本文衔接 OC 底层探索 13 继续探索类的加载,我们已知通过 readClass() 读取了编译器写的类(or元类),同时给 cls 赋了 name 和把cls 插入到了类/元类的表中,此时cls不仅有了地址还有了 name。此时的类是什么样子的呢?我们读取一下 cls 的内存情况,见下图:

通过上面lldb调试,我们发现cls 的 bits 是0000,并无数据. 继续执行到 realizeClassWithoutSwift() 中:
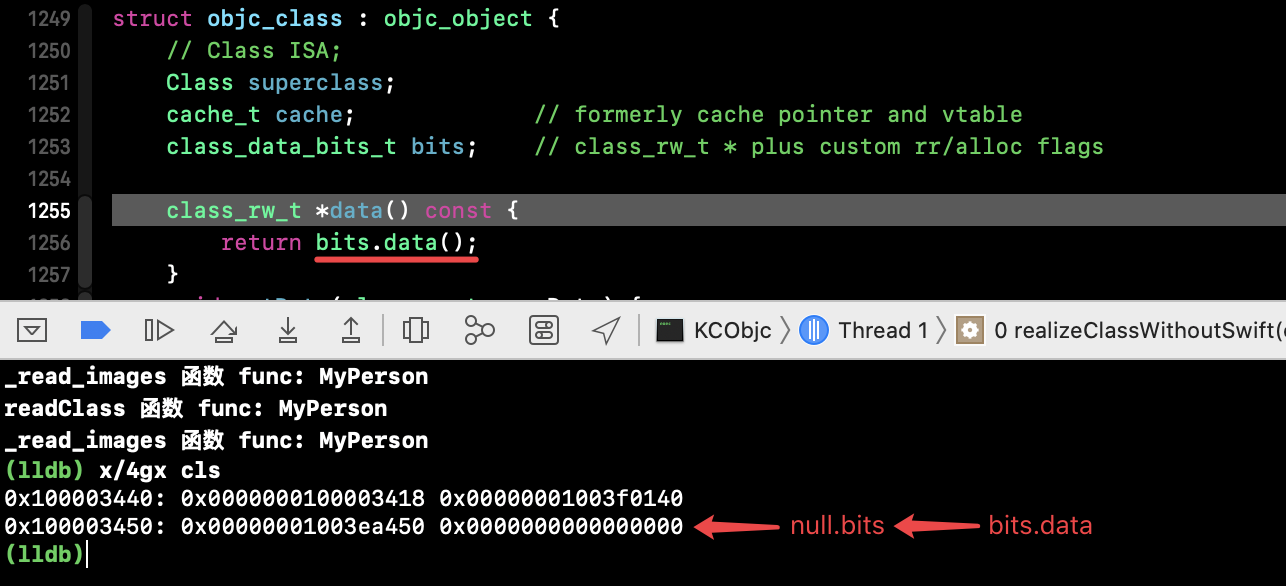
此时其实 cls 的内存还没有分配完毕,初始化和赋值还未处理好,内存还没有完善。
那么 auto ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data(); 进行了 data 的读取,这里的 data 是读的什么呢?
--> cls 的内存情况虽未完备,但是它现在已经从编译器读出来了,是有其唯一地址的,我们试着读取下 cls 指针的内容:
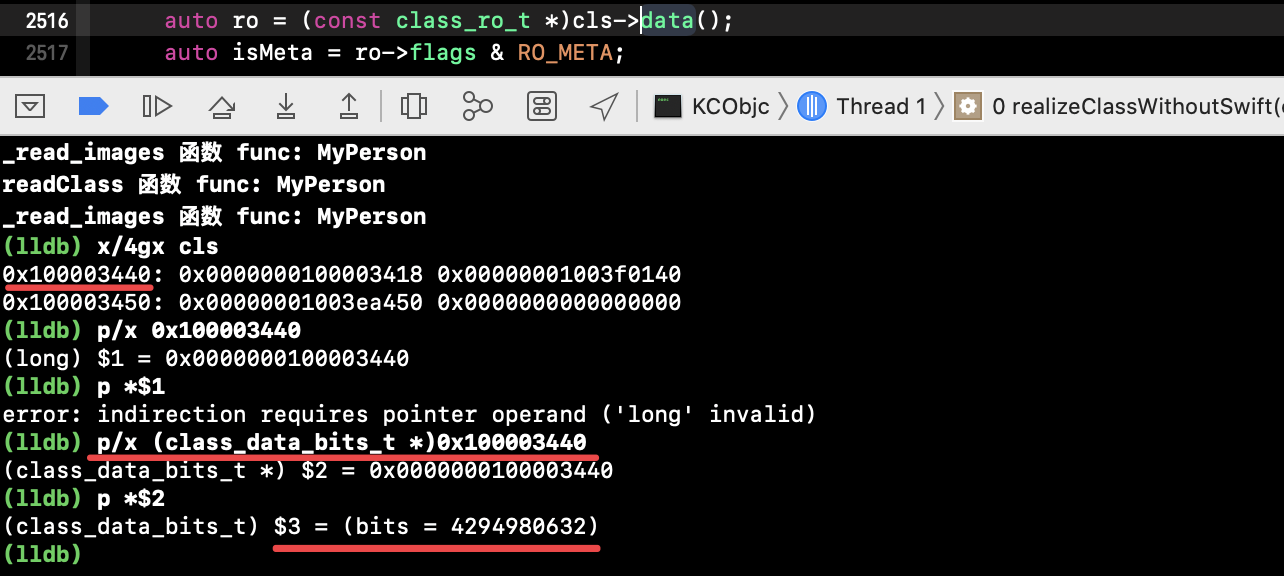
显然,bits 是有值的。 即我们可通过 cls 的地址指针进行识别数据的。
问题:cls 是什么时候 bits 有值的呢?
下面继续 _read_images() 的源码分析。
Fix up remapped classes 未进入跳过,协议和分类我们这里暂时不对其进行具体的分析;
一点点扩展:
非懒加载的类才会走进下面3637行代码,直接跑工程并未进去,我们如何走进去呢 --> 给 MyPerson 类添加 +load() 方法:
load 方法的实现为何就会使 MyPerson 的方法提前加载呢? --> load 方法是在 load_images 时就会调用的 --> 若类都没有实现如何 load_images 呢 --> so 方法都提前了
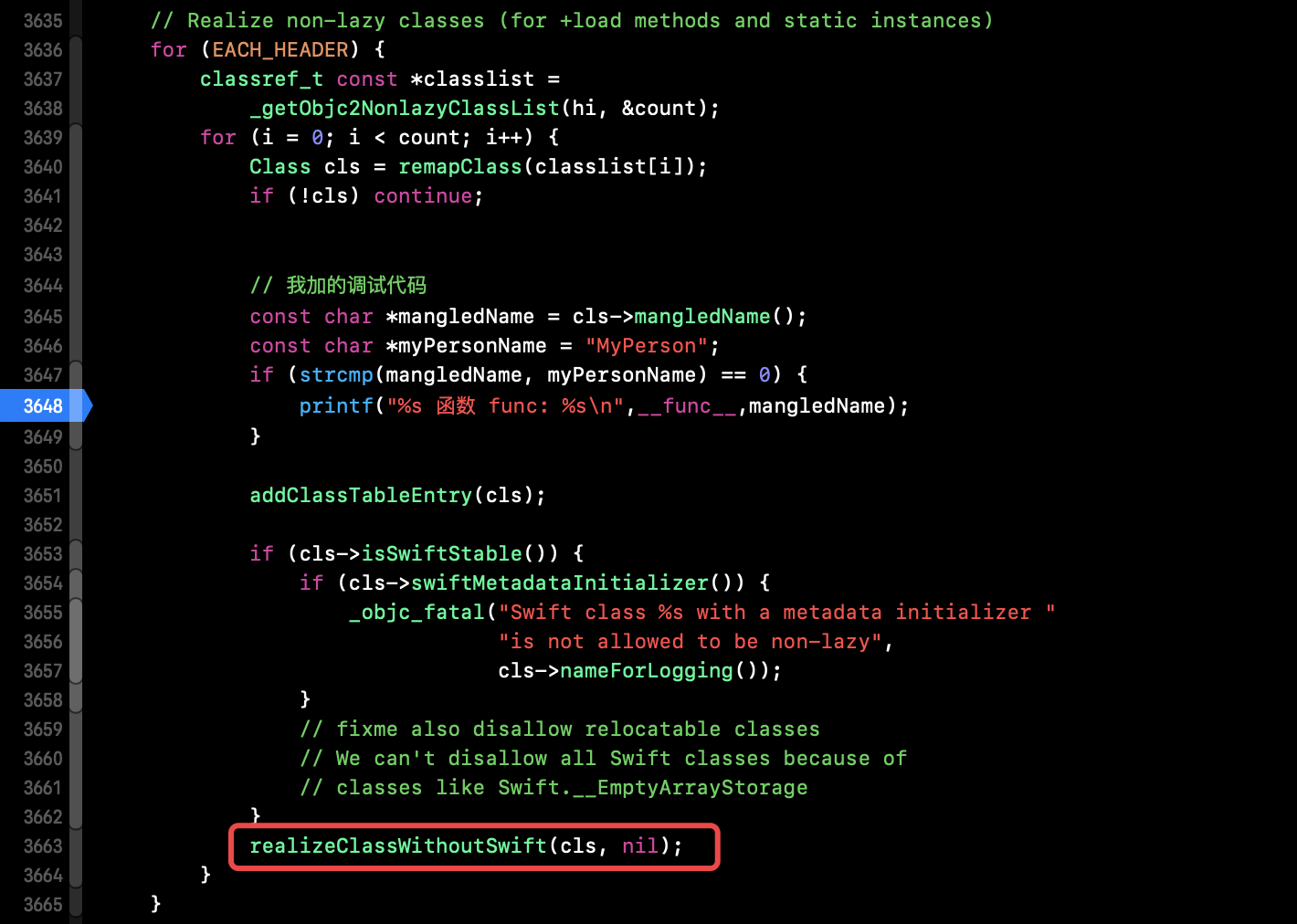
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);// 在此之前,cls 还只是一个地址和名字,但是 data 数据信息还是macho中,还并未加载读取到cls的内存中。通过 realizeClassWithoutSwift() 实现,下面对此函数源码进行探究。
tip: 我们之前已知,在消息的转发中 lookUpIMPAndForward 流程中,类必须是已经实现的,若没有实现则必须 realizeClassWithoutSwift() 实现。这里就可知了原因,类必须是已经存在完备的,若是类没有实现,我们无法调其中任何方法的,alloc init 自然也是无法操作实例化出来。
那么 懒加载呢?我们注释掉 +load{} 方法,run,打印堆栈信息:

我们在 main.m 中调用了 MyPerson *objc2 = [MyPerson alloc]; // 懒加载 - 敌不动我不动,敌动我动。
懒加载的意义:若没有懒加载,那么我们所有的类的实现 全部处理(代码实现、方法排序、临时变量等)有大量的工作要做,这些都要在 main 函数前处理完,那么会造成 main 函数的启动很慢;懒加载使我们不调用的类不先加载,节省了内存,提高了性能。<-- 这里也验证了为何 load 方法能不写就不写的原因。
下面进行进入 realizeClassWithoutSwift() 流程分析。
一、类的加载
realizeClassWithoutSwift() 源码分析:
1 /*********************************************************************** 2 * realizeClassWithoutSwift 3 * Performs first-time initialization on class cls, 4 * including allocating its read-write data. 5 * Does not perform any Swift-side initialization. 6 * Returns the real class structure for the class. 7 * Locking: runtimeLock must be write-locked by the caller 8 **********************************************************************/ 9 static Class realizeClassWithoutSwift(Class cls, Class previously) 10 { 11 runtimeLock.assertLocked(); 12 13 class_rw_t *rw; 14 Class supercls; 15 Class metacls; 16 17 if (!cls) return nil; 18 if (cls->isRealized()) return cls; 19 ASSERT(cls == remapClass(cls)); 20 21 // fixme verify class is not in an un-dlopened part of the shared cache? 22 23 auto ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data(); 24 auto isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META;// 元类判断 25 if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) { 26 // This was a future class. rw data is already allocated. 27 rw = cls->data(); 28 ro = cls->data()->ro(); 29 ASSERT(!isMeta); 30 cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE); 31 } else { 32 // Normal class. Allocate writeable class data. 33 rw = objc::zalloc<class_rw_t>();// 开辟空间 34 rw->set_ro(ro);// ro 数据赋值给 rw 35 rw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING|isMeta; 36 cls->setData(rw);// cls 重新将 rw 作为其 data 赋值 37 } 38 39 #if FAST_CACHE_META 40 if (isMeta) cls->cache.setBit(FAST_CACHE_META); 41 #endif 42 43 // Choose an index for this class. 44 // Sets cls->instancesRequireRawIsa if indexes no more indexes are available 45 cls->chooseClassArrayIndex(); 46 47 if (PrintConnecting) { 48 _objc_inform("CLASS: realizing class '%s'%s %p %p #%u %s%s", 49 cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? " (meta)" : "", 50 (void*)cls, ro, cls->classArrayIndex(), 51 cls->isSwiftStable() ? "(swift)" : "", 52 cls->isSwiftLegacy() ? "(pre-stable swift)" : ""); 53 } 54 55 // Realize superclass and metaclass, if they aren't already. 56 // This needs to be done after RW_REALIZED is set above, for root classes. 57 // This needs to be done after class index is chosen, for root metaclasses. 58 // This assumes that none of those classes have Swift contents, 59 // or that Swift's initializers have already been called. 60 // fixme that assumption will be wrong if we add support 61 // for ObjC subclasses of Swift classes.// cls 的所有的父类 元类 全部实现、确定 --> 继承链确定下来 62 supercls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->superclass), nil);// 父类 递归 63 metacls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->ISA()), nil);// 元类 递归 64 65 #if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA // isa 的设置 66 if (isMeta) { 67 // Metaclasses do not need any features from non pointer ISA 68 // This allows for a faspath for classes in objc_retain/objc_release. 69 cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsa(); 70 } else { 71 // Disable non-pointer isa for some classes and/or platforms. 72 // Set instancesRequireRawIsa. 73 bool instancesRequireRawIsa = cls->instancesRequireRawIsa(); 74 bool rawIsaIsInherited = false; 75 static bool hackedDispatch = false; 76 77 if (DisableNonpointerIsa) { 78 // Non-pointer isa disabled by environment or app SDK version 79 instancesRequireRawIsa = true; 80 } 81 else if (!hackedDispatch && 0 == strcmp(ro->name, "OS_object")) 82 { 83 // hack for libdispatch et al - isa also acts as vtable pointer 84 hackedDispatch = true; 85 instancesRequireRawIsa = true; 86 } 87 else if (supercls && supercls->superclass && 88 supercls->instancesRequireRawIsa()) 89 { 90 // This is also propagated by addSubclass() 91 // but nonpointer isa setup needs it earlier. 92 // Special case: instancesRequireRawIsa does not propagate 93 // from root class to root metaclass 94 instancesRequireRawIsa = true; 95 rawIsaIsInherited = true; 96 } 97 98 if (instancesRequireRawIsa) { 99 cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsaRecursively(rawIsaIsInherited); 100 } 101 } 102 // SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA 103 #endif 104 // 更新父类和元类 105 // Update superclass and metaclass in case of remapping 106 cls->superclass = supercls; 107 cls->initClassIsa(metacls); 108 109 // Reconcile instance variable offsets / layout. 110 // This may reallocate class_ro_t, updating our ro variable. 111 if (supercls && !isMeta) reconcileInstanceVariables(cls, supercls, ro); 112 113 // Set fastInstanceSize if it wasn't set already. 114 cls->setInstanceSize(ro->instanceSize); 115 116 // Copy some flags from ro to rw 117 if (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_STRUCTORS) { 118 cls->setHasCxxDtor(); 119 if (! (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_DTOR_ONLY)) { 120 cls->setHasCxxCtor(); 121 } 122 } 123 124 // Propagate the associated objects forbidden flag from ro or from 125 // the superclass. 126 if ((ro->flags & RO_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS) || 127 (supercls && supercls->forbidsAssociatedObjects())) 128 { 129 rw->flags |= RW_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS; 130 } 131 132 // Connect this class to its superclass's subclass lists 133 if (supercls) { 134 addSubclass(supercls, cls); 135 } else { 136 addRootClass(cls); 137 } 138 139 // Attach categories 140 methodizeClass(cls, previously); 141 142 return cls; 143 }
我们仍然是通过自己的类 MyPerson 进行分析(系统类毕竟看不见其具体操作,自己写的类更易分析)。
1、源码分析
如下图 2500行(上面源码23行)读取 cls 对应的地址中的 data 信息,并对其进行格式强转, ro 中具体数据信息见下图:
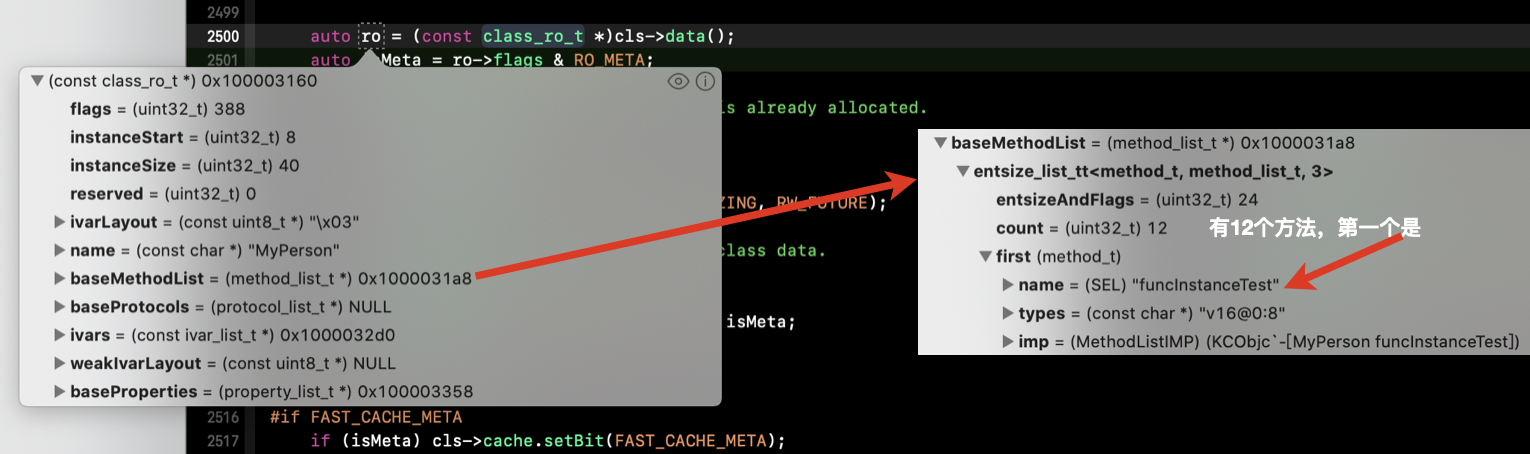
源码23行起,所做操作:取 macho 格式中的 data 数据:ro(原始,只读的 干净内存) 进行 class_ro_t 格式强转 --> 开辟 rw(可读写的 脏内存) 空间 --> rw 赋值为 ro --> cls 重新赋值 rw 为 data.
问题:1、为何要在开辟出一份 rw 呢? --> 因为 iOS 的运行时,内存会被不断插入添加删除操作,防止对我们的原始数据的修改,所以 copy 一份干净内存 ro 到 rw 里面;
2、为何有了一个 rw了 还要有一个 rwe 呢?--> 因为并非每个类都会进行动态的操作,为避免内存的大量操作,我们只对进行了动态操作的类进行 rwe。rw 是从 ro 读取拷贝的。
关于 干净/脏内存 可以看下 WWDC 的视频介绍: Advancements in the Objective-C runtime。
get_ro 代码:
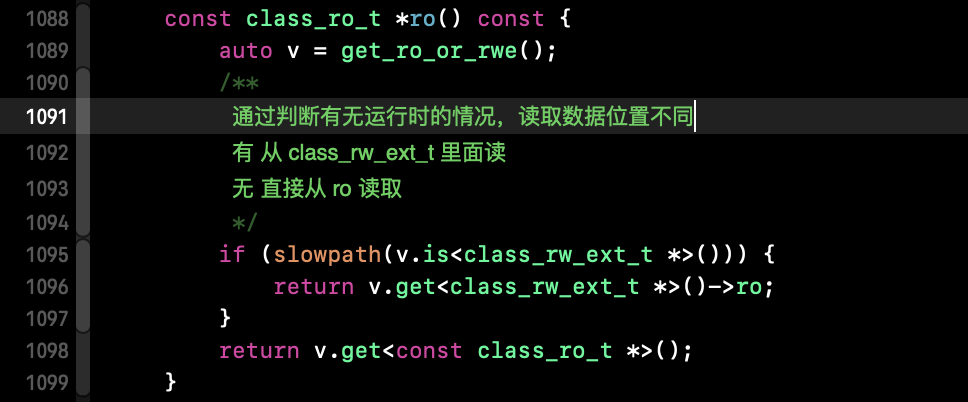
1)36行 setData(rw) :
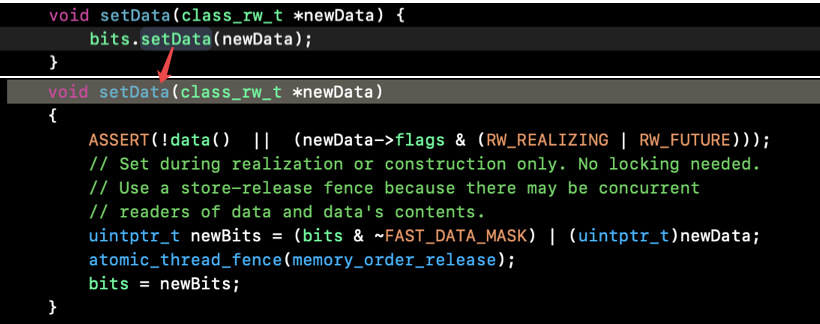
2)我们继续向下执行(上面源码的62行):

realizeClassWithoutSwift() 方法递归:cls 的所有 父类 元类 全部实现确定下来 --> 继承链的确定(这里是 MyPerson 的继承链)
3)继续读代码(上面源码65行起),isa 的设置,继续执行,cls 如下(地址:MyPerson 的元类信息):
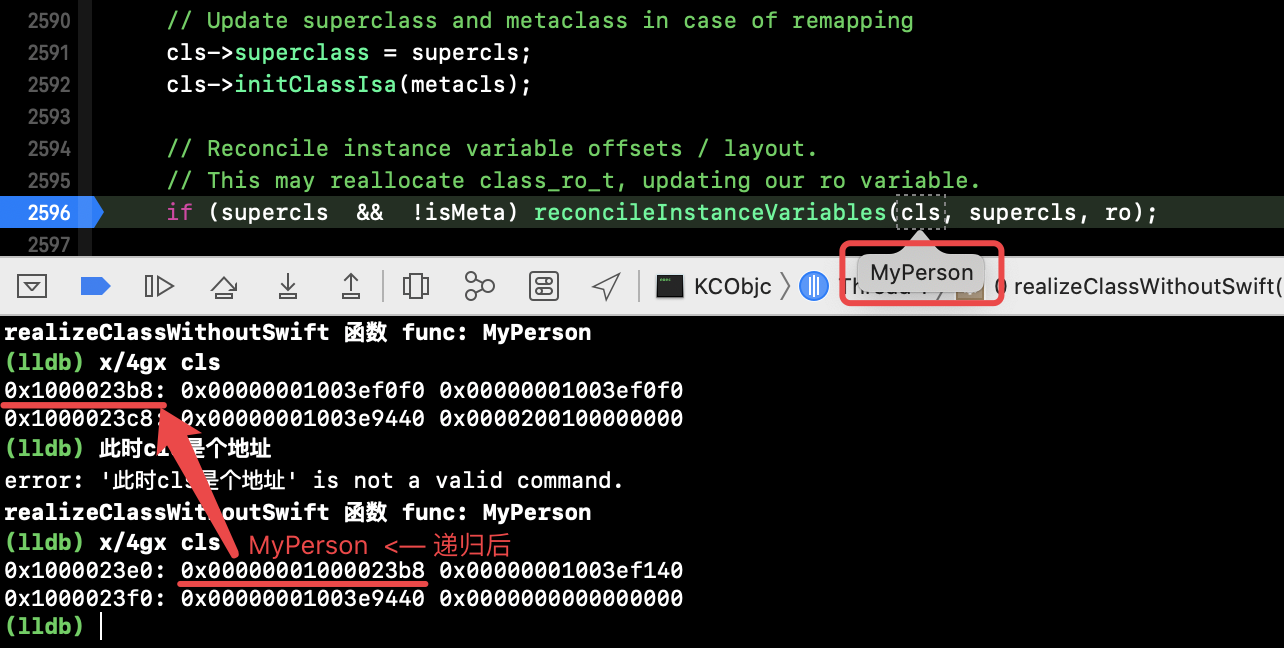
此时 bits 仍是无值的,继续执行。
4)setInstanceSize() 执行后 bits 开始有值了,然后继续对 Cxx 信息处理,见下图:

读取一下地址中的数据,各信息都是存在的(见下图)。而我们的内存 bits 目前是 0x00000034。
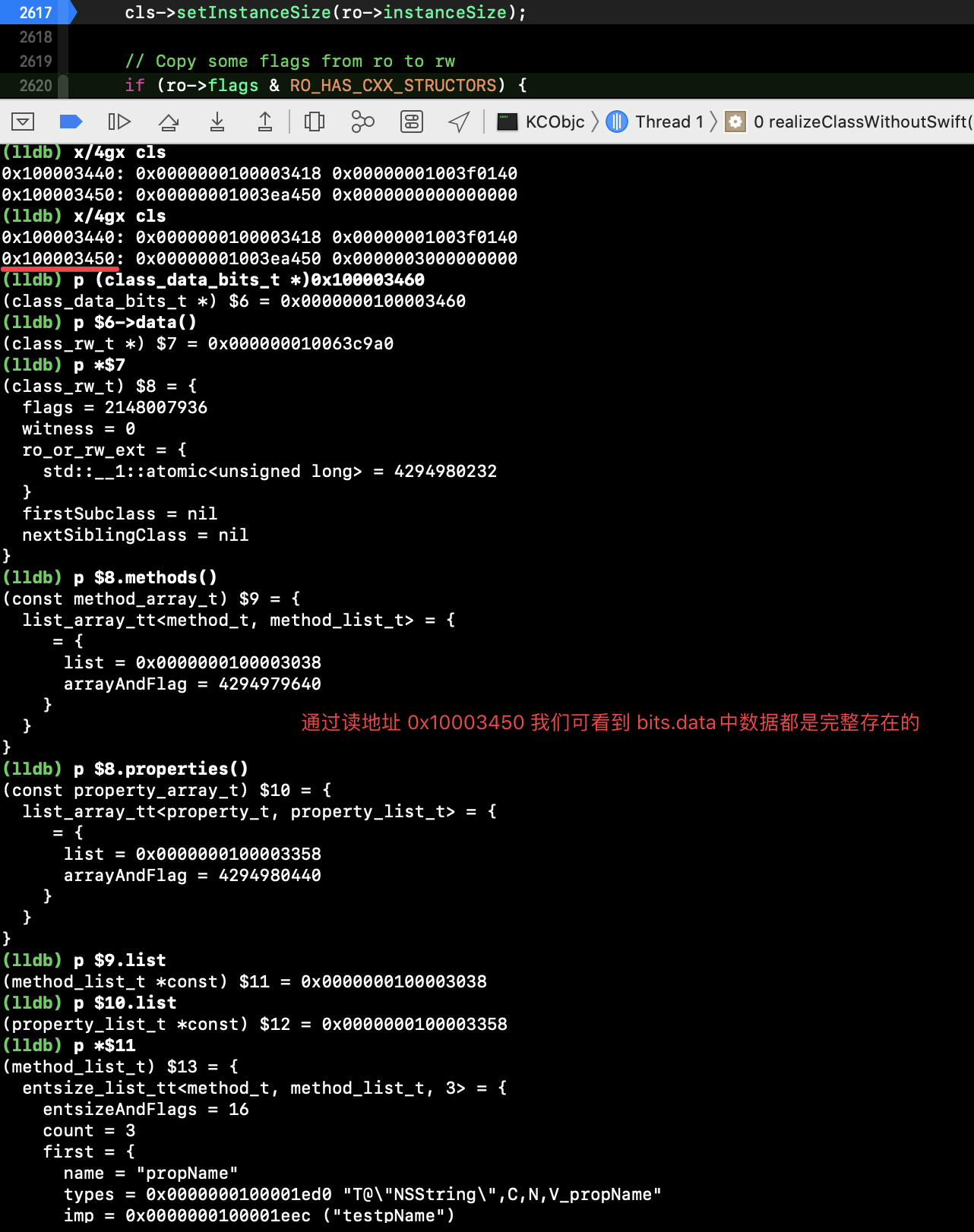
放开内部断点直接运行到 main 函数中:
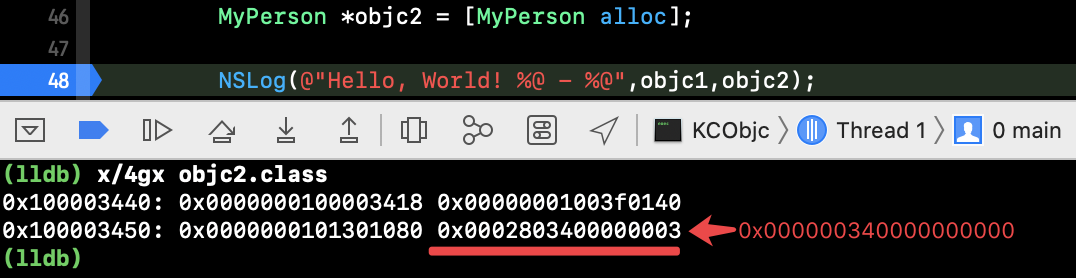
可看到 bits 的内存地址是 0x000280340000003 除了 ‘34’ 其他的值是何时赋的呢?后面再进行探究。
5)我们继续源码的流程,在 Cxx 的处理之后走到 methodizeClass(cls, previously),cls 的方法的处理。
2、methodizeClass() 方法的处理
1 源码2 2 /*********************************************************************** 3 * methodizeClass 4 * Fixes up cls's method list, protocol list, and property list. 5 * Attaches any outstanding categories. 6 * Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller 7 **********************************************************************/ 8 static void methodizeClass(Class cls, Class previously) 9 { 10 runtimeLock.assertLocked(); 11 12 bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass(); 13 auto rw = cls->data(); 14 auto ro = rw->ro(); 15 auto rwe = rw->ext(); 16 17 // Methodizing for the first time 18 if (PrintConnecting) { 19 _objc_inform("CLASS: methodizing class '%s' %s", 20 cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? "(meta)" : ""); 21 } 22 23 // Install methods and properties that the class implements itself. 24 method_list_t *list = ro->baseMethods(); 25 if (list) {// 方法 list 26 prepareMethodLists(cls, &list, 1, YES, isBundleClass(cls)); 27 if (rwe) rwe->methods.attachLists(&list, 1); 28 } 29 30 property_list_t *proplist = ro->baseProperties; 31 if (rwe && proplist) {// 属性 list 32 rwe->properties.attachLists(&proplist, 1); 33 } 34 35 protocol_list_t *protolist = ro->baseProtocols; 36 if (rwe && protolist) {// 协议 list 37 rwe->protocols.attachLists(&protolist, 1); 38 } 39 40 // Root classes get bonus method implementations if they don't have 41 // them already. These apply before category replacements. 42 if (cls->isRootMetaclass()) { 43 // root metaclass 44 addMethod(cls, @selector(initialize), (IMP)&objc_noop_imp, "", NO); 45 } 46 47 // Attach categories. 附着关联分类 48 if (previously) { 49 if (isMeta) { 50 objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously, 51 ATTACH_METACLASS); 52 } else { 53 // When a class relocates, categories with class methods 54 // may be registered on the class itself rather than on 55 // the metaclass. Tell attachToClass to look for those. 56 objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously, 57 ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS); 58 } 59 } 60 objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, cls, 61 isMeta ? ATTACH_METACLASS : ATTACH_CLASS); 62 63 #if DEBUG 64 // Debug: sanity-check all SELs; log method list contents 65 for (const auto& meth : rw->methods()) { 66 if (PrintConnecting) { 67 _objc_inform("METHOD %c[%s %s]", isMeta ? '+' : '-', 68 cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(meth.name)); 69 } 70 ASSERT(sel_registerName(sel_getName(meth.name)) == meth.name); 71 } 72 #endif 73 }
方法列表的准备,prepareMethodLists(); 。
1 static void 2 prepareMethodLists(Class cls, method_list_t **addedLists, int addedCount, 3 bool baseMethods, bool methodsFromBundle) 4 { 5 runtimeLock.assertLocked(); 6 7 if (addedCount == 0) return; 8 9 // There exist RR/AWZ/Core special cases for some class's base methods. 10 // But this code should never need to scan base methods for RR/AWZ/Core: 11 // default RR/AWZ/Core cannot be set before setInitialized(). 12 // Therefore we need not handle any special cases here. 13 if (baseMethods) { 14 ASSERT(cls->hasCustomAWZ() && cls->hasCustomRR() && cls->hasCustomCore()); 15 } 16 17 // Add method lists to array. 18 // Reallocate un-fixed method lists. 19 // The new methods are PREPENDED to the method list array. 20 21 for (int i = 0; i < addedCount; i++) { 22 method_list_t *mlist = addedLists[i]; 23 ASSERT(mlist); 24 25 // Fixup selectors if necessary 26 if (!mlist->isFixedUp()) { 27 // 方法排序 28 fixupMethodList(mlist, methodsFromBundle, true/*sort*/); 29 } 30 } 31 32 // If the class is initialized, then scan for method implementations 33 // tracked by the class's flags. If it's not initialized yet, 34 // then objc_class::setInitialized() will take care of it. 35 if (cls->isInitialized()) { 36 objc::AWZScanner::scanAddedMethodLists(cls, addedLists, addedCount); 37 objc::RRScanner::scanAddedMethodLists(cls, addedLists, addedCount); 38 objc::CoreScanner::scanAddedMethodLists(cls, addedLists, addedCount); 39 } 40 }
方法排序 fixupMethodList() :
1 static void 2 fixupMethodList(method_list_t *mlist, bool bundleCopy, bool sort) 3 { 4 runtimeLock.assertLocked(); 5 ASSERT(!mlist->isFixedUp()); 6 7 // fixme lock less in attachMethodLists ? 8 // dyld3 may have already uniqued, but not sorted, the list 9 if (!mlist->isUniqued()) { 10 mutex_locker_t lock(selLock); 11 12 // Unique selectors in list. 13 for (auto& meth : *mlist) { 14 const char *name = sel_cname(meth.name); 15 meth.name = sel_registerNameNoLock(name, bundleCopy); 16 } 17 } 18 19 // Sort by selector address. 20 // 根据 方法的地址 进行排序 21 /** 22 若方法重名则根据 sel 排序: 23 1、sel 混乱则进行 fixedUp 2、sel 没有混乱则根据 imp 排序 24 */ 25 26 if (sort) { 27 method_t::SortBySELAddress sorter; 28 /** 29 struct method_t { 30 SEL name; 31 const char *types; 32 MethodListIMP imp; 33 34 struct SortBySELAddress : 35 public std::binary_function<const method_t&, 36 const method_t&, bool> 37 { 38 bool operator() (const method_t& lhs, 39 const method_t& rhs) 40 { return lhs.name < rhs.name; }// 根据名字进行排序 41 }; 42 }; 43 */ 44 std::stable_sort(mlist->begin(), mlist->end(), sorter); 45 } 46 47 // Mark method list as uniqued and sorted 48 mlist->setFixedUp(); 49 }
方法排序前 ro->baseMethods() 的list:
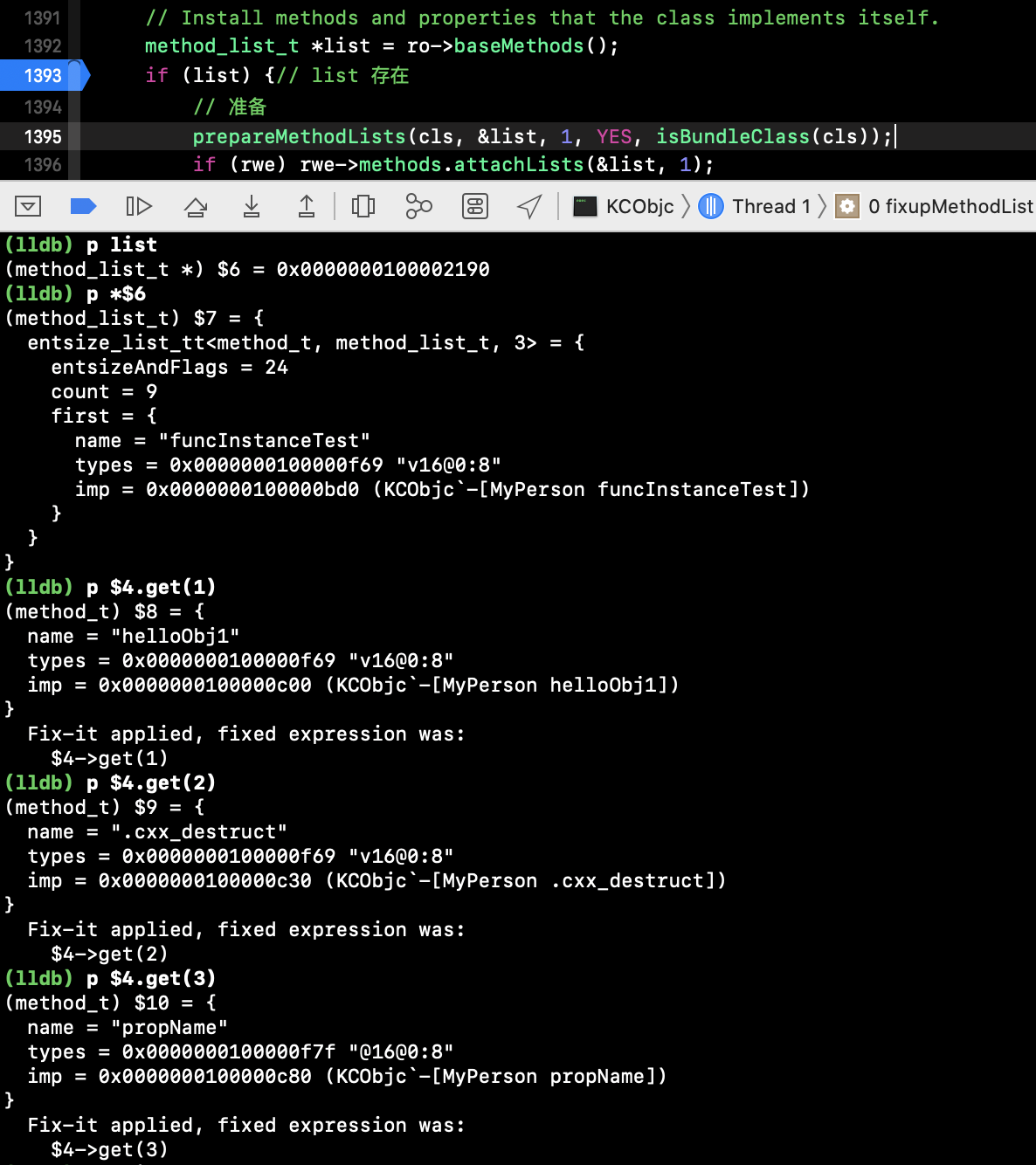
方法排序后 fixupMethodList() 的 list:
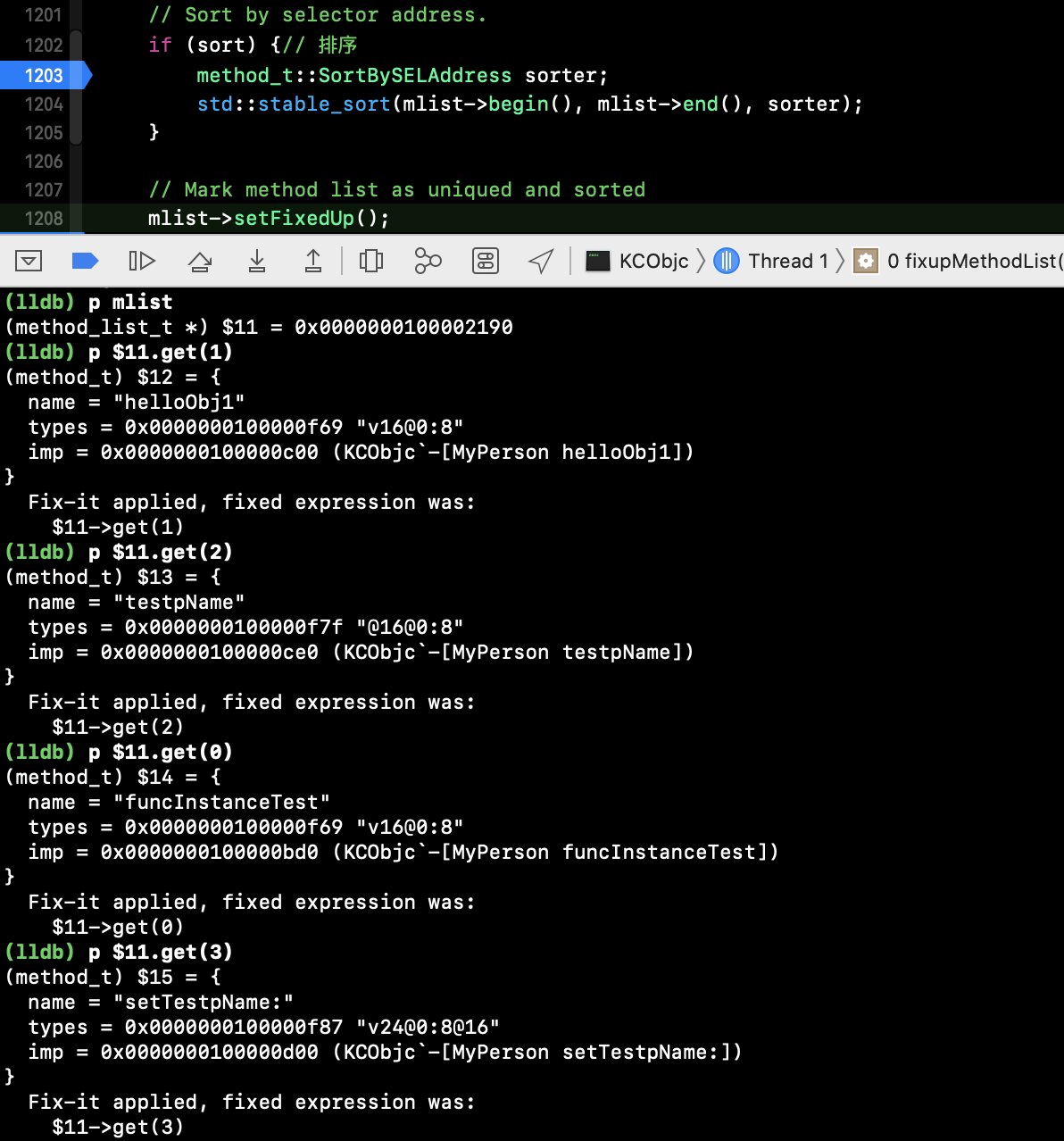
类加载流程的执行总结:

以上我们探究的是本类的加载,我们给本类添加分类后是如何加载的呢?
OC 底层探索 15 继续探究。