一.运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?

运行结果:

在Java中,内容相同的字串常量(“Hello”)只保存一份以节约内存,所以s0,s1,s2实际上引用的是同一个对象。
编译器在编译s2一句时,会去掉“+”号,直接把两个字串连接起来得一个字串(“Hello”)。这种优化工作由Java编译器自动完成。
当直接使用new关键字创建字符串对象时,虽然值一致(都是“Hello”),但仍然是两个独立的对象。
二.请查看String.equals()方法的实现代码,注意学习其实现方法。
public class StringEquals {
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1=new String("Hello");
String s2=new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
String s3="Hello";
String s4="Hello";
System.out.println(s3==s4);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
}
结果截图

使用equals()或equalsIgnoreCase()方法比较两字串内容是否相同,用于比较两个内容,使用==比较两字串变量是否引用同一字串对象,==是对对象的地址进行比较的,s1和s2是new的两个不同对象,所以他们的地址是不同的,所以用==判断的时候是错误的,但是两个的内容是一样的,都是hello,所以用equals函数判断内容的时候是对的,s3和s4,String类是维持着一个String池的,这个池初始化为空的,当我们String x = "hello"的时候,hello就会被放入这个池中,当我们再次String y = "hello"的时候,他首先去检查池中是否存在一个和hello内容一样的对象,如果存在的话就会把这个引用返回给y,如果不存在的话,就会创建一个并放入到池中。所以s3和s4的地址是一样的,所以用==判断的时候是正确的,用equals函数判断内容的时候是对的。
三.请阅读JDK中String类上述方法的源码,模仿其编程方式,编写一个MyCounter类,它的方法也支持上述的“级联”调用特性,其调用示例为:
MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1);
MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3);
….
public class MyCounter
{public static void main(String[] args)
{ String s="aqz";
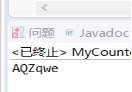
String result=s.trim().toUpperCase().concat("qwe");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
四.String.equals()方法、整理String类的Length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、 toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用说明、阅读笔记
String.equals()是用来比较两个两字串内容是否相同,用于比较两个内容,使用==比较两字串变量是否引用同一字串对象,==是对对象的地址进行比较的。
Length():获取字串长度
charAt():获取指定位置的字符
getChars():获取从指定位置起的子串复制到字符数组中
replace():子串替换
toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase():大小写转换
trim():去除头尾空格
toCharArray():将字符串对象转换为字符数组
length():public int length()//用来求字符串长度
String s=”dwfs”;
System.out.println(s.length());
charAt():public charAt(int index)//index 是字符下标,返回字符串中指定位置的字符
String s=”Hello”;
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));
getChars():public int getChars()//将字符从此字符串复制到目标字符数组
String s= "abc";
Char[] ch = new char[8];
str.getChars(2,3,ch,0);
replace():public int replace()//替换字符串
String s=”****”;
System.out.println(s.replace(“****”,”***”));
toUpperase():public String toUpperCase()//将字符串全部转换成大写
System.out.println(new String(“hello”).toUpperCase());
toLowerCse():public String toLowerCase()//将字符串全部转换成小写
System.out.println(new String(“HELLO”).toLowerCase());
trim():public String trim()//是去两边空格的方法
String x=” a bc ”;
System.out.println(x.trim());/
toCharArray(): String x=”abcd”;// 将字符串对象中的字符转换为一个字符数组
char myChar[]=x.toCharArray();
System.out.println(“myChar[1]”+myChar[1]);