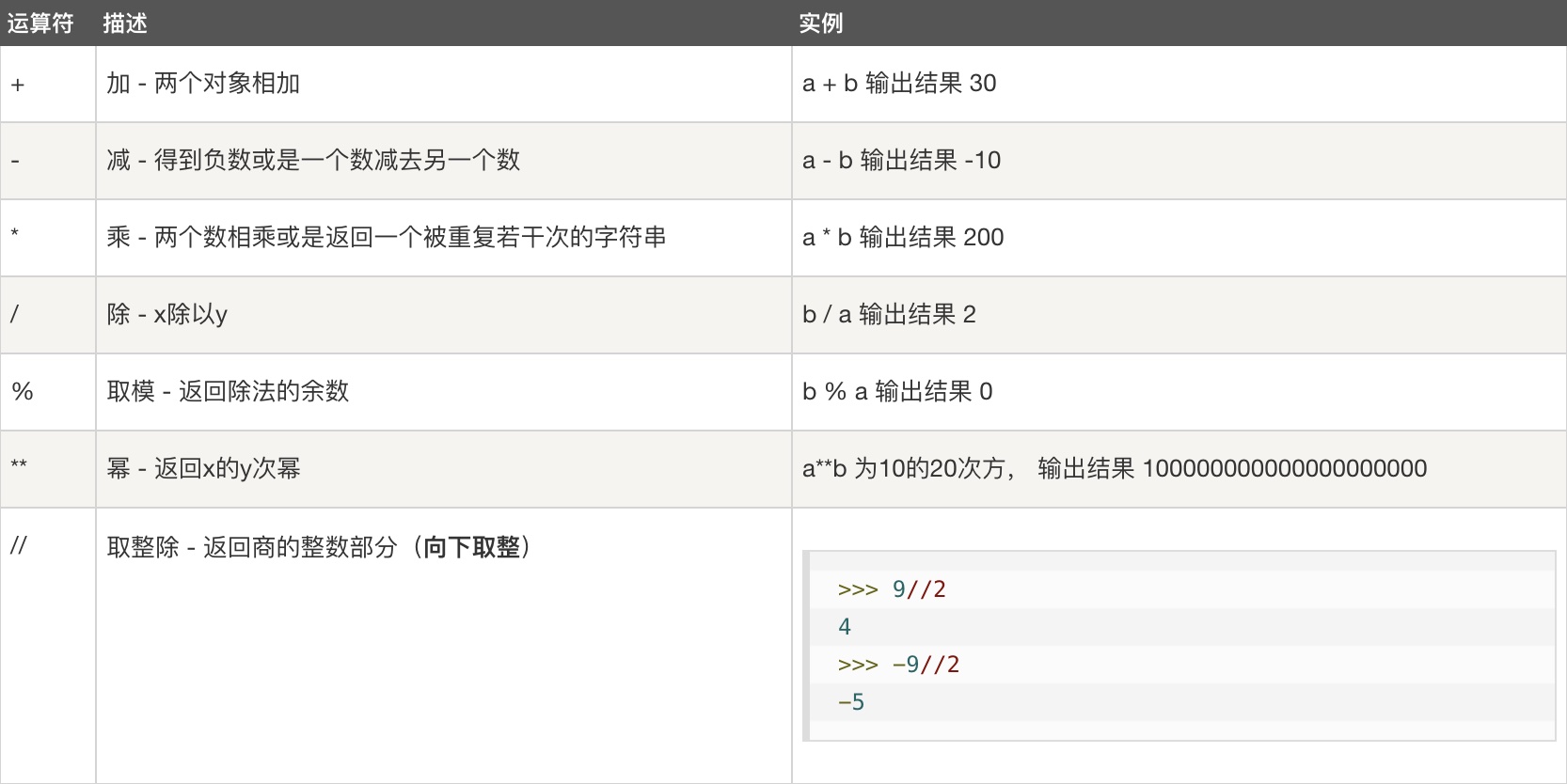
2、比较运算符(了解)
1>1-----------------false
1<1-----------------false
1>=1----------------true
1<=1----------------true
1=1-----------------报错 /#=相当于赋值
1==1----------------true
1!=1---------------true
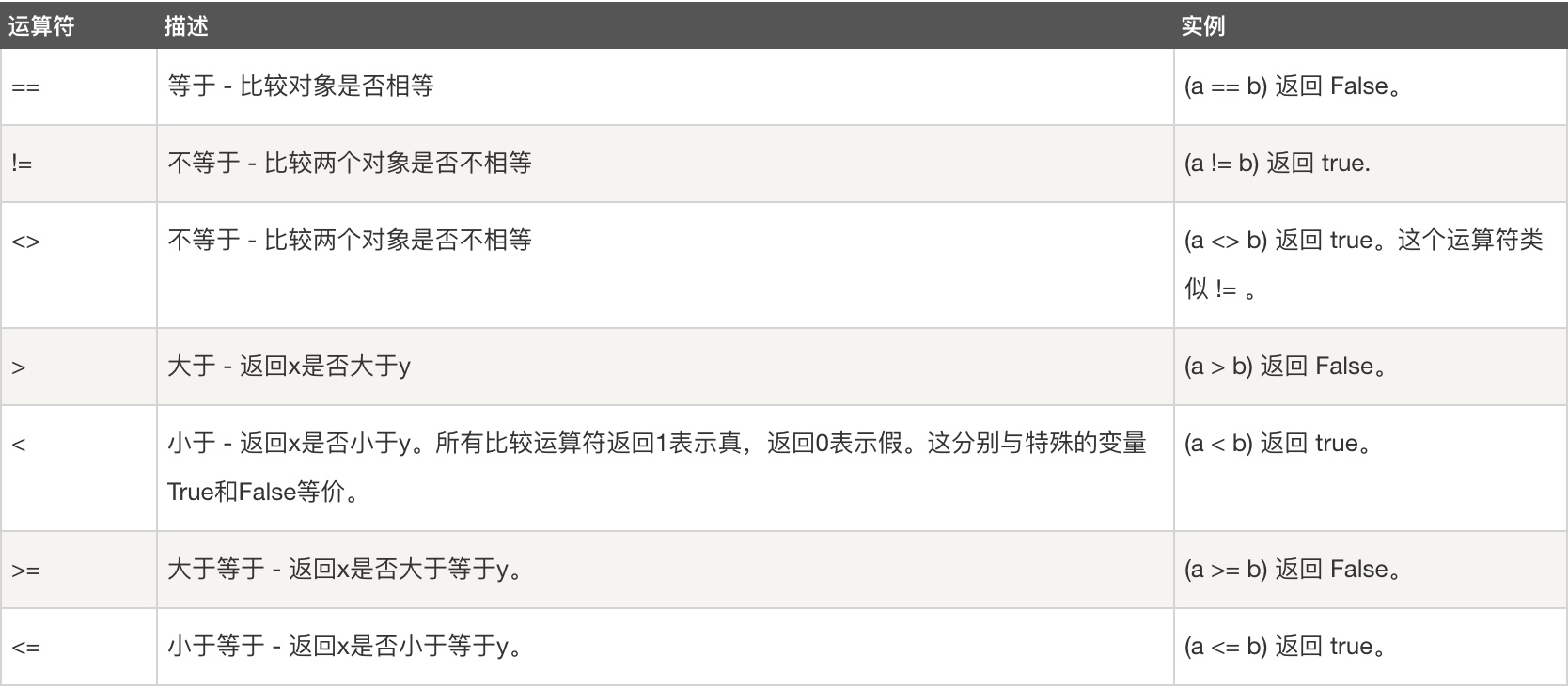
3、赋值运算符(掌握)
-
age=19
age=age+1
print(age)--------- 20
-
age=19
age + = 1
print(age)---------20
-
age=19
age*=10
print(age)------190
4、逻辑运算符(掌握)
and or not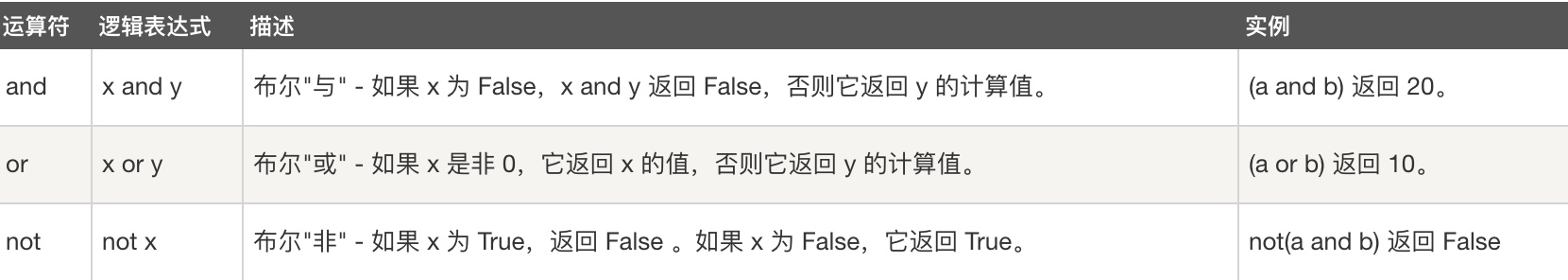
5、身份运算符(掌握)
is比较的是ID

is和==的区别:is用于判断两个变量引用对象是否为同一个(是否在同一块内存空间中), ==用于判断引用变量的值是否相等。
x=10
y=10
print(x is y)
print(x == y)
true
true
x=257
y=257
print(x is y)
print(x == y)
false
true
x=10
y=11
print(x is y)
print(x == y)
false
false
id相同的值一定相同,值相同的id不一定相同 小整数池的除外
Python 运算符优先级(了解)
1*(3>2)*1
3>2
true
2+(3+4)*2/5
4.8
链式赋值(考试必考)
a=10
b=10
c=10
d=10
print(f'a:{a},b:{b},c:{c},d:{d}')
>
a:10,b:10,c:10,d:10
x=y=z=10
print(x,y,z)
10 10 10
交叉赋值
x=10
y=20
z=x /#x=z=10
x=y /#x=y=20
y=z /#y=z=10
print(x,y)
20 10
x=10
y=20
x,y=y,x
print(x,y)
20 10
解压缩(考试必考)

*name_list=['nick','egon','tank']
x=name_list[0]
y=name_list[1]
z=name_list[2]
print(f'x:{x},y:{y},z:{z}')
> x:nick,y:egon,z:tank
**name_list=['nick','egon','tank']
x,y,z=name_list
print(f'x:{x}',y:{y},z:{z}')
> x:nick,y:egon,z:tank
***bobby_list['piao','read','listen','run','fishing','swimming','music']
print(bobby_list[0])
>piao
print(hobby_list[2])
print(hobby_list[3])
>listen
>run
##hobby_list['piao','666']
hobby1,hobby2=hobby_list
print(hobby1)
print(hobby2)
>piao
666
##hobby_list=['list','listen','swimming','handsome','read']
_,hobby1,_hobby2,_=hobby_list
print(hobby1)
print(hobby2)
listen
handsome
##hobby_list=['piao','listen','swimming','running','666','2333','23456']
_,hobby1,_hobby2,*_=hobby_list
print(hobby1)
print(hobby2)
listen
running
##hobby_list=[['piao','listen','swimming','running','666','2333','23456']]
hobby1,*_,hobby2=hobby_list
print(hobby1)
print(hobby2)
print(a)
piao /#第一个
23456 /#最后一个
【'listen','swimming','running','666','2333'】