111、二叉树的最小深度
基本思想:
广度优先搜索
具体实现:
1、根节点入列
2、循环条件是 直到清空队列
3、节点出列以后判断左右子树
如果左右子树都为空,返回现在的深度
如果左孩子存在,加入队列,原深度加1
如果右孩子存在,加入队列,原深度加1
depth+1此时并不会改变depth
代码:
class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 que = collections.deque([(root, 1)]) while que: node, depth = que.popleft() if not node.left and not node.right: return depth if node.left: que.append((node.left, depth + 1)) if node.right: que.append((node.right, depth + 1)) return 0
套东哥框架
class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 que = collections.deque([root]) depth = 1 while que: for _ in range(len(que)): node = que.popleft() if not node.left and not node.right: return depth if node.left: que.append(node.left) if node.right: que.append(node.right) depth += 1 return depth
752、打开转盘锁
基本思想:
广度优先算法
具体实现:
函数是顺序执行,遇到return语句或者最后一行函数语句就返回。而变成generator的函数,在每次调用next()的时候执行,遇到yield语句返回,再次执行时从上次返回的yield语句处继续执行。
在最后一个for循环那就相当于执行next了。
代码:
class Solution: def openLock(self, deadends: List[str], target: str) -> int: def neighbors(node):
for i in range(4): x = int(node[i]) for d in (-1, 1): y = (x + d) % 10 yield node[:i] + str(y) + node[i+1:] dead = set(deadends) queue = collections.deque([('0000', 0)]) seen = {'0000'} while queue: node, depth = queue.popleft() if node == target: return depth if node in dead: continue for nei in neighbors(node): if nei not in seen: seen.add(nei) queue.append((nei, depth+1)) return -1
套东哥框架
class Solution:
def openLock(self, deadends: List[str], target: str) -> int:
def turnup(s, i):
s_list = list(s)
if s_list[i] == '9':
s_list[i] = '0'
else:
s_list[i] = str(int(s_list[i])+1)
return "".join(s_list)
def turndown(s, i):
res = list(s) # 字符串变数列
s_list = list(s)
if s_list[i] == '0':
s_list[i] = '9'
else:
s_list[i] = str(int(s_list[i])-1)
return "".join(s_list)
digits = "".join([str(x) for x in range(10)])+"0"
n = 4
start = "0"*n
queue = deque([start])
visited = set() #记录已经穷举过的密码
visited.add(start)
res = 0
while queue:
for _ in range(len(queue)):
combination = queue.popleft()
if combination in deadends:
continue
if combination == target:
return res
for i in range(n): #四位数密码挨个开始转
tmp = turnup(combination, i)
if tmp not in visited:
queue.append(tmp)
visited.add(tmp)
tmp = turndown(combination, i)
if tmp not in visited:
queue.append(tmp)
visited.add(tmp)
res += 1
return -1
773、滑动谜题
基本思想:
BFS
具体实现:
1、二维数组摊平变成一维数组
创建一个数组,数组内元素的索引是0在一维数组中的位置
数组内的元素,是0相邻数组在一维数组中的索引
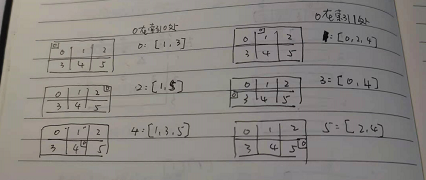
2、看0的位置和上下左右的数字进行交换
代码:
class Solution: def slidingPuzzle(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> int: neighbor = [[1,3],[0,2,4],[1,5],[0,4],[1,3,5],[2,4]] m, n = 2, 3 start = "" target = "123450" step =0 # 将2x3的数组转换成字符串 for i in range(m): for j in range(n): start += chr(board[i][j]+ord('0')) # BFS visited = [] queue = collections.deque([start]) while queue: sz = len(queue) for _ in range(sz): cur = queue.popleft() # 判断是否达到目标局面 if cur == target: return step i = 0 while(cur[i]!='0'): i+=1 #找到0的索引 #将数字0和相邻的数字交换位置 for adj in neighbor[i]: #adj就是相邻数字的索引 new_board = list(cur) #当前字符串变成列表 new_board[adj], new_board[i] = new_board[i], new_board[adj] new_board = "".join(new_board) #交换完以后将列表变成字符串 if(new_board not in visited): #防止交换到以前存在过的,防止走回头路 queue.append(new_board) visited.append(new_board) step +=1 return -1