可以把Condiftion理解为一把高级的琐,它提供了比Lock, RLock更高级的功能,允许我们能够控制复杂的线程同步问题。threadiong.Condition在内部维护一个琐对象(默认是RLock),可以在创建Condigtion对象的时候把琐对象作为参数传入。Condition也提供了acquire, release方法,其含义与琐的acquire, release方法一致,其实它只是简单的调用内部琐对象的对应的方法而已。基于此同步原语, 我实现了一个基本简单的线程安全的优先队列:
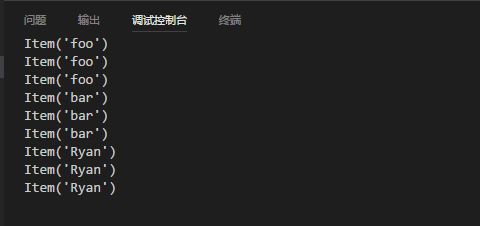
import heapq import threading # import time class Item: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name def __repr__(self): return 'Item({!r})'.format(self.name) class PriorityQueue: def __init__(self): self._queue = [] self._index = 0 self.mutex = threading.Lock() self.cond = threading.Condition() def push(self, item, priority): self.cond.acquire() heapq.heappush(self._queue, (-priority, self._index, item)) # 存入一个三元组, 默认构造的是小顶堆 self._index += 1 self.cond.notify() # 唤醒一个挂起的线程 self.cond.release() def pop(self): self.cond.acquire() if len(self._queue) == 0: # 当队列中数据的数量为0 的时候, 阻塞线程, 要实现线程安全的容器, 其实不难, 了解相关同步原语的机制, 设计好程序执行时的逻辑顺序(在哪些地方阻塞, 哪些地方唤醒) self.cond.wait() # wait方法释放内部所占用的锁, 同时线程被挂起, 知道接收到通知或超时, 当线程被唤醒并重新占用锁, 程序继续执行下去 else: x = heapq.heappop(self._queue)[-1] # 逆序输出 self.cond.release() return x def test1(p, item, index): for i in range(3): p.push(Item(item), index) def test2(p): for i in range(3): print(p.pop()) if __name__ == '__main__': p = PriorityQueue() t1 = threading.Thread(target=test1, args=(p, 'foo', 1)) t3 = threading.Thread(target=test1, args=(p, 'bar', 2)) t4 = threading.Thread(target=test1, args=(p, 'Ryan', 28)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=test2, args=(p,)) t5 = threading.Thread(target=test2, args=(p,)) t6 = threading.Thread(target=test2, args=(p,)) t1.start() t2.start() t1.join() t2.join() t3.start() t5.start() t3.join() t5.join() t4.start() t6.start() t4.join() t6.join()
我还实现了一个基于event 线程安全的优先队列,请看<基于condition 实现的线程安全的优先队列(python实现)>