Book Imformation :
<Pratical Programming : An Introduction to Computer Science Using Python 3> 2nd Edtion

Author : Paul Gries,Jennifer Campbell,Jason Montojo
Page : Chapter 2.3 to Chapter 2.5
1.A type consists of two things:
(1).a set of values
(2).a set of operations(操作, 运算) that can be applied to those values
if an operator(运算符) can be applied to more than one type of value,it's called an overloaded operator(重载运算符).
2.As for floating-point numbers,they are not exactly the fractions(分数) you learned before,take 2/3 and 5/3 for example:
1 2 / 3 2 0.6666666666666666 3 5 / 3 4 1.6666666666666667
This is fishy(可疑的, 值得怀疑的): both of them should have an infinite number of 6s after the decimal point.The problem is that computers have finite amount of memory,and the information that can be stored is limited.The number 0.6666666666666666 turns out to be the closest value to 2/3,so as to 5/3.
(Question:Why the number 0.6666666666666666 turns out to be the closest value to 2/3?)
3.Operator precedence(运算符优先级)
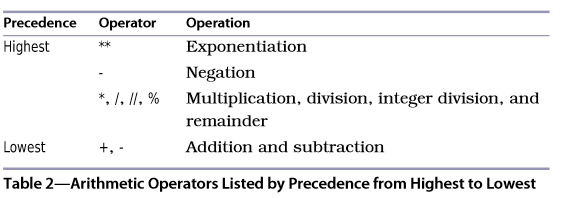
Table 2 shows the order of precedence for arithmetic operators.
It is a good rule to parenthesize complicated expressions even when you don't need to like 1 + 1.7 + (3.2 * 4.4) - (16 / 3),but not use parentheses(括号) in simple expressions such as 3.1 * 5.
If we use 0.6666666666666666 in a calculation, the error may get compounded:
1 >>> 2 / 3 + 1 2 1.6666666666666665 3 >>> 5 / 3 4 1.6666666666666667
in many programming languages,1 + 2 / 3 is not equal to 5 / 3.
4.A name that refers to a value is called variable(变量).
You create a variable by assigning(赋值) it a value:
1 >>> degree_celsius = 26.0
This statement is called assignment statement(赋值语句).
5.Values, Variables, and Computer Memory
In our memory model,a variable contains the memory address of the object(对象) to which it refers:
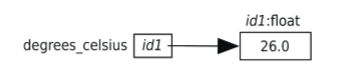
We use the following terminology:

6.Augmented Assignment(复合赋值)

Note that the operator is applied after the expression on the right is evaluated:
1 >>> d = 2 2 >>> d *= 3 + 4 3 >>> d 4 14
7.How Python Tells You Something Went Wrong
Broadly speaking,there are two kinds of errors in Python:
(1).syntax errors(语法错误)
which happen when you type something that isn't valid Python code.
e.g.
1 >>> 2 + 2 File "<stdin>", line 1 3 2 + 4 ^ 5 SyntaxError: invalid syntax
1 >>> 12 = x 2 File "<stdin>", line 1 3 SyntaxError: can't assign to literal
A literal is any value,like 12 and 26.0
(2).semantic errors(语义错误)
which happen when you tells Python to do something that it just can't do.
e.g.
1 >>> 3 + moogah 2 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 3 NameError: name 'moogah' is not defined