原题:线性判别分析仅在线性可分数据上能获得理想结果,试设计一个改进方法,使其能够用于非线性可分数据。
这里我采用二次判别分析来对原来的西瓜数据集进行分类,同样采用sklearn里的二次判别库。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import colors from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis file1 = open('c:quantwatermelon.csv','r') data = [line.strip(' ').split(',') for line in file1] X = [[float(raw[-3]), float(raw[-2])] for raw in data[1:]] y = [1 if raw[-1]=='xcaxc7' else 0 for raw in data[1:]] X = np.array(X) y = np.array(y) #######################################################################以上是西瓜 # colormap cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap( 'red_blue_classes', {'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)], 'green': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 0.7, 0.7)], 'blue': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 1, 1)]}) plt.cm.register_cmap(cmap=cmap) ############################################################################### # plot functions def plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred): plt.figure() plt.title('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis of Watermelon') plt.xlabel('Sugar Rate') plt.ylabel('Density') tp = (y == y_pred) # True Positive //Boolean matrix tp0, tp1 = tp[y == 0], tp[y == 1] print tp X0, X1 = X[y == 0], X[y == 1] X0_tp, X0_fp = X0[tp0], X0[~tp0] X1_tp, X1_fp = X1[tp1], X1[~tp1] # class 0: dots plt.plot(X0_tp[:, 0], X0_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='red') plt.plot(X0_fp[:, 0], X0_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#990000') # dark red # class 1: dots plt.plot(X1_tp[:, 0], X1_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='blue') plt.plot(X1_fp[:, 0], X1_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#000099') # dark blue # class 0 and 1 : areas nx, ny = 200, 100 x_min, x_max = plt.xlim() y_min, y_max = plt.ylim() xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, nx), np.linspace(y_min, y_max, ny)) Z = lda.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) Z = Z[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape) plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes', norm=colors.Normalize(0., 1.)) plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, [0.5], linewidths=2., colors='k') # means plt.plot(lda.means_[0][0], lda.means_[0][1], 'o', color='black', markersize=10) plt.plot(lda.means_[1][0], lda.means_[1][1], 'o', color='black', markersize=10) ############################################################################### # Linear Discriminant Analysis qda = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariances=True) y_pred = qda.fit(X, y).predict(X) plot_data(qda, X, y, y_pred) plt.axis('tight') plt.suptitle('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis of Watermelon') plt.show()
二次判别分析结果和线性判别分析结果分别如下:
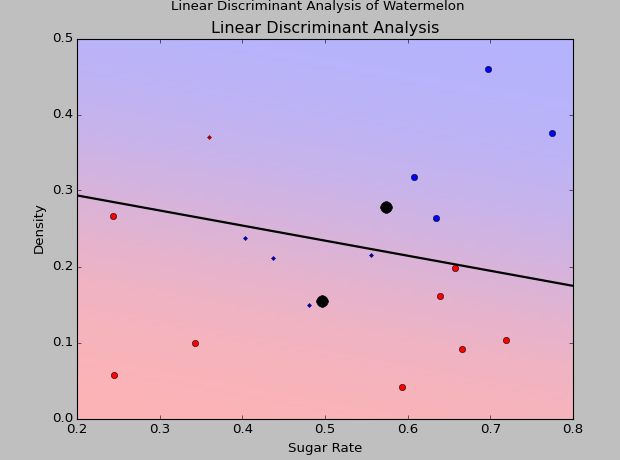
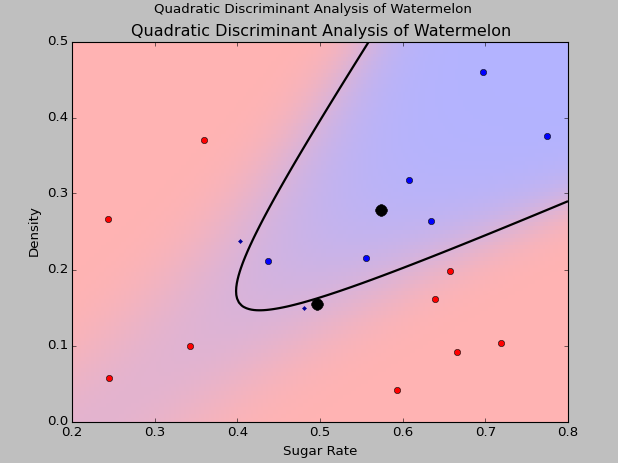
可以看到对于线性不可分数据,二次判别分析的效果非常好。