前面几节的网络骨架, 如VGGNet和ResNet等, 虽从各个角度出发提升了物体检测性能, 但究其根本是为ImageNet的图像分类任务而设计的。 而图像分类与物体检测两个任务天然存在着落差, 分类任务侧重全图的特征提取, 深层的特征图分辨率很低; 而物体检测需要定位出物体位置, 特征图分辨率不宜过小, 因此造成了以下两种缺陷:
·大物体难以定位: 对于FPN等网络, 大物体对应在较深的特征图上检测, 由于网络较深时下采样率较大, 物体的边缘难以精确预测, 增加了回归边界的难度。
·小物体难以检测: 对于传统网络, 由于下采样率大造成小物体在较深的特征图上几乎不可见; FPN虽从较浅的特征图来检测小物体, 但浅层的语义信息较弱, 且融合深层特征时使用的上采样操作也会增加物体检测的难度。
针对以上问题, 旷视科技提出了专为物体检测设计的DetNet结构,引入了空洞卷积, 使得模型兼具较大感受野与较高分辨率, 同时避免了3.6节中FPN的多次上采样, 实现了较好的检测效果。
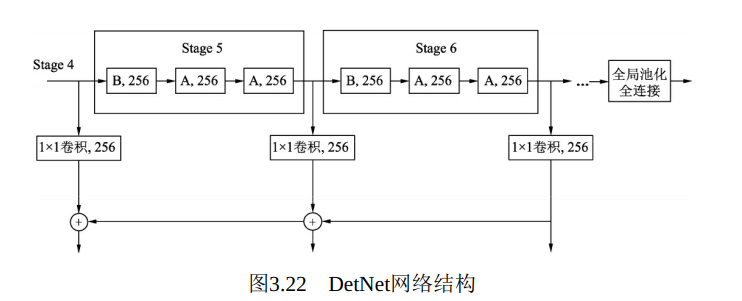
DetNet的网络结构如图3.22所示, 仍然选择性能优越的ResNet-50作为基础结构, 并保持前4个stage与ResNet-50相同, 具体的结构细节有以下3点:
·引入了一个新的Stage 6, 用于物体检测。 Stage 5与Stage 6使用了DetNet提出的Bottleneck结构, 最大的特点是利用空洞数为2的3×3卷积取代了步长为2的3×3卷积.
·Stage 5与Stage 6的每一个Bottleneck输出的特征图尺寸都为原图的, 通道数都为256, 而传统的Backbone通常是特征图尺寸递减, 通道数递增.
·在组成特征金字塔时, 由于特征图大小完全相同, 因此可以直接从右向左传递相加, 避免了上一节的上采样操作。 为了进一步融合各通道的特征, 需要对每一个阶段的输出进行1×1卷积后再与后一Stage传回的特征相加。
DetNet这种精心设计的结构, 在增加感受野的同时, 获得了较大的特征图尺寸, 有利于物体的定位。 与此同时, 由于各Stage的特征图尺寸相同, 避免了上一节的上采样, 既一定程度上降低了计算量, 又有利于小物体的检测。
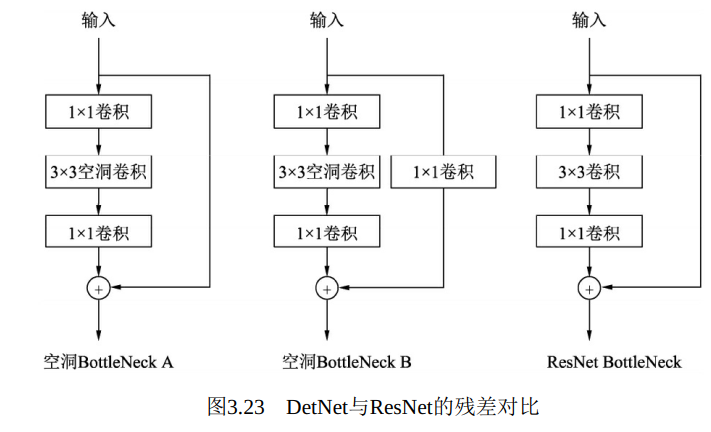
DetNet中Bottleneck的细节如图3.23所示, 左侧的两个Bottleneck A与Bottleneck B分别对应图3.22的A与B, 右侧的为原始的ResNet残差结构。 DetNet与ResNet两者的基本思想都是卷积堆叠层与恒等映射的相加, 区别在于DetNet使用了空洞数为2的3×3卷积, 这样使得特征图尺寸保持不变, 而ResNet是使用了步长为2的3×3卷积。 B相比于A, 在恒等映射部分增加了一个1×1卷积, 这样做可以区分开不同的Stage, 并且实验发现这种做法对于特征金字塔式的检测非常重要
.
使用PyTorch来实现DetNet的两个Bottleneck结构A和B, 新建一个detnet_bott-leneck.py文件, 代码如下:

1 import torch 2 from torch import nn 3 4 class DetBottleneck(nn.Module): 5 6 # 初始化时extra为False时为Bottleneck A, 为True时则为Bottleneck B 7 def __init__(self, inplaces, planes, stride=1, extra=False): 8 9 super(DetBottleneck, self).__init__() 10 # 构建连续3个卷积层的Bottleneck 11 self.bottleneck = nn.Sequential( 12 nn.Conv2d(inplaces, planes, 1, bias =False), 13 nn.BatchNorm2d(planes), 14 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 15 nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, dilation=2, bias=False), 16 nn.BatchNorm2d(planes), 17 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 18 nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, 1, bias=False), 19 nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) 20 ) 21 22 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) 23 self.extra = extra 24 25 # Bottleneck B的1×1卷积 26 if self.extra: 27 self.extra_conv = nn.Sequential( 28 nn.Conv2d(inplaces, planes, 1, bias=False), 29 nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) 30 ) 31 32 def forward(self, x): 33 # 对于Bottleneck B来讲, 需要对恒等映射增加卷积处理, 与ResNet类似 34 if self.extra: 35 indentity = self.extra_conv(x) 36 else: 37 indentity = x 38 out = self.bottleneck(x) 39 out += indentity 40 out = self.relu(out) 41 42 return out

1 import torch 2 from detnet_bottleneck import DetBottleneck 3 4 bottleneck_b = DetBottleneck(1024, 256, 1, True).cuda() 5 print(bottleneck_b) 6 >> DetBottleneck( 7 (bottleneck): Sequential( 8 (0): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 9 (1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 10 (2): ReLU(inplace=True) 11 (3): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), dilation=(2, 2), bias=False) 12 (4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 13 (5): ReLU(inplace=True) 14 (6): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 15 (7): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 16 ) 17 (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) 18 (extra_conv): Sequential( 19 (0): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 20 (1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 21 ) 22 ) 23 24 bottleneck_a1 = DetBottleneck(256,256).cuda() 25 print(bottleneck_a1) 26 >> 27 DetBottleneck( 28 (bottleneck): Sequential( 29 (0): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 30 (1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 31 (2): ReLU(inplace=True) 32 (3): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), dilation=(2, 2), bias=False) 33 (4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 34 (5): ReLU(inplace=True) 35 (6): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 36 (7): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 37 ) 38 (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) 39 ) 40 41 42 bottleneck_a2 = DetBottleneck(256, 256).cuda() 43 print(bottleneck_a2) 44 >> DetBottleneck( 45 (bottleneck): Sequential( 46 (0): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 47 (1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 48 (2): ReLU(inplace=True) 49 (3): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), dilation=(2, 2), bias=False) 50 (4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 51 (5): ReLU(inplace=True) 52 (6): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) 53 (7): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) 54 ) 55 (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) 56 ) 57 58 input = torch.randn(1, 1024, 14, 14).cuda() 59 60 # 将input作为某一层的特征图, 依次传入Bottleneck B、 A1与A2三个模块 61 output1 = bottleneck_b(input) 62 output2 = bottleneck_a1(output1) 63 output3 = bottleneck_a2(output2) 64 65 # 三个Bottleneck输出的特征图大小完全相同 66 print(output1.shape) 67 >> torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14]) 68 print(output2.shape) 69 >> torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14]) 70 print(output3.shape) 71 >> torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])
