目录
一、背景
在学习算法的过程中,除了熟练掌握各种算法的程序逻辑外,还经常需要用到一些测试案例对算法的时间复杂度做具体的测试。本文将通过打造一个测试类工具包,让我们可以更简便地研究排序算法的时间复杂度。
二、概念
2.1、时间复杂度的定义
即从序列的初始状态到经过排序算法后形成的最终排序状态这个过程所花费的时间度量
2.2、时间复杂度的比较
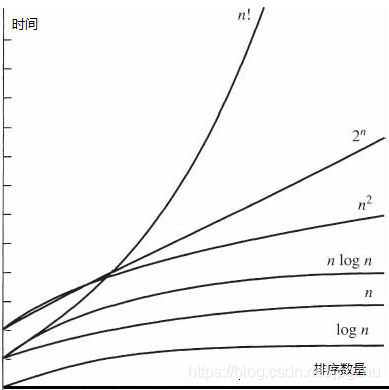
| 排序算法 | 时间复杂度(平均) | 时间复杂度(最好) | 时间复杂度(最坏) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 冒泡排序 | O(n2) | O(n) | O(n2) |
| 选择排序 | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(n2) |
| 插入排序 | O(n2) | O(n) | O(n2) |
| 希尔排序 | O(n logn) | O(n log2n) | O(n log2n) |
| 归并排序 | O(n logn) | O(n logn) | O(n logn) |
| 快速排序 | O(n logn) | O(n logn) | O(n2) |
| 堆排序 | O(n logn) | O(n logn) | O(n logn) |
- 时间复杂度曲线
三、测试类
3.1、程序结构
- 为便于文章书写,该测试类只实现了插入排序与快速排序,读者可根据接口定义自行加入其他排序算法。
3.2、测试工具类
- 生成一个乱序的数组
- 生成一个从0开始的近乎顺序的整型数组
- 对整型数组做完全拷贝
- 判断整型数组是否已经升序排列
- 遍历打印数组
- 通过排序接口,调用各种排序算法进行测试
/**
* 整数排序测试工具类
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-06
*/
public class SortUtils {
/**
* 生成一个乱序的数组
*
* @param count 数组的数量
* @param startRanger 数字范围起始值
* @param endRanger 数字范围终止值
* @return 乱序的整数数组
*/
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int count, int startRanger, int endRanger) {
if (startRanger <= endRanger) {
int[] arr = new int[count];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
arr[i] = startRanger + random.nextInt(endRanger - startRanger );
}
return arr;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 生成一个从0开始的近乎顺序的整型数组
*
* @param count 数组的数量
* @param swapCount 数字范围起始值
* @return 近乎顺序的整型数组
*/
public static int[] generateNearlyOrderedArray(int count, int swapCount) {
int[] arr = new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < swapCount; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(count);
int y = random.nextInt(count);
int temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
/**
* 对整型数组做完全拷贝
*
* @param source 源数组
* @return 数组拷贝
*/
public static int[] copyArray(int[] source) {
if (source != null) {
int dest[] = new int[source.length];
for (int i = 0; i < source.length; i++) {
dest[i] = source[i];
}
return dest;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 判断整型数组是否已经升序排列
*
* @param arr 整型数组
* @return 已经升序排列为true否则为false
*/
public static boolean isSorted(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 遍历打印数组
* @param arr 整型数组
*/
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
if (arr!=null) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
System.out.print(",");
} else {
System.out.println("]");
}
}
}else{
System.out.println("数组为空!");
}
}
/**
* 通过排序接口,调用各种排序算法进行测试
* @param sortName 排序算法名称
* @param sort 排序统一接口
* @param arr 整型数组
*/
public static void testSort(final String sortName,Sort sort,int[] arr){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS");
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(sortName+"排序开始时间:" + sdf.format(start));
sort.sort(arr);
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(sortName+"排序结束时间:" + sdf.format(end));
System.out.println(sortName+"排序耗用了" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
//断言判断该数组是否已实现升序排序
assert(isSorted(arr));
}
}
3.3、 排序算法接口定义
- 在测试工具类SortUtils testSort方法中调用该接口定义
--public static void testSort(final String sortName,Sort sort,int[] arr)
/**
* 整型数组排序统一接口定义
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-06
*/
public interface Sort {
/**
* 整型排序
* @param arr 待排序数组
*/
void sort(int[] arr);
}
3.4、 各种排序算法的实现
- 我们可以通过实现排序接口加入各种排序算法,本文章仅演示插入排序及快速排序
- 插入排序
/**
* 插入排序
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-06
*/
public class InsertSort implements Sort {
@Override
public void sort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j > 0 && (arr[j - 1] > temp); j--) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
- 快速排序
/**
* 快速排序
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-06
*/
public class QuickSort implements Sort {
@Override
public void sort(int[] arr) {
quick(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
private void quick(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int partitionIndex = partition(arr, left, right);
quick(arr, left, partitionIndex - 1);
quick(arr, partitionIndex + 1, right);
}
}
private int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int pivot = left;
int index = pivot + 1;
for (int i = index; i <= right; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[pivot]) {
swap(arr, i, index);
index++;
}
}
swap(arr, pivot, index - 1);
return index - 1;
}
private void swap(int arr[], int x, int y) {
int temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
}
- 其他排序
public class othersSort implements Sort {
@Override
public void sort(int[] arr) {
// 自行实现其他各种排序算法
....
}
}
}
3.5、 测试主程序
- 文中仅对以上实现的两种排序算法进行比较,读者实现其他排序算法后可自行扩充。
/**
* 整数排序测试类
* * @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-06
*/
public class SortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count=100000;
// 产生一个随机数组
int[] arr1 = SortUtils.generateRandomArray(count, 0, count);
// 对随机数组产生一个拷贝
int[] arr2 = SortUtils.copyArray(arr1);
// 进行插入排序
SortUtils.testSort("随机乱序的插入排序",new InsertSort(),arr1);
// 进行快速排序
SortUtils.testSort("随机乱序的快速排序",new QuickSort(),arr2);
// 产生一个随机数组
int[] arr3 = SortUtils.generateNearlyOrderedArray(count, 100);
// 对随机数组产生一个拷贝
int[] arr4 = SortUtils.copyArray(arr3);
// 进行插入排序
SortUtils.testSort("相对顺序的插入排序",new InsertSort(),arr3);
// 进行快速排序
SortUtils.testSort("相对顺序的快速排序",new QuickSort(),arr4);
}
}
3.6、 测试分析
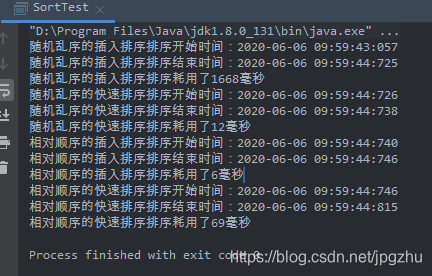
- 通过以上测试主程序及测试工具包的运行,我们清晰地看到了以下结论:
-- 在对数量较大且乱序的数组进行排序时,快速排序的性能明显要好于插入排序。
-- 但即使数量较大,如果数组相对有序时,插入排序的性能不比快速排序差。
-- 我们还发现排序数量相同的情况下,数组越乱序,快速排序性能越好。
四、写在最后
在日常学习上,逻辑思维非常重要,特别是在数据结构和算法的学习过程中,建立逻辑+套路的结构思维化,具备结构化思维,才能将问题分析地更全面、更深刻。