WaveNet初步理解
paper 是DeepMind使用CNN来做语音生成的工作,这个模型直接使用声音的原始波形进行训练的。目前github上开源了一个tensorflow-wavenet项目
文章主要内容有几点:
1.文章中,通过该模型进行语音生成任务,结果很接近真人发出的声音
2.Wavenet还可以抓取不同说话者的特征,有高保真度
3.使用音乐文件来训练该模型,可以生成新的高保真度的音乐片段
4.还可以加入判别模型,使之完成语音识别任务
模型结构

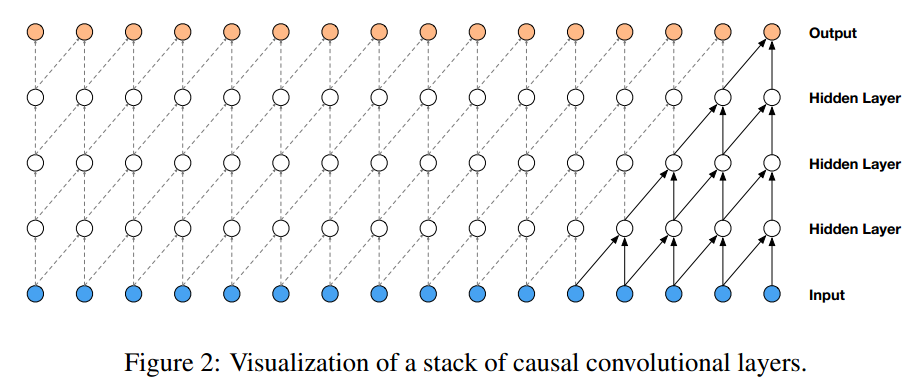
为了提高receptive field, 文章使用dilated convolution技术(跳着卷积)。虽然音频是连续的,但是将其进行量化,降维到256dims,转换成了分类问题。文章基于的条件分布概率模型,是通过causal convolutional网络结构来实现的。
input
原始音频文件是16bit的整数值序列存储,为了便于运算,文章使用了ulaw压缩编码,将音频16bit归一化后降低到了256dims。
G711编码的声音清晰度好,语音自然度高,但是压缩效率低,输出为8bit,主要分为ulaw和alaw。alaw也叫G711a,输入时13位(s16的高13位),在欧洲和中国使用广泛;ulaw也叫G711u,输入14位,主要北美和日本使用。编码算法多以查表为主,基础值+平均偏移。
convolution

在wavenet中采用causal convolutions,保证
中不包含
中的信息。
对于1D数据信息,输出label为输入信息的偏移。
input: x: 0-255 int
output: label: x向负方向shift 1. 使用前t个采样点来预测第t+1个采样点,空缺位补0.
eg: x=[1,2,3,4,5] y=[2,3,4,5,0]
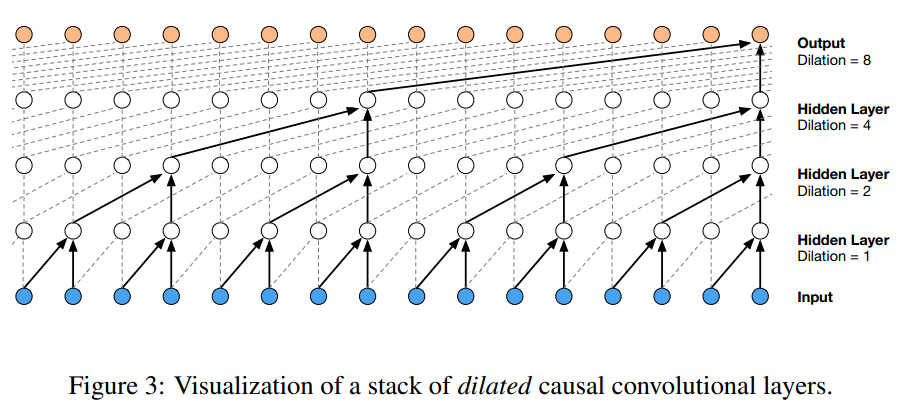
由于声波采样非常密集,为了提高receptive field,paper使用了dilated convolutions,可以在保持在原本卷积层数量的参数情况下,指数级的增长receptive field。
Gated Activation Units
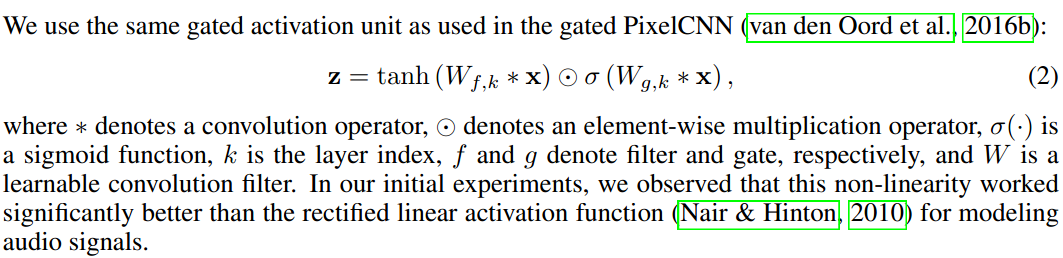
在声音信号建模中,非线性模型效果更好。
residual block and skip connection
WaveNet中使用residual block and skip connection技术是用来加速模型收敛速度的,并且使得梯度能够传到更深的模型。
Residual and skip connection技术是KaimingHe在2015年ResNet paper 提出的。
ResNet产生的背景是当网络越深时的学习越难,主要原因是梯度弥散或爆炸(vanishing/exploding gradients)。有一种解决方案是采用标准化,标准化的初始化数据或中间层的标准化(batch normalization)。当网络的深度继续增加,训练精确度达到饱和后,会出现急剧衰退,一个深度合适的模型增加更多的网络层会导致更高的训练错误,这并不是由过拟合导致的。ResNet通过引入一个深度残差学习网络来解决衰退问题。
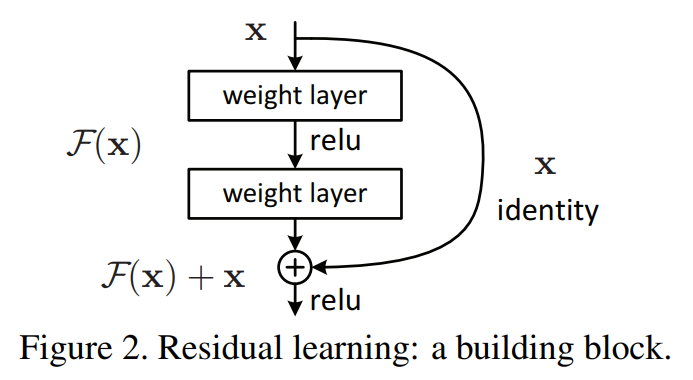
构造方式是增加恒等映射(identity mapping,即f(x)=x),明确让网络层去拟合残差映射,将期望的潜在映射指为H(x),非线性层匹配其他映射F(x)=H(x)-x。通过多个非线性网络层去逼近恒等映射是有困难的,重新公式化后H(x)=F(x)+x,如果恒等映射时最优的,则非线性网络的权重向0逼近,以此来逼近恒等映射。
ResNet paper中实验表明,恒等映射足以解决网络衰退问题,并且恒等映射是经济的(introduce neither extra parameter nor computation complexity)。
公式化输入输出:
Ws只有在匹配维度时才使用,例如pooling操作前后。
Code
fake code
def loss(input_batch):
'''Creates a WaveNet network and returns the autoencoding loss.
with tf.name_scope(name):
# ulaw编码,return 0-255
input_batch = mu_law_encode(input_batch,
self.quantization_channels)
encoded = one_hot(input_batch)
#wavenet model output
raw_output = self._create_network(encoded)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 向左偏移一位,即减去第一位,保证每次是预测下一个输出。
# encoded=[0,0,0,0,1,2,3,4,5], encoded.shape=(1,9,1)
# shifted.shape=(1,8,1),[0,0,0,1,2,3,4,5]
shifted = tf.slice(encoded, [0, 1, 0],
[-1, tf.shape(encoded)[1] - 1, -1])
# 补零,shifted.shape=(1,9,1),[0,0,0,1,2,3,4,5,0]
shifted = tf.pad(shifted, [[0, 0], [0, 1], [0, 0]])
#将模型预测转换shape为prediction
prediction = tf.reshape(raw_output,
[-1, self.quantization_channels])
#loss函数
loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
prediction,
tf.reshape(shifted, [-1, self.quantization_channels]))
reduced_loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
return reduced_loss
def create_network(input_batch):
outputs = []
current_layer = input_batch
current_layer = create_causal_layer(current_layer)
# Add all defined dilation layers. #18 layers
for layer_index, dilation in enumerate(self.dilations):
output, current_layer = create_dilation_layer(
current_layer, layer_index, dilation)
outputs.append(output)
# Perform (+) -> ReLU -> 1x1 conv -> ReLU -> 1x1 conv to the output.
total = sum(outputs)
transformed1 = tf.nn.relu(total)
conv1 = tf.nn.conv1d(transformed1, w1, stride=1, padding="SAME")
transformed2 = tf.nn.relu(conv1)
conv2 = tf.nn.conv1d(transformed2, w2, stride=1, padding="SAME")
return conv2
def create_dilation_layer(input_batch, layer_index, dilation):
'''Creates a single causal dilated convolution layer.
The layer contains a gated filter that connects to dense output
and to a skip connection:
|-> [gate] -| |-> 1x1 conv -> skip output
| |-> (*) -|
input -|-> [filter] -| |-> 1x1 conv -|
| |-> (+) -> dense output
|------------------------------------|
Where `[gate]` and `[filter]` are causal convolutions with a
non-linear activation at the output.
'''
conv_filter = causal_conv(input_batch, weights_filter, dilation)
conv_gate = causal_conv(input_batch, weights_gate, dilation)
out = tf.tanh(conv_filter) * tf.sigmoid(conv_gate)
transformed = tf.nn.conv1d(
out, weights_dense, stride=1, padding="SAME", name="dense")
skip_contribution = tf.nn.conv1d(
out, weights_skip, stride=1, padding="SAME", name="skip")
#返回skip output和(残差+input)
return skip_contribution, input_batch + transformed
def create_causal_layer():
detail source code
实现方式巧妙,直接见源码分析
source code
causal_conv
def time_to_batch(value, dilation, name=None):
with tf.name_scope('time_to_batch'):
#value=[[[0],[0],[0],[0],[1],[2],[3],[4],[5]]]
#value.shape=(1,9,1) dilation=4
shape = tf.shape(value)
#pad_elements=4-1-(9+4-1)%4=3
pad_elements = dilation - 1 - (shape[1] + dilation - 1) % dilation
#padded=[[[0],[0],[0],[0],[1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[0],[0],[0]]]
padded = tf.pad(value, [[0, 0], [0, pad_elements], [0, 0]])
#reshape=[[[0,0,0],[0,1,2],[3,4,5],[0,0,0]]]
#reshape.shape=(3,4,1)
reshaped = tf.reshape(padded, [-1, dilation, shape[2]])
#transposed=[[[0,0,3,0],[0,1,4,0],[0,2,5,0]]]
#transposed.shape=(4,3,1)
transposed = tf.transpose(reshaped, perm=[1, 0, 2])
#return shape=(4,3,1)
return tf.reshape(transposed, [shape[0] * dilation, -1, shape[2]])
def batch_to_time(value, dilation, name=None):
with tf.name_scope('batch_to_time'):
shape = tf.shape(value)
prepared = tf.reshape(value, [dilation, -1, shape[2]])
transposed = tf.transpose(prepared, perm=[1, 0, 2])
#最后返回的是前面time_to_batch的最初输入数值的shape
#return shape为(1,9,1)
return tf.reshape(transposed,
[tf.div(shape[0], dilation), -1, shape[2]])
##if filter_width=2,dilation=4, value=[[[1],[2],[3],[4],[5]]] value.shape=(1,5,1)
def causal_conv(value, filter_, dilation, name='causal_conv'):
with tf.name_scope(name):
# Pad beforehand to preserve causality.
filter_width = tf.shape(filter_)[0]
#padding=[[0, 0], [4, 0], [0, 0]]
padding = [[0, 0], [(filter_width - 1) * dilation, 0], [0, 0]]
#第二个维度前边增加4个0,shape:(1,5,1)->(1,9,1)
#padded=[[[0],[0],[0],[0],[1],[2],[3],[4],[5]]]
padded = tf.pad(value, padding)
if dilation > 1:
#return shape=(4,3,1)
transformed = time_to_batch(padded, dilation)
conv = tf.nn.conv1d(transformed, filter_, stride=1, padding='SAME')
restored = batch_to_time(conv, dilation)
else:
restored = tf.nn.conv1d(padded, filter_, stride=1, padding='SAME')
# Remove excess elements at the end.
result = tf.slice(restored,
[0, 0, 0],
[-1, tf.shape(value)[1], -1])
#result.shape = padded.shape
return result
dilation_layer
def _create_dilation_layer(self, input_batch, layer_index, dilation):
'''Creates a single causal dilated convolution layer.
The layer contains a gated filter that connects to dense output
and to a skip connection:
|-> [gate] -| |-> 1x1 conv -> skip output
| |-> (*) -|
input -|-> [filter] -| |-> 1x1 conv -|
| |-> (+) -> dense output
|------------------------------------|
Where `[gate]` and `[filter]` are causal convolutions with a
non-linear activation at the output.
'''
variables = self.variables['dilated_stack'][layer_index]
weights_filter = variables['filter']
weights_gate = variables['gate']
conv_filter = causal_conv(input_batch, weights_filter, dilation)
conv_gate = causal_conv(input_batch, weights_gate, dilation)
if self.use_biases:
filter_bias = variables['filter_bias']
gate_bias = variables['gate_bias']
conv_filter = tf.add(conv_filter, filter_bias)
conv_gate = tf.add(conv_gate, gate_bias)
#gate和filter共同输出
out = tf.tanh(conv_filter) * tf.sigmoid(conv_gate)
# The 1x1 conv to produce the residual output
weights_dense = variables['dense']
transformed = tf.nn.conv1d(
out, weights_dense, stride=1, padding="SAME", name="dense")
# The 1x1 conv to produce the skip output
weights_skip = variables['skip']
#skip output
skip_contribution = tf.nn.conv1d(
out, weights_skip, stride=1, padding="SAME", name="skip")
if self.use_biases:
dense_bias = variables['dense_bias']
skip_bias = variables['skip_bias']
transformed = transformed + dense_bias
skip_contribution = skip_contribution + skip_bias
#返回skip output和(残差+input)
return skip_contribution, input_batch + transformed
network
def _create_network(self, input_batch):
'''Construct the WaveNet network.'''
outputs = []
current_layer = input_batch
current_layer = self._create_causal_layer(current_layer)
# Add all defined dilation layers. #18 layers
with tf.name_scope('dilated_stack'):
for layer_index, dilation in enumerate(self.dilations):
with tf.name_scope('layer{}'.format(layer_index)):
output, current_layer = self._create_dilation_layer(
current_layer, layer_index, dilation)
outputs.append(output)
#postprocess层
with tf.name_scope('postprocessing'):
# Perform (+) -> ReLU -> 1x1 conv -> ReLU -> 1x1 conv to
# postprocess the output.
# conv weight
w1 = self.variables['postprocessing']['postprocess1']
w2 = self.variables['postprocessing']['postprocess2']
if self.use_biases:
b1 = self.variables['postprocessing']['postprocess1_bias']
b2 = self.variables['postprocessing']['postprocess2_bias']
# We skip connections from the outputs of each layer, adding them
# all up here.
#将每一层的skip connection输出累加
total = sum(outputs)
transformed1 = tf.nn.relu(total)
conv1 = tf.nn.conv1d(transformed1, w1, stride=1, padding="SAME")
if self.use_biases:
conv1 = tf.add(conv1, b1)
transformed2 = tf.nn.relu(conv1)
conv2 = tf.nn.conv1d(transformed2, w2, stride=1, padding="SAME")
if self.use_biases:
conv2 = tf.add(conv2, b2)
return conv2
Reference
WAVENET
github open source code
【Emotibot Tech】WaveNet语音合成与深度生成模型解析
WaveNet 分析和实现
谷歌WaveNet如何通过深度学习方法来生成声音?
谷歌WaveNet 源码详解
技术 | DeepMind语音生成模型WaveNet的TensorFlow实现
Pixel CNN, Wavenet, GCNN笔记
一些ResNet的参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27082562
https://tracholar.github.io/wiki/machine-learning/residual-network.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/22071346
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/22447440
http://blog.csdn.net/mao_feng/article/details/52734438
http://blog.csdn.net/bea_tree/article/details/51817142
http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-hnytmiyq-pt.html
http://pengshuang.space/2017/08/05/Resnet-学习笔记/
G711编码:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Μ-law_algorithm
http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-fgyvjsfz-bmq.html
http://www.21ic.com/evm/audio/201705/721797.htm
