阻塞队列:
Queue接口与List、Set同一级别,都是继承了Collection接口。LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
BlockingQueue接口的实现类

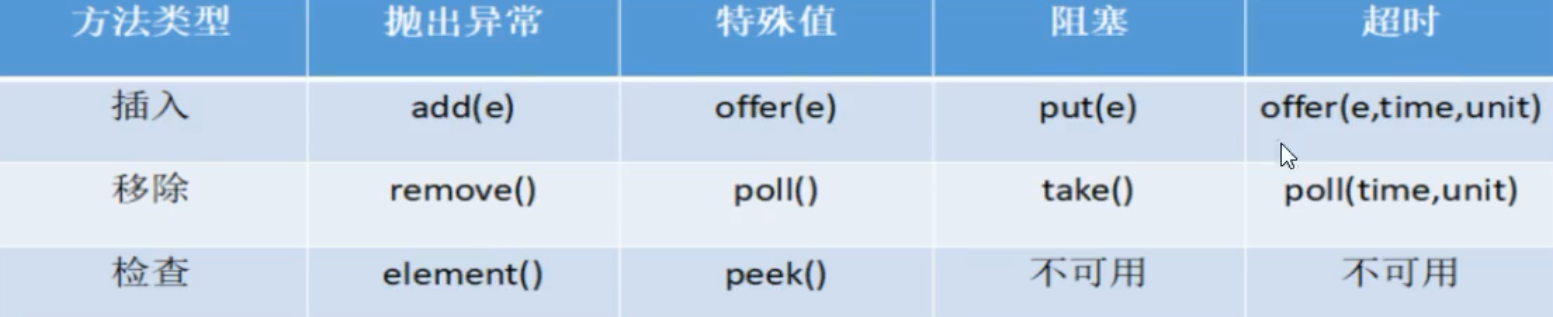
BlockingQUeue的核心方法

一、ArrayBlockingQueue
1、抛出异常:
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 1、抛出异常:add/remove
System.out.println(queue.add("a"));
System.out.println(queue.add("b"));
System.out.println(queue.add("c"));
// 超出队列长度报错:Queue full
// System.out.println(queue.add("x"));
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
// 队列中没有元素报错:NoSuchElementException
//queue.remove();
2、特殊值
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 2、特殊值:offer/poll
System.out.println(queue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(queue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(queue.offer("c"));
// 插入不进去元素会返回false
System.out.println(queue.offer("x"));
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
// 取不到数据会返回null
System.out.println(queue.poll());
3、阻塞
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 3、阻塞
queue.put("a");
queue.put("b");
queue.put("c");
// 队列插入不了数据,会一直卡住
// queue.put("x");
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
// 检索并删除此队列的头,如有必要,请等待直到元素可用
System.out.println(queue.take());
4、超时
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 3、超时
System.out.println(queue.offer("a", 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer("b", 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer("c", 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// 队列已满会等待指定的时间,返回false
System.out.println(queue.offer("x", 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// 队列已满会等待指定的时间,返回null
System.out.println(queue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
二、SynchronizeousQueue:生产一个消费一个
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author zhangzhixi
* @date 2021-4-20 22:08
*/
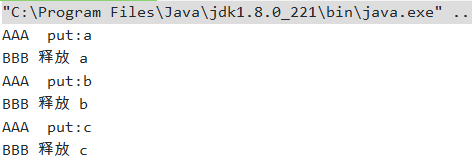
public class Demo_05_阻塞队列 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<String> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
// 一个线程用来生产
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put:" + "a");
queue.put("a");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put:" + "b");
queue.put("b");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put:" + "c");
queue.put("c");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "AAA").start();
// 一个线程用来消费
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" 释放 " +queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" 释放 " +queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" 释放 " +queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "BBB").start();
}
}