46、全排列
基本思想:
回溯算法
具体实现:
与组合问题的不同,不在for循环中使用stratindex
因为全排列问题每次都要从头搜索,例如元素1在[1,2]中已经使用过了,但是在[2,1]中还要再使用一次1。
但是路径中出现过的数字,就不要再添加进来了

代码:
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { if (nums.length == 0) return result; backtrack(nums, path); return result; } public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> path) { if (path.size() == nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); } for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 如果path中已有,则跳过 if (path.contains(nums[i])) { continue; } path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, path); path.removeLast(); } } }
47、全排列II
具体实现:
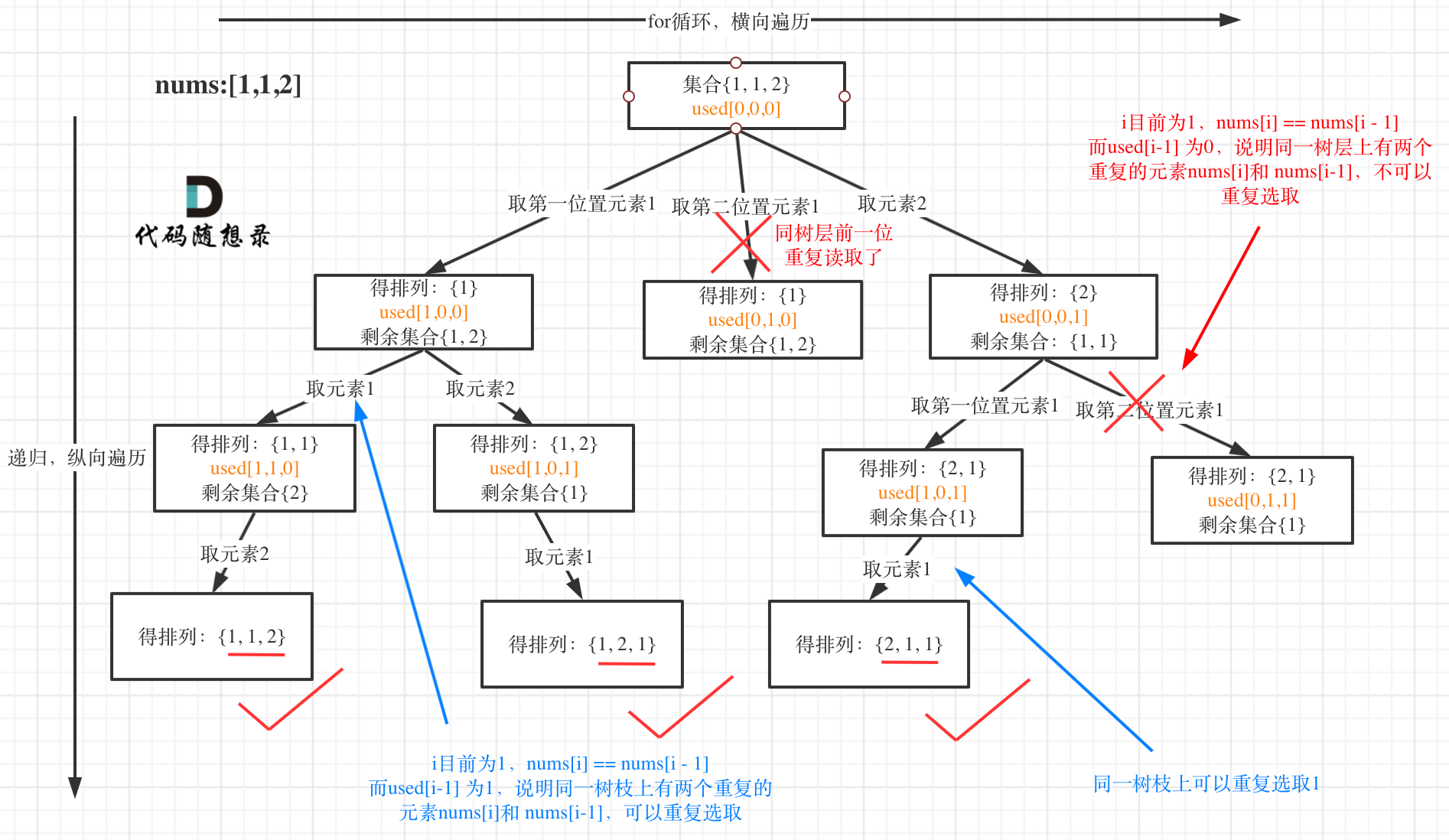
代码:
class Solution { //存放结果 List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); //暂存结果 List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length]; Arrays.fill(used, false); Arrays.sort(nums); backTrack(nums, used); return result; } private void backTrack(int[] nums, boolean[] used) { if (path.size() == nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // used[i - 1] == true,说明同⼀树⽀nums[i - 1]使⽤过 // used[i - 1] == false,说明同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过 // 如果同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过则直接跳过 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) { continue; } //如果同⼀树⽀nums[i]没使⽤过开始处理 if (used[i] == false) { used[i] = true;//标记同⼀树⽀nums[i]使⽤过,防止同一树支重复使用 path.add(nums[i]); backTrack(nums, used); path.remove(path.size() - 1);//回溯,说明同⼀树层nums[i]使⽤过,防止下一树层重复 used[i] = false;//回溯 } } } }