策略模式
定义
定义一簇算法类,将每个算法分别封装起来,让他们可以互相替换,策略模式可以使算法的变化独立于使用它们的客户端
场景
使用策略模式,可以避免冗长的if-else 或 switch分支判断
实现
-
策略的定义
策略的定义需要定义一个策略接口和一组实现这个接口的策略类,因为所有的策略类都实现相同的接口
public interface Strategy{
void algorithm();
}
public class ConcreteStrategyA implements Strategy {
@Override
public void algorithm() {
//具体的算法...
}
}
public class ConcreteStrategyB implements Strategy {
@Override
public void algorithm() {
//具体的算法...
}
}
-
策略的创建
在使用的时候,一般会通过类型来判断创建哪个策略来使用,在策略上下文中,可以使用map维护好策略类
-
策略的使用
策略模式包含一组可选策略,在使用策略时,一般如何确定使用哪个策略呢?最常见的是运行时动态确定使用哪种策略。程序在运行期间,根据配置、计算结果、网络等这些不确定因素,动态决定使用哪种策略
public class StrategyContext{
private static final Map<String, Strategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
static {
strategies.put("A", new ConcreteStrategyA());
strategies.put("B", new ConcreteStrategyB());
}
private static Strategy getStrategy(String type) {
if (type == null || type.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("type should not be empty.");
}
return strategies.get(type);
}
public void algorithm(String type){
Strategy strategy = this.getStrategy(type);
strategy.algorithm();
}
}
UML
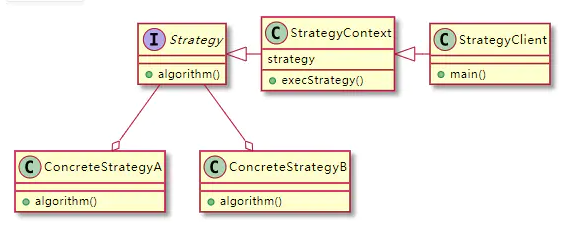
策略模式的创建和使用--Spring和自定义注解
在介绍策略模式时,在上下文中使用了map存储好的策略实例,在根据type获取具体的策略,调用策略算法。
当需要添加一种策略时,需要修改context代码,这违反了开闭原则:对修改关闭,对扩展开放。
要实现对扩展开放,就要对type和具体的策略实现类在代码中进行关联,可以使用自定义注解的方式,在注解中指定策略的type。
策略上下文实现类实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口,在该接口中编写策略类型与bean的关系并维护到策略上下文中。
package com.masterlink.strategy;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class StrategyDemoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {
private final Set<Class<?>> nonAnnotatedClasses = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64));
private final StrategyContext strategyContext;
private StrategyDemoBeanPostProcessor(StrategyContext context) {
this.strategyContext = context;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(bean.getClass())) {
// 获取使用 @StrategyDemo 注解的Class信息
Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean);
Class<Strategy> orderStrategyClass = (Class<Strategy>) targetClass;
StrategyDemo ann = findAnnotation(targetClass);
if (ann != null) {
processListener(ann, orderStrategyClass);
}
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
protected void processListener(StrategyDemo annotation,
Class<Strategy> classes) {
// 注册策略
this.strategyContext
.registerStrategy(annotation.type(), classes);
}
private StrategyDemo findAnnotation(Class<?> clazz) {
StrategyDemo ann = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(clazz, StrategyDemo.class);
return ann;
}
}
@Component
public class StrategyContext implements ApplicationContextAware {
private final Map<String, Class<Strategy>> strategyClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private final Map<String, Strategy> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 注册策略
* @param type
* @param strategyClass
*/
public void registerStrategy(String type, Class<Strategy> strategyClass){
if (strategyClassMap.containsKey(type)){
throw new RuntimeException("strategy type:"+type+" exist");
}
strategyClassMap.put(type, strategyClass);
}
/**
* 执行策略
* @param type
*/
public void algorithm(String type){
Strategy strategy = this.getStrategy(type);
strategy.algorithm();
}
private Strategy getStrategy(String type) {
if (type == null || type.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("type should not be empty.");
}
Class<Strategy> strategyClass = strategyClassMap.get(type);
return createOrGetStrategy(type, strategyClass);
}
private Strategy createOrGetStrategy(String type,Class<Strategy> strategyClass ){
if (beanMap.containsKey(type)){
return beanMap.get(type);
}
Strategy strategy = this.applicationContext.getBean(strategyClass);
beanMap.put(type, strategy);
return strategy;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
实用案例
在我们的平台中,有一部分是使用的netty框架编写的tcp服务,在服务端,需要将二进制转换为对象,在协议设计阶段,定义第一个字节表示对象类型,比如int,String等,第二三个字节,表示数据长度,后面的字节位传输内容。
比如,
0x01, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x09,解析出来的内容是int类型数字9。
0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 解析出的内容是String类型,内容是 123。
在不使用策略模式的时候,需要将第一个字节解析出来,然会使用if--else判断类型,对后继的字节进行解析。
在实际的实现过程中,是使用了策略模式,并且使用注解的方式表示数据类型,实现过程如下。
定义策略接口和注解
定义 CodecStrategyType 注解和编码解码器的策略接口 CodecStrategy
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CodecStrategyType {
/**
* 编码解码类型
* @return
*/
byte type();
}
public interface CodecStrategy<T> {
T decoding(byte[] buffer);
}
/*
* 通用解码接口
*/
public interface Codec {
Object decoding(byte[] bytes);
}
策略实现
实现两种类型的解码器: Integer 和 String
/**
* integer解码
*/
@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte)0x01)
@Service
public class IntgerCodecStrategy implements CodecStrategy<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer decoding(byte[] buffer) {
int value;
value = (int) ((buffer[3] & 0xFF)
| ((buffer[2] & 0xFF)<<8)
| ((buffer[1] & 0xFF)<<16)
| ((buffer[0] & 0xFF)<<24));
return value;
}
}
@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte)0x02)
@Service
public class StringCodecStrategy implements CodecStrategy<String> {
@Override
public String decoding(byte[] bufferr) {
return new String(bufferr);
}
}
策略上下文和策略注册
策略上下文类 CodecStrategyContext 提供了统一解码入口,将 byte[] 转换为 Object 类型,同时提供策略的注解接口 void registerStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass) ,注册解码类型对应的策略实现类。
策略上下文类同时还提供了策略Bean的创建,根据类型从Spring 的 ApplicationContext 获取策略bean,并缓存到map。
策略Bean处理类 CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor 中解析 CodecStrategyType 注解中指定的类型。
@Component
public class CodecStrategyContext implements ApplicationContextAware, Codec {
private final Map<Byte, Class<CodecStrategy<?>>> strategyClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private final Map<Byte, CodecStrategy<?>> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 注册策略
* @param type
* @param strategyClass
*/
public void registerStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass){
if (strategyClassMap.containsKey(type)){
throw new RuntimeException("strategy type:"+type+" exist");
}
strategyClassMap.put(type, strategyClass);
}
/**
* 执行策略
*/
@Override
public Object decoding(byte[] bytes){
Byte type = bytes[0];
CodecStrategy<?> strategy =this.getStrategy(type);
byte l1 = bytes[1];
byte l2= bytes[2];
short length = (short) ((l2 & 0xFF)
| ((l1 & 0xFF)<<8));
byte[] contentBytes = new byte[length];
arraycopy(bytes,3,contentBytes,0, length);
return strategy.decoding(contentBytes);
}
private CodecStrategy<?> getStrategy(Byte type) {
Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass = strategyClassMap.get(type);
return createOrGetStrategy(type, strategyClass);
}
private CodecStrategy<?> createOrGetStrategy(Byte type, Class<CodecStrategy<?>> strategyClass ){
if (beanMap.containsKey(type)){
return beanMap.get(type);
}
CodecStrategy<?> strategy = this.applicationContext.getBean(strategyClass);
beanMap.put(type, strategy);
return strategy;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
@Component
public class CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {
private final Set<Class<?>> nonAnnotatedClasses = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64));
private final CodecStrategyContext strategyContext;
private CodecStrategyTypeBeanPostProcessor(CodecStrategyContext context) {
this.strategyContext = context;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(bean.getClass())) {
// 获取使用 @StrategyDemo 注解的Class信息
Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean);
Class<CodecStrategy<?>> orderStrategyClass = (Class<CodecStrategy<?>>) targetClass;
CodecStrategyType ann = findAnnotation(targetClass);
if (ann != null) {
processListener(ann, orderStrategyClass);
}
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
protected void processListener(CodecStrategyType annotation,
Class<CodecStrategy<?>> classes) {
// 注册策略
this.strategyContext
.registerStrategy(annotation.type(), classes);
}
private CodecStrategyType findAnnotation(Class<?> clazz) {
CodecStrategyType ann = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(clazz, CodecStrategyType.class);
return ann;
}
}
使用和测试
测试Integer和String类型的策略:
- 0x01, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x09,解析出来的内容是int类型数字9。
- 0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 解析出的内容是String类型,内容是 123。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {CodecStrategyTest.CodecStrategyTestConfig.class})
public class CodecStrategyTest {
@Resource
Codec codec;
@Test
public void testInterDecoding(){
byte[] buffer = new byte[]{
0x01,0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00,0x00, 0x09
};
Integer decoding = (Integer)codec.decoding(buffer);
assertThat(decoding)
.isNotNull()
.isEqualTo(9);
}
@Test
public void testStringDecoding(){
byte[] buffer = new byte[]{
0x02, 0x00, 0x03, 0x31, 0x32,0x33
};
String decoding = (String)codec.decoding(buffer);
assertThat(decoding)
.isNotNull()
.isEqualTo("123");
}
@ComponentScan({"com.masterlink.strategy"})
@Configuration
public static class CodecStrategyTestConfig {
}
}
扩展复杂类型
自定义复杂类型User类,对应协议类型为 0xA0, 第2 、3 字节表示整个对象的字段长度,紧接着是 Integer 类型的age 和 String 类型的name,
比如 0xA0, 0x00 0x10 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x17, 0x00, 0x08, 0x5A,0x68,0x61,0x6E,0x67,0x53, 0x61,0x6E, 对应的user对象是
{
"age": 23,
"name": "ZhangSan"
}
@Data
public class User {
private Integer age;
private String name;
}
实现解码策略类
已知 User 中的基础类型依赖了 Integer 和 String ,所以在User的解码策略类中,依赖了 IntgerCodecStrategy 和 StringCodecStrategy
@CodecStrategyType(type = (byte) (0xA0))
@Service
public class UserCodeStrategy implements CodecStrategy<User> {
private final StringCodecStrategy stringCodecStrategy;
private final IntgerCodecStrategy intgerCodecStrategy;
public UserCodeStrategy(StringCodecStrategy stringCodecStrategy, IntgerCodecStrategy intgerCodecStrategy) {
this.stringCodecStrategy = stringCodecStrategy;
this.intgerCodecStrategy = intgerCodecStrategy;
}
@Override
public User decoding(byte[] buffer) {
byte ageL1 = buffer[0];
byte ageL2 = buffer[1];
short ageLength = (short) ((ageL2 & 0xFF)
| ((ageL1 & 0xFF)<<8));
byte[] ageBytes = new byte[ageLength];
System.arraycopy(buffer,2, ageBytes,0,ageLength);
byte nameL1 = buffer[0+ageLength];
byte nameL2 = buffer[1+ageLength];
short nameLength = (short) ((nameL2 & 0xFF)
| ((nameL1 & 0xFF)<<8));
byte[] nameBytes = new byte[nameLength];
System.arraycopy(buffer,2+ageLength+2, nameBytes,0,nameLength);
User user = new User();
user.setAge(intgerCodecStrategy.decoding(ageBytes));
user.setName(stringCodecStrategy.decoding(nameBytes));
return user;
}
}
测试
通过测试可以发现很轻松的就扩展了一个复杂类型的解码算法,这样随着协议的增加,可以做到对修改代码关闭,对扩展代码开放,符合开闭原则。
@Test
public void testUserDecoding(){
byte[] buffer = new byte[]{
(byte)0xA0, (byte)0x00 ,(byte)0x10 ,(byte)0x00, (byte)0x04,
(byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x17, (byte)0x00,
(byte)0x08, (byte)0x5A, (byte)0x68, (byte)0x61, (byte)0x6E,
(byte)0x67, (byte)0x53, (byte)0x61, (byte)0x6E
};
User user = (User)codec.decoding(buffer);
assertThat(user)
.isNotNull();
assertThat(user.getAge()).isEqualTo(23);
assertThat(user.getName()).isEqualTo("ZhangSan");
}
总结
- 使用策略模式,可以避免冗长的if-else 或 switch分支判断
- 掌握自定义注解的是使用方式
- 与使用
@Service("name")注解相比,自定义注解方式支撑和扩展的类型或更灵活
关注我的公众号,一起探索新知识新技术
