前言
在我们的实际开发中,经常要写路径,不管是链接,重定向还是转发,这都是需要路径的。那这一篇我给大家详细的分享一下Web中的各种路径问题。
世界上一切东西都是相对的,对于这点而言,相信大家并不陌生,由于这篇文章是针对于WEB阶段来讲的,所以以下绝对路径和相对路径都是针对于整个互联网而言的。
在JavaWeb中需要写的路径大概分为四大类:
1)客户端路径
超链接、表单、重定向
2)服务端路径
转发、包含
3)获取资源路径
servletContext获取资源、ClassLoader获取资源、Class获取资源
4)<url-pattern>路径
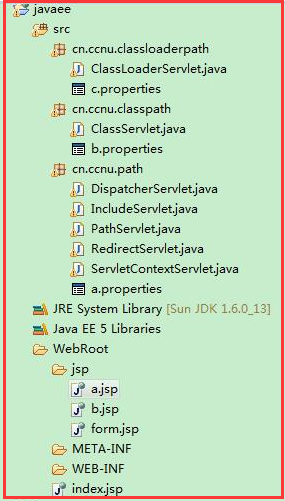
在本文中使用下图构建Web项目的目录:
一、客户端路径
客户端路径是指运行在浏览器上的路径。
比如:表单、超链接、js(location.href)、Ajax(url)、CSS和JS的引入以及重定向等。路径分为绝对路径和相对路径,相对路径又分为相对主机的路径和相对于当前请求的路径。
1.1、超链接
超链接有三种书写路径的方式
1)绝对路径
2)以"/"开头的相对路径
3)不以"/"开头的相对路径
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>页面A</title> </head> <body> <!-- 超链接有三种书写路径的方式 1,绝对地址 2,以"/"开头的相对地址 3,不以"/"开头的相对地址 --> <!-- 1.绝对地址 --> <!-- 完整的URL --> <a href="http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp">这是绝对地址超链接</a><br/> <!-- 2.以"/"开头的相对地址 --> <!-- /代表了整个web项目,即:http://localhost:8080/ --> <a href="/javaee/jsp/b.jsp">这是以"/"开头的相对地址超链接</a><br/> <!-- 3.不以"/"开头的相对地址 --> <!-- 不以/开头,则相对于当前资源的路径 当前资源的路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/ 而b.jsp也在此路径下 所以直接书写b.jsp --> <a href="b.jsp">这是不以"/"开头的相对地址超链接</a><br/> </body> </html>
分析:
1)绝对路径(以协议开头的路径):最终请求路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp
2)相对路径:
2.1) 相对于主机的路径(以“/”开头):相对于当前主机(可以简单理解为ip地址,如果想深入了解请研究tomcat的Server.xml文件。这里是localhost)的路径,请求的最终路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp
2.2)相对于请求的路径(不以“/”开头):相对于当前请求(浏览器的请求)的路径。
1.2、表单
表单有三种书写路径的方式
1)绝对路径
2)以"/"开头的相对路径
3)不以"/"开头的相对路径
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 表单提交到jsp中 --> <!-- 表当提交路径有三种书写方式 1,绝对地址 2,以"/"开头的相对地址 3,不以"/"开头的相对地址 --> <form action="http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="提交---绝对地址 "> </form> <!-- 以/开头的相对地址 此时的/代表整个web项目,即:http://localhost:8080/ --> <form action="/javaee/jsp/b.jsp" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="提交---以/开头的相对地址"> </form> <form action="b.jsp" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="提交---不以/开头的相对地址 "> </form> <!-- 表单提交到Servlet --> <!-- 表单提交到Servlet有三种书写方式 1,绝对路径 2,以"/"开头的相对地址 3,不以"/"开头的相对地址 --> <!-- 1.绝对地址 --> <!-- 完整的URL --> <form action="http://localhost:8080/javaee/PathServlet" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="表单提交到Servlet---绝对地址"> </form> <!-- 2.以/开头的相对地址 --> <!-- 此时的/代表整个web项目,即:http://localhost:8080/ --> <form action="/javaee/PathServlet" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="表单提交到Servlet---以/开头的相对地址"> </form> <!-- 3.不以/开头的相对地址 --> <!-- 不以/开头的相对路径是相对于当前资源的路径 此时form.jsp的地址为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/form.jsp 所以当前资源路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp 而要提交的Servlet的路径为Http://localhost:8080/javaee/PathServlet 所以路径为当前路径的上一级路径下 即路径为:../PathServlet 注:.代表当前路径 ..代表当前路径的上一级路径 --> <form action="../PathServlet" methoe="get"> username:<input type="text" name="username" value=""> <input type="submit" value="表单提交到Servlet---不以/开头的相对地址"> </form> </body> </html>
1.3、重定向
表单有三种书写路径的方式
1)绝对路径
2)以"/"开头的相对路径
3)不以"/"开头的相对路径
注意:在这里中我们一般只会用相对路径,不会去用绝对路径
import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp"); /* * 2.以"/"开头的相对路径 * 此时,/代表整个web工程的路径,即http://localhost:8080/ */ // response.sendRedirect("/javaee/jsp/b.jsp"); /* * 3.不以"/"开头的相对路径 * 此时是相对于当前资源的相对路径 * 当前资源路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/RedirectServlet * 即表示:RedirectServlet在路径http://localhost:8080/javaee之下 * 而b.jsp在http://localhost:8080/javaee/jsp/b.jsp * 所以最终地址写为:jsp/b.jsp */ // response.sendRedirect("jsp/b.jsp"); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
二、服务端路径
服务端路径是指在服务器上面运行的请求,比如请求转发(常用)、请求包含等。服务端的路径有两种:相对于当前应用的路径和相对于当前请求的路径。
2.1、请求转发
请求转发有两种书写路径的方式
2)以"/"开头的相对路径
3)不以"/"开头的相对路径
注意:服务器端的路径不能是绝对路径,只能是相对路径,也分为以/开头和不以/开头两种
import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /* * 1.以"/"开头的相对路径 * 2.不以"/"开头的相对路径 */ public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /* * 1.以"/"开头的相对路径 * 此时,/代表当前web项目,即:http://localhost:8080/javaee */ // request.getRequestDispatcher("/jsp/b.jsp").forward(request, response); /* * 2.不以"/"开头的相对路径 * 相对于当前资源的相对路径 * 此时,当前资源的路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/DispatcherServlet * 所以要转发去的资源的路径以:http://localhost:8080/javaee开头 */ request.getRequestDispatcher("jsp/b.jsp").forward(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
注意:所有Web层框架的底层使用的都是Web的基础Filter(Struts)或Servlet(SpringMVC),请求都是request,响应都是response,所以各个Web层框架的转发或重定向底层都是利用request和response进行的。
2.2、请求包含
请求包含和上面的请求转发路径方式一样的
import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /* * 请求包含不能书写绝对地址,只能书写相对地址 * 1.以"/"开头的相对路径 * 2.不以"/"开头的相对路径 */ public class IncludeServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /* * 1.以"/"开头的相对路径 * 此时,/代表当前web项目,即:http://localhost:8080/javaee */ // request.getRequestDispatcher("/jsp/b.jsp").include(request, response); /* * 2.不以"/"开头的相对路径 * 相对于当前资源的相对路径 * 此时,当前资源的路径为:http://localhost:8080/javaee/IncludeServlet * 所以要转发去的资源的路径以:http://localhost:8080/javaee开头 */ request.getRequestDispatcher("jsp/b.jsp").include(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
三、资源获取路径
获取资源的路径主要有3种,分别是ServletContext、Class和ClassLoader。其中ServletContext是WEB阶段的,Tomcat提供的一种获取资源的方式;Class和ClassLoader获取资源主要是JavaAPI提供的一种获取流的方式,
由于这是JDK提供的,所以不仅局限于Web,在普通Java类中也可以使用,主要用于获取src目录及其子目录下的文件流。
3.1、ServletContext获取资源
这里ServletContext获取资源的路径是相对系统的绝对路径(在Windows中是带盘符的,可以用来获取上传或下载文件的具体路径)。
基本语法:servletContext.getRealPath("路径");参数中的路径必须是相对路径,可以“/”开头,也可以不使用“/”开头,但无论是否使用“/”开头都是相对当前应用路径,建议以"/"开头(这样可以尽量统一)。
另外获取ServletContext的方法如下:
1)使用request获取: request.getSession().getServletContext();
2)在Servlet中获取:this.getServletContext();
3)使用FilterConfig对象获取(在Filter中使用):config.getServletContext();
ServletContext获取资源必须是相对路径,不能是绝对路径,但不管是以/开头,还是不以/开头, 都是相对于当前资源的相对路径 。
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String path1 = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/a.properties"); String path2 = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("a.properties"); System.out.println(path1); System.out.println(path2); //输出的地址一样 } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
3.2、ClassLoader获取资源
和Class获取资源类似。只是不同的写法而已,也是用于获取文件流的。
用法:classLoader.getResourceAsStream("路径")。参数中的路径可以以“/”开头,也可以不以“/”开头(建议)。但带不带“/”的都表示相对于当前类的路径。
ClassLoader类加载器不能通过绝对地址来加载资源,只能通过相对地址来加载资源 但相对地址不管前面加不加/都是相当于类路径的相对地址
public class ClassLoaderServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /* * 加了/,其地址是相对于类路径的相对地址 */ // InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("/cn/ccnu/classloaderpath/c.properties"); // Properties prop = new Properties(); // prop.load(in); // System.out.println(prop.getProperty("url")); /* * 不加/,其地址是相对于类路径的相对地址 */ InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("cn/ccnu/classloaderpath/c.properties"); Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(in); System.out.println(prop.getProperty("url")); /* * 总结:不能使用绝对地址,而只能只用相对地址 * 且不管加不加/的相对地址,都是相对于类路径的相对地址 * */ } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
3.3、Class获取资源
Class获取资源主要是用作自己写的配置文件,用来读取内容。
用法:clazz.getResourceAsStream("路径")。参数中的路径可以以“/”开头,也可以不以“/”开头。其中带“/”的表示相对于当前类的路径,不以“/”开头表示相对于当前class所在目录的路径。
Class读取资源不能是绝对路径,只能是相对路径,又分为以/开头或者是不以/开头 。
public class ClassServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /* * 1.以/开头的相对路径 * 此时的/代表类路径,即:/javaee/WEB-INF/classes */ // InputStream in = ClassServlet.class.getResourceAsStream("/cn/ccnu/classpath/b.properties"); // Properties porp = new Properties(); // porp.load(in); // System.out.println(porp.getProperty("url")); /* * 2.不以/开头的相对路径 * 此时相对的是:类ClassServlet.class的路径,即:javaeeWEB-INFclassescnccnuclasspath * 即:/javaee/WEB-INF/classes/cn/ccnu/classpath */ InputStream in = ClassServlet.class.getResourceAsStream("b.properties"); Properties porp = new Properties(); porp.load(in); System.out.println(porp.getProperty("url")); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
四、<url-pattern>路径
这里的路径仅仅是指web.xml文件中的标签内容。这个路径是虚拟的路径,只有相对路径(相对于当前应用的路径),但相对路径的写法可以是精确查询和模糊查询。
要么以“*”开关,要么为“/”开头,当通常情况看下,我们都会以"/"开头。
<!—精确查询,是相对于当前应用--> <url-pattern>/servlet/testPath</url-pattern> <!—模糊查询,表示匹配servlet目录下的所有文件或请求。/*表示匹配所有--> <url-pattern>/servlet/*</url-pattern> <!—模糊查询,表示匹配所有后缀名为do的文件或请求--> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
五、总结
1)客户端是带“/”相对当前主机。
2)服务端(包括上述的服务端、url-pattern路径和ServletContext路径)带不带“/”都是相对当前应用(建议带上)。
3)Class带“/”是相对当前类路径。不带“/”是相对于当前位置。
4)ClassLoader无论带不带“/”都是当前类路径(建议带上)。
喜欢就点个“推荐”哦!