官网地址(https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html)而且是中文的
Elastic的快速入门
1、基础概念
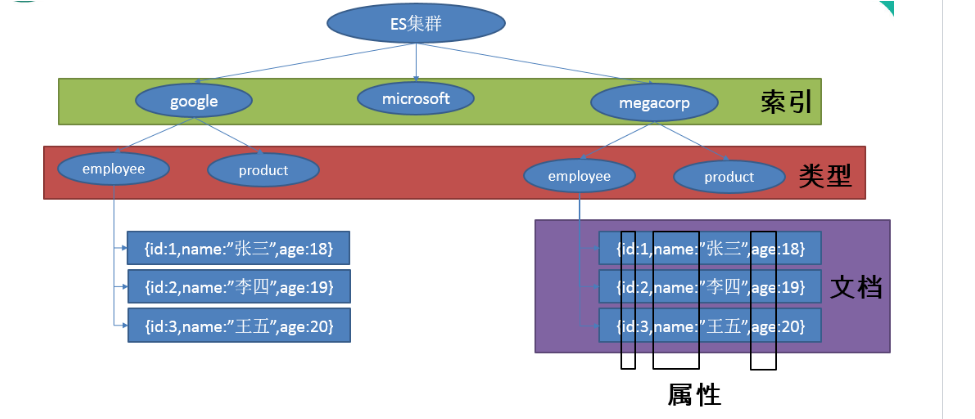
面向文档,JSON作为序列化格式,ElasticSearch的基本概念
索引(名词):
如前所述,一个 索引 类似于传统关系数据库中的一个 数据库 ,是一个存储关系型文档的地方。 索引 (index) 的复数词为 indices 或 indexes 。
索引(动词):
索引一个文档 就是存储一个文档到一个 索引 (名词)中以便它可以被检索和查询到。这非常类似于 SQL 语句中的 INSERT 关键词,除了文档已存在时新文档会替换旧文档情况之外。
类型:相当于数据库中的表
文档:相当于数据库中的行,即每条数据都叫一个文档
属性:相当于数据库中的列,即文档的属性
2、测试
下载POSTMAN(https://www.getpostman.com/downloads/),并使用POSTMAN测试
具体查看官方示例(https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_indexing_employee_documents.html)
重点:PUT请求+请求体
官网介绍:
你也许已经注意到 索引 这个词在 Elasticsearch 语境中包含多重意思, 所以有必要做一点儿说明: 索引(名词): 如前所述,一个 索引 类似于传统关系数据库中的一个 数据库 ,是一个存储关系型文档的地方。 索引 (index) 的复数词为 indices 或 indexes 。 索引(动词): 索引一个文档 就是存储一个文档到一个 索引 (名词)中以便它可以被检索和查询到。这非常类似于 SQL 语句中的 INSERT 关键词,除了文档已存在时新文档会替换旧文档情况之外。 倒排索引: 关系型数据库通过增加一个 索引 比如一个 B树(B-tree)索引 到指定的列上,以便提升数据检索速度。Elasticsearch 和 Lucene 使用了一个叫做 倒排索引 的结构来达到相同的目的。 + 默认的,一个文档中的每一个属性都是 被索引 的(有一个倒排索引)和可搜索的。一个没有倒排索引的属性是不能被搜索到的。我们将在 倒排索引 讨论倒排索引的更多细节。
根据官网举一个例子
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_indexing_employee_documents.html
PUT /megacorp/employee/1 { "first_name" : "John", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] }
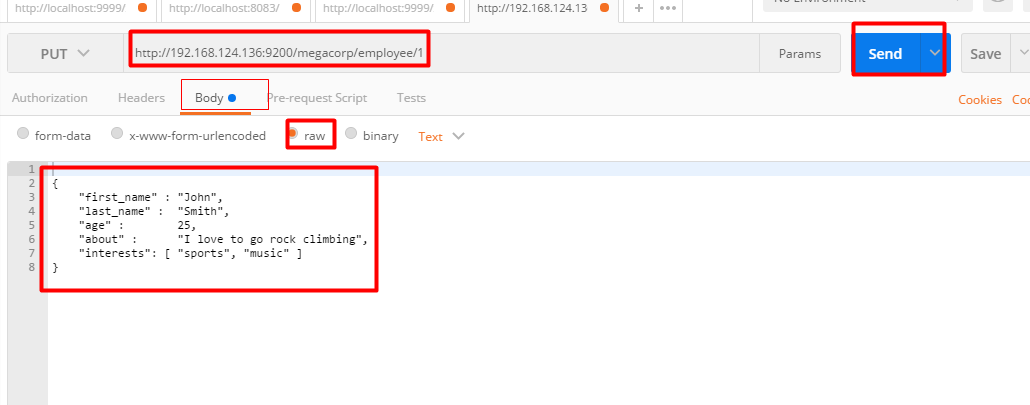
执行结果

检索文档
官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_retrieving_a_document.html
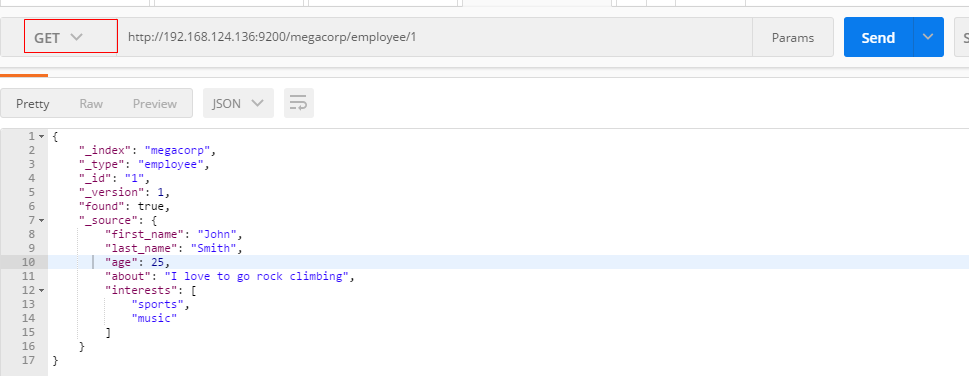
重点:GET请求+URI+index+type+ID
GET /megacorp/employee/1
轻量检索
重点:GET请求+index+type+_search+条件(非必须)
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_search_lite.html
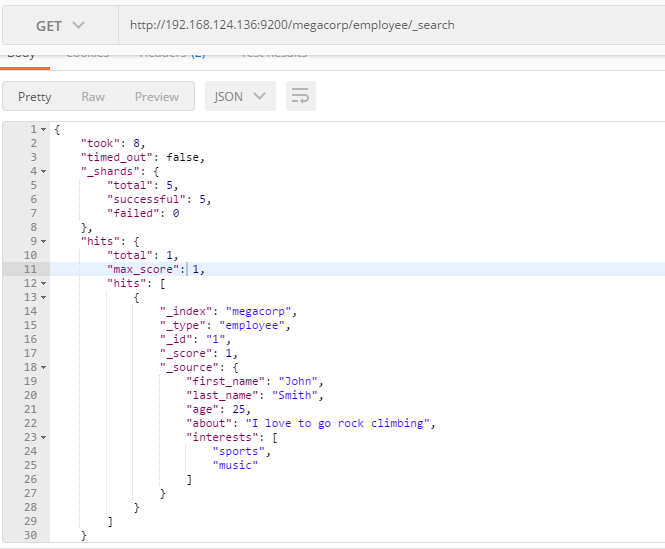
搜索所有雇员: _search
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
搜索结果:
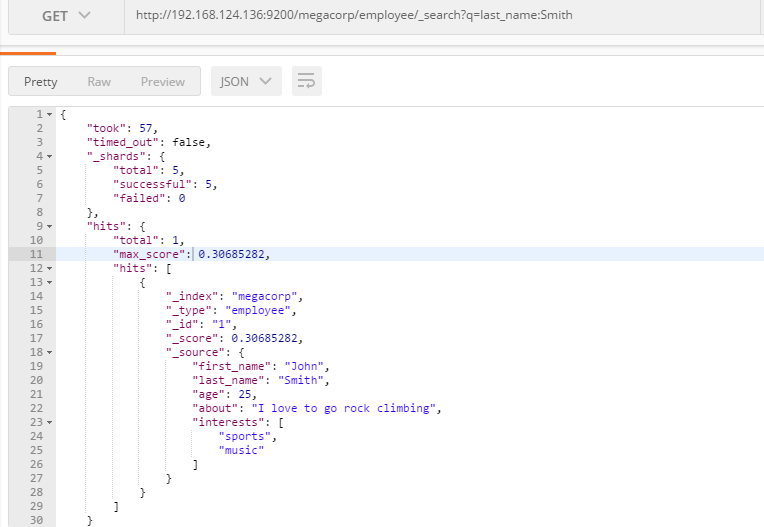
高亮搜索:URL参数
GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:Smith
使用查询表达式
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_search_with_query_dsl.html
重点:GET+URI+index+type+_search+请求体【match】
Query-string 搜索通过命令非常方便地进行临时性的即席搜索 ,但它有自身的局限性(参见 轻量 搜索 )。Elasticsearch 提供一个丰富灵活的查询语言叫做 查询表达式 ,它支持构建更加复杂和健壮的查询。
领域特定语言 (DSL), 指定了使用一个 JSON 请求。我们可以像这样重写之前的查询所有 Smith 的搜索 :
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "last_name" : "Smith" } } }
返回结果与之前的查询一样,但还是可以看到有一些变化。其中之一是,不再使用 query-string 参数,而是一个请求体替代。这个请求使用 JSON 构造,并使用了一个 match 查询(属于查询类型之一,后续将会了解)。
、更加复杂的查询
重点:GET+URI+index+type+_search + 请求体【match+filter】
现在尝试下更复杂的搜索。 同样搜索姓氏为 Smith 的雇员,但这次我们只需要年龄大于 30 的。查询需要稍作调整,使用过滤器 filter ,它支持高效地执行一个结构化查询。
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "bool": { "must": { "match" : { "last_name" : "smith" } }, "filter": { "range" : { "age" : { "gt" : 30 } } } } } }
6、全文搜索
官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_full_text_search.html
重点:GET+index+type+_search+请求体【match】 ==》看相关性得分
截止目前的搜索相对都很简单:单个姓名,通过年龄过滤。现在尝试下稍微高级点儿的全文搜索——一项传统数据库确实很难搞定的任务。
搜索下所有喜欢攀岩(rock climbing)的雇员:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }
显然我们依旧使用之前的 match 查询在about 属性上搜索 “rock climbing” 。得到两个匹配的文档:
{ ... "hits": { "total": 2, "max_score": 0.16273327, "hits": [ { ... "_score": 0.16273327, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } }, { ... "_score": 0.016878016, "_source": { "first_name": "Jane", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 32, "about": "I like to collect rock albums", "interests": [ "music" ] } } ] } }
"_score":相关性得分
Elasticsearch 默认按照相关性得分排序,即每个文档跟查询的匹配程度。第一个最高得分的结果很明显:John Smith 的 about属性清楚地写着 “rock climbing” 。
但为什么 Jane Smith 也作为结果返回了呢?原因是她的 about 属性里提到了 “rock” 。因为只有 “rock” 而没有 “climbing” ,所以她的相关性得分低于 John 的。
这是一个很好的案例,阐明了 Elasticsearch 如何 在 全文属性上搜索并返回相关性最强的结果。Elasticsearch中的 相关性 概念非常重要,也是完全区别于传统关系型数据库的一个概念,数据库中的一条记录要么匹配要么不匹配。
7、短语搜索
官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_phrase_search.html
重点:GET+index+type+_search+请求体【match_phrase 】
找出一个属性中的独立单词是没有问题的,但有时候想要精确匹配一系列单词或者短语 。 比如, 我们想执行这样一个查询,仅匹配同时包含 “rock” 和 “climbing” ,并且 二者以短语 “rock climbing” 的形式紧挨着的雇员记录。
为此对 match 查询稍作调整,使用一个叫做 match_phrase 的查询:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }
返回的信息
{ ... "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.23013961, "hits": [ { ... "_score": 0.23013961, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } } ] } }
8、高亮搜索
官当文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/highlighting-intro.html
重点:GET+index+type+_search+请求体【match_phrase+highlight】==>返回关键字加了em标签
许多应用都倾向于在每个搜索结果中 高亮 部分文本片段,以便让用户知道为何该文档符合查询条件。在 Elasticsearch 中检索出高亮片段也很容易。
再次执行前面的查询,并增加一个新的 highlight 参数:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } }, "highlight": { "fields" : { "about" : {} } } }
当执行该查询时,返回结果与之前一样,与此同时结果中还多了一个叫做 highlight 的部分。这个部分包含了 about 属性匹配的文本片段,并以 HTML 标签 <em></em> 封装:
{ ... "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.23013961, "hits": [ { ... "_score": 0.23013961, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] }, "highlight": { "about": [ "I love to go <em>rock</em> <em>climbing</em>" ] } } ] } }
9、分析
官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_analytics.html#_analytics
重点:GET+index+type+_search+请求体【aggs-field】
aggs:聚合
终于到了最后一个业务需求:支持管理者对雇员目录做分析。 Elasticsearch 有一个功能叫聚合(aggregations),允许我们基于数据生成一些精细的分析结果。聚合与 SQL 中的 GROUP BY 类似但更强大。
举个例子,挖掘出雇员中最受欢迎的兴趣爱好:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "aggs": { "all_interests": { "terms": { "field": "interests" } } } }
会报错
Fielddata is disabled on text fields by default. Set fielddata=true on [inte
默认情况下,字段数据在文本字段上禁用。设置字段数据= TRUE
首先开启数据结构
PUT megacorp/_mapping/employee/ { "properties": { "interests": { "type": "text", "fielddata": true } } }
然后在进行请求
{ ... "hits": { ... }, "aggregations": { "all_interests": { "buckets": [ { "key": "music", "doc_count": 2 }, { "key": "forestry", "doc_count": 1 }, { "key": "sports", "doc_count": 1 } ] } } }
可以看到,两位员工对音乐感兴趣,一位对林地感兴趣,一位对运动感兴趣。这些聚合并非预先统计,而是从匹配当前查询的文档中即时生成。
如果想知道叫 Smith 的雇员中最受欢迎的兴趣爱好,可以直接添加适当的查询来组合查询:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query": { "match": { "last_name": "smith" } }, "aggs": { "all_interests": { "terms": { "field": "interests" } } } }
all_interests 聚合已经变为只包含匹配查询的文档:
... "all_interests": { "buckets": [ { "key": "music", "doc_count": 2 }, { "key": "sports", "doc_count": 1 } ] }
聚合还支持分级汇总 。比如,查询特定兴趣爱好员工的平均年龄:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "aggs" : { "all_interests" : { "terms" : { "field" : "interests" }, "aggs" : { "avg_age" : { "avg" : { "field" : "age" } } } } } }
输出基本是第一次聚合的加强版。依然有一个兴趣及数量的列表,只不过每个兴趣都有了一个附加的 avg_age 属性,代表有这个兴趣爱好的所有员工的平均年龄。
即使现在不太理解这些语法也没有关系,依然很容易了解到复杂聚合及分组通过 Elasticsearch 特性实现得很完美。可提取的数据类型毫无限制。
4、SpringBoot+ElasticSearch
1、新建项目SpringBoot1.5+Web+Nosql-->ElasticSearch
2、springBoot默认支持两种技术和ES进行交互
1、Jest【需要导入使用】
利用JestClient和服务器的9200端口进行http通信
2、SpringData ElasticSearch【默认】
1)、客户端:Client节点信息: clusterNodes: clusterName
2)、ElasticsearchTemplate操作es
3)、编写ElasticsearchRepository子接口
1、Jest
1、注释SpringDataElasticSearch的依赖,并导入Jest【5.xx】的相关依赖
<!--<dependency>-->
<!--<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>-->
<!--<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>-->
<!--</dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.searchbox</groupId>
<artifactId>jest</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>
2、修改配置文件application.yml
spring: elasticsearch: jest: uris: http://10.138.223.126:9200
3、创建 bean.Article
package com.wdjr.springboot.bean; import io.searchbox.annotations.JestId; public class Article { @JestId private Integer id; private String autor; private String title; private String content; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getAutor() { return autor; } public void setAutor(String autor) { this.autor = autor; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } }
4、运行程序
5、编写Jest Cilent的测试类
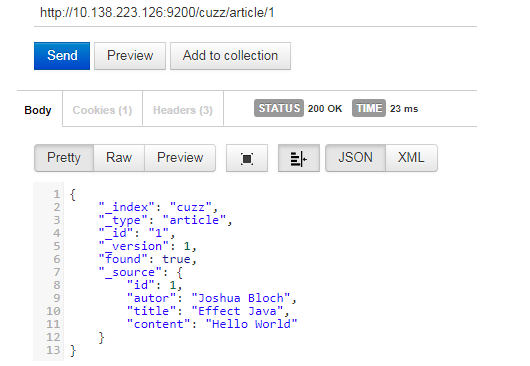
向wdjr-article中插入数据
@Test public void contextLoads() { // 给Es中索引(保存)一个文档 Article article = new Article(); article.setId(1); article.setTitle("Effect Java"); article.setAutor("Joshua Bloch"); article.setContent("Hello World"); // 构建一个索引功能 Index index = new Index.Builder(article).index("cuzz").type("article").build(); try { //执行 jestClient.execute(index); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
查询数据
@Test public void search(){ // 查询表达式 String json = "{ " + " "query" : { " + " "match" : { " + " "content" : "Hello" " + " } " + " } " + "}"; // 构建搜索操作 Search search = new Search.Builder(json).addIndex("cuzz").addType("article").build(); // 执行 try { SearchResult result = jestClient.execute(search); System.out.println(result.getJsonString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
2、在Docker中安装适合版本的ES【2.4.6】
docker pull elasticsearch:2.4.6 docker run -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms256m -Xmx256m" -d -p 9201:9200 -p 9301:9300 --name ES02 id
3、编写配置文件
spring: data: elasticsearch: cluster-name: elasticsearch cluster-nodes: 10.138.223.126:9301
4、修改pom文件,把使用data-elasticsearch,把刚才注释删除
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
5、操作ElasticSearch有两种方式
1)、编写一个ElasticsearchRepositry
2)、编写一个ElasticsearchTemplate
6、ElasticsearchRepositry的操作
1)、新建一个bean/Book类,注意:@Document(indexName = "cuzz", type="book")
/** * @Author: cuzz * @Date: 2018/9/27 18:32 * @Description: */ @Document(indexName = "cuzz",type="book") @Data public class Book { private Integer id; private String bookName; private String auto; public Book() { super(); } public Book(Integer id, String bookName, String auto) { super(); this.id = id; this.bookName = bookName; this.auto = auto; } }
2)、新建一个repositry/BookRepositry
方法编写参考官方文档
/** * @Author: cuzz * @Date: 2018/9/27 18:33 * @Description: */ public interface BookRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Book, Integer> { //自定义查询方法 public List<Book> findByBookNameLike(String bookName); }
3)、编写测试类
@Autowired BookRepositry bookRepositry; @Test public void testSearch(){ for (Book book : bookRepositry.findByBookNameLike("Effect")) { System.out.println(book); } }