1.$与#区别
结论:
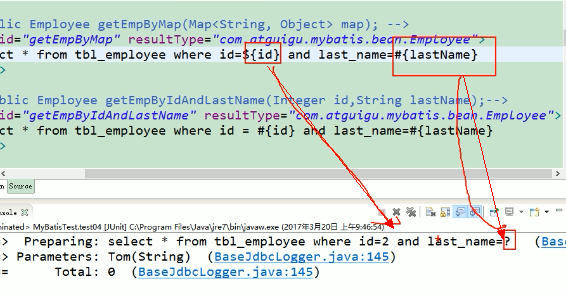
===========================参数值的获取====================================== #{}:可以获取map中的值或者pojo对象属性的值; ${}:可以获取map中的值或者pojo对象属性的值; select * from tbl_employee where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName} Preparing: select * from tbl_employee where id=2 and last_name=? 区别: #{}:是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中;PreparedStatement;防止sql注入 ${}:取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中;会有安全问题; 大多情况下,我们去参数的值都应该去使用#{}; 原生jdbc不支持占位符的地方我们就可以使用${}进行取值 比如分表、排序。。。;按照年份分表拆分 select * from ${year}_salary where xxx; select * from tbl_employee order by ${f_name} ${order} #{}:更丰富的用法: 规定参数的一些规则: javaType、 jdbcType、 mode(存储过程)、 numericScale、 resultMap、 typeHandler、 jdbcTypeName、 expression(未来准备支持的功能); jdbcType通常需要在某种特定的条件下被设置: 在我们数据为null的时候,有些数据库可能不能识别mybatis对null的默认处理。比如Oracle(报错); JdbcType OTHER:无效的类型;因为mybatis对所有的null都映射的是原生Jdbc的OTHER类型,oracle不能正确处理; 由于全局配置中:jdbcTypeForNull=OTHER;oracle不支持;两种办法 1、#{email,jdbcType=OTHER}; 2、jdbcTypeForNull=NULL <setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/>
2.返回值为Map<String,Employee>类型的对象
mapper接口类如下:
package com.atguigu.mybatis.dao; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee; public interface EmployeeMapper { //多条记录封装一个map:Map<Integer,Employee>:键是这条记录的主键,值是记录封装后的javaBean //@MapKey:告诉mybatis封装这个map的时候使用哪个属性作为map的key @MapKey("lastName") public Map<String, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName); }
xml文件
<!--public Map<Integer, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName); -->
<select id="getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName}
</select>
自动映射配置
方式一: 开启mapUnderscoreToCamelCase=true配置就可以了
方式二: 自定义resultMap

resultMap封装单实例关联查询
sql语句如下:
<!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);--> <select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp"> SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.d_id d_id, d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id} </select>
POJO对象:employee对象中有对象类型属性dept
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String gender;
private Department dept;
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, String gender) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
}
public Department getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Department dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email="
+ email + ", gender=" + gender + "]";
}
}
dept对象
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
private List<Employee> emps;
public List<Employee> getEmps() {
return emps;
}
public void setEmps(List<Employee> emps) {
this.emps = emps;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDepartmentName() {
return departmentName;
}
public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) {
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Department [id=" + id + ", departmentName=" + departmentName
+ "]";
}
}
关联查询中resultMap定义如下:
方式一:通过dept.属性方式:
<!-- 联合查询:级联属性封装结果集 方式一: 使用dept. --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="did" property="dept.id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="dept.departmentName"/> </resultMap>
方式二:通过association标签关联对象
<!-- 使用association定义关联的单个对象的封装规则; --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp2"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象 property="dept":指定哪个属性是联合的对象 javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略] --> <association property="dept" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department">
<!--
column="did":指select语句中的did, 对应Department的property属性是id
column="dept_name" 指select语句中的dept_name字段,对应Department实例中的departmentName属性
-->
<id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> </association> </resultMap>
association分步查询
1.可以设置懒加载,在需要的时候才去查询sql语句

<!-- 2、settings包含很多重要的设置项 setting:用来设置每一个设置项 name:设置项名 value:设置项取值 --> <settings> <!-- <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> --> <setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/> <!--显示的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings>
2.使用association分步查询
1)返回结果集:
<!-- 使用association进行分步查询: 1、先按照员工id查询员工信息 2、根据查询员工信息中的d_id值去部门表查出部门信息 3、部门设置到员工中; --> <!-- id last_name email gender d_id --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpByStep"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <!-- association定义关联对象的封装规则 select:表明当前属性是调用select指定的方法查出的结果 column:指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法 流程:使用select指定的方法(传入column指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给property指定的属性
select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" ----通过departmentMapper.getDeptById方法查询出对应dept对象并赋值给dept对象属性.
--> <association property="dept" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"> </association> </resultMap> <!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);--> <select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} <if test="_parameter!=null"> and 1=1 </if> </select> <!-- 可以使用延迟加载(懒加载);(按需加载) Employee==>Dept: 我们每次查询Employee对象的时候,都将一起查询出来。 部门信息在我们使用的时候再去查询; 分段查询的基础之上加上两个配置:
查询sql如下:
<!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);--> <select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep"> select id ,last_name ,email ,gender ,d_id from tbl_employee where id=#{id} <if test="_parameter!=null"> and 1=1 </if> </select>
3.结果集中的select属性指向的mapper中的方法的xml文件:com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper
<!--public Department getDeptById(Integer id); --> <select id="getDeptById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department"> select id,dept_name departmentName from tbl_dept where id=#{id} </select>
resultMap封装集合
1.通过使用<collection>标签可以让封装对象中的集合.
实例:
<!-- 场景二: 查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来:注释在DepartmentMapper.xml中 -->
查询sql如下:
<!-- public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); --> <select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept"> SELECT d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name, e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender gender FROM tbl_dept d LEFT JOIN tbl_employee e ON d.id=e.d_id WHERE d.id=#{id} </select>
domain对象

package com.atguigu.mybatis.bean; import java.util.List; public class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName; private List<Employee> emps; public List<Employee> getEmps() { return emps; } public void setEmps(List<Employee> emps) { this.emps = emps; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getDepartmentName() { return departmentName; } public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) { this.departmentName = departmentName; } @Override public String toString() { return "Department [id=" + id + ", departmentName=" + departmentName + "]"; } }
mapper接口

public interface DepartmentMapper { public Department getDeptById(Integer id); //场景二 public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id); }
mapper.xml文件
<!-- public class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName; private List<Employee> emps; did dept_name || eid last_name email gender --> <!--嵌套结果集的方式,使用collection标签定义关联的集合类型的属性封装规则 --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDept"> <id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> <!-- collection定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则 ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型 --> <collection property="emps" ofType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> <!-- 定义这个集合中元素的封装规则 --> <id column="eid" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> </collection> </resultMap>
resultMap分步骤封装集合
类似于association标签封装单个对象.使用<Collection>标签的select属性指定那个mapper下的哪个方法,通过column属性给这个方法传参.从而达到分步骤查询.当延迟加载开启时,会有延迟的效果在.
实例如下:
场景: 将部门Department对象中的emps(List<employees>类型)的属性通过延迟加载赋值
查询sql如下:
<!-- public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id); --> <select id="getDeptByIdStep" resultMap="MyDeptStep"> select id,dept_name from tbl_dept where id=#{id} </select>
Department.xml文件的写法

<!-- collection:分段查询 --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDeptStep"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <id column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> <!-- 调用select属性指定的mapper(com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus)下的方法(getEmpsByDeptId),传递的参数是column中指定参数,从而达到给dept对象的emps属性赋值的效果.而且当开启延迟加载时会有延迟效果.--> <!-- 扩展:多列的值传递过去: 将多列的值封装map传递; column="{key1=column1,key2=column2}" fetchType="lazy":表示使用延迟加载; - lazy:延迟 - eager:立即 --> <collection property="emps" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus.getEmpsByDeptId" column="{deptId=id}" fetchType="lazy"></collection> </resultMap>
com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus.getEmpsByDeptId即com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus文件中的getEmpsByDeptId方法.EmployeeMapperPlus.java类如下:

package com.atguigu.mybatis.dao; import java.util.List; import com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee; public interface EmployeeMapperPlus { public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id); public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id); public List<Employee> getEmpsByDeptId(Integer deptId); }
xml中sql写法
<!-- 场景二: 查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来:注释在DepartmentMapper.xml中 --> <!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByDeptId(Integer deptId); --> <select id="getEmpsByDeptId" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where d_id=#{deptId} </select>
动态sql
trim标签解释: https://blog.csdn.net/wt_better/article/details/80992014
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperDynamicSQL"> <!-- • if:判断 • choose (when, otherwise):分支选择;带了break的swtich-case 如果带了id就用id查,如果带了lastName就用lastName查;只会进入其中一个 • trim 字符串截取(where(封装查询条件), set(封装修改条件)) • foreach 遍历集合 --> <!-- 查询员工,要求,携带了哪个字段查询条件就带上这个字段的值 --> <!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee); --> <select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee <!-- where --> <where> <!-- test:判断表达式(OGNL) OGNL参照PPT或者官方文档。 c:if test 从参数中取值进行判断 遇见特殊符号应该去写转义字符: &&: --> <if test="id!=null"> id=#{id} </if> <if test="lastName!=null && lastName!="""> and last_name like #{lastName} </if> <if test="email!=null and email.trim()!="""> and email=#{email} </if> <!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --> <if test="gender==0 or gender==1"> and gender=#{gender} </if> </where> </select> <!--public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionTrim(Employee employee); --> <select id="getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee <!-- 后面多出的and或者or where标签不能解决 prefix="":前缀:trim标签体中是整个字符串拼串 后的结果。 prefix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个前缀 prefixOverrides="": 前缀覆盖: 去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符 suffix="":后缀 suffix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个后缀 suffixOverrides="" 后缀覆盖:去掉整个字符串后面多余的字符 --> <!-- 自定义字符串的截取规则 --> <trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and"> <if test="id!=null"> id=#{id} and </if> <if test="lastName!=null && lastName!="""> last_name like #{lastName} and </if> <if test="email!=null and email.trim()!="""> email=#{email} and </if> <!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --> <if test="gender==0 or gender==1"> gender=#{gender} </if> </trim> </select> <!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionChoose(Employee employee); --> <select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee <where> <!-- 如果带了id就用id查,如果带了lastName就用lastName查;只会进入其中一个 --> <choose> <when test="id!=null"> id=#{id} </when> <when test="lastName!=null"> last_name like #{lastName} </when> <when test="email!=null"> email = #{email} </when> <otherwise> gender = 0 </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select> <!--public void updateEmp(Employee employee); --> <update id="updateEmp"> <!-- Set标签的使用 --> update tbl_employee <set> <if test="lastName!=null"> last_name=#{lastName}, </if> <if test="email!=null"> email=#{email}, </if> <if test="gender!=null"> gender=#{gender} </if> </set> where id=#{id} <!-- Trim:更新拼串 update tbl_employee <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="lastName!=null"> last_name=#{lastName}, </if> <if test="email!=null"> email=#{email}, </if> <if test="gender!=null"> gender=#{gender} </if> </trim> where id=#{id} --> </update> <!--public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionForeach(List<Integer> ids); --> <select id="getEmpsByConditionForeach" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee <!-- collection:指定要遍历的集合: list类型的参数会特殊处理封装在map中,map的key就叫list item:将当前遍历出的元素赋值给指定的变量 separator:每个元素之间的分隔符 open:遍历出所有结果拼接一个开始的字符 close:遍历出所有结果拼接一个结束的字符 index:索引。遍历list的时候是index就是索引,item就是当前值 遍历map的时候index表示的就是map的key,item就是map的值 #{变量名}就能取出变量的值也就是当前遍历出的元素 --> <foreach collection="ids" item="item_id" separator="," open="where id in(" close=")"> #{item_id} </foreach> </select> <!-- 批量保存 --> <!--public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps); --> <!--MySQL下批量保存:可以foreach遍历 mysql支持values(),(),()语法--> <insert id="addEmps"> insert into tbl_employee( <include refid="insertColumn"></include> ) values <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=","> (#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.dept.id}) </foreach> </insert><!-- --> <!-- 这种方式需要数据库连接属性allowMultiQueries=true; 这种分号分隔多个sql可以用于其他的批量操作(删除,修改) --> <!-- <insert id="addEmps"> <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=";"> insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender,d_id) values(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.dept.id}) </foreach> </insert> --> <!-- Oracle数据库批量保存: Oracle不支持values(),(),() Oracle支持的批量方式 1、多个insert放在begin - end里面 begin insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email) values(employees_seq.nextval,'test_001','test_001@atguigu.com'); insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email) values(employees_seq.nextval,'test_002','test_002@atguigu.com'); end; 2、利用中间表: insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email) select employees_seq.nextval,lastName,email from( select 'test_a_01' lastName,'test_a_e01' email from dual union select 'test_a_02' lastName,'test_a_e02' email from dual union select 'test_a_03' lastName,'test_a_e03' email from dual ) --> <insert id="addEmps" databaseId="oracle"> <!-- oracle第一种批量方式 --> <!-- <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" open="begin" close="end;"> insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email) values(employees_seq.nextval,#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email}); </foreach> --> <!-- oracle第二种批量方式 --> insert into employees( <!-- 引用外部定义的sql --> <include refid="insertColumn"> <property name="testColomn" value="abc"/> </include> ) <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator="union" open="select employees_seq.nextval,lastName,email from(" close=")"> select #{emp.lastName} lastName,#{emp.email} email from dual </foreach> </insert> <!-- 两个内置参数: 不只是方法传递过来的参数可以被用来判断,取值。。。 mybatis默认还有两个内置参数: _parameter:代表整个参数 单个参数:_parameter就是这个参数 多个参数:参数会被封装为一个map;_parameter就是代表这个map _databaseId:如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签。 _databaseId就是代表当前数据库的别名oracle --> <!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); --> <select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> <!-- bind:可以将OGNL表达式的值绑定到一个变量中,方便后来引用这个变量的值 --> <bind name="_lastName" value="'%'+lastName+'%'"/> <if test="_databaseId=='mysql'"> select * from tbl_employee <if test="_parameter!=null"> where last_name like #{lastName} </if> </if> <if test="_databaseId=='oracle'"> select * from employees <if test="_parameter!=null"> where last_name like #{_parameter.lastName} </if> </if> </select> <!-- 抽取可重用的sql片段。方便后面引用 1、sql抽取:经常将要查询的列名,或者插入用的列名抽取出来方便引用 2、include来引用已经抽取的sql: 3、include还可以自定义一些property,sql标签内部就能使用自定义的属性 include-property:取值的正确方式${prop}, #{不能使用这种方式} --> <sql id="insertColumn"> <if test="_databaseId=='oracle'"> employee_id,last_name,email </if> <if test="_databaseId=='mysql'"> last_name,email,gender,d_id </if> </sql> </mapper>
