通过上一篇博客我们可以轻松搭建strtus2的环境,接下来由我来继续介绍spring的环境搭建以及spring注入的简单使用
相关链接:eclipse中SSH三大k框架环境搭建<一>
eclipse中SSH三大框架环境搭建<三>
本例业务需求:将数据库一张表的信息通过JDBC查询出来并显示在页面中
流程:action控制层-->service业务层-->dao数据层-->数据库
第1步:我们还是需要加入spring开发中所需要的jar包
找到下载并解压好的spring文件,然后找到该文件下的libs目录下文件,我们可以将所有jar包复制到我们web项目下的lib目录下

注意:1>***.javadoc.jar文档和***.sources.jar源码我们可以不拷贝到我们的项目中,如果想加深自己的理解小编建议大家看看源码(毕竟这是第一手资料)
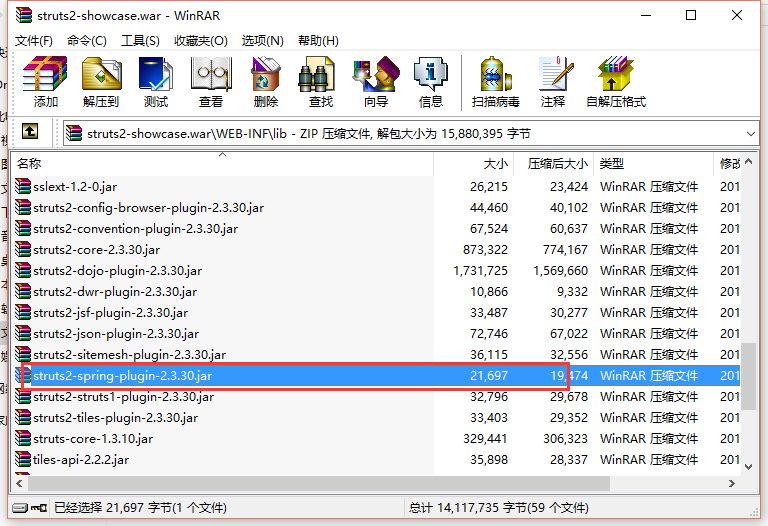
2>我们还需要加入commons-logging.jar包。用来记录程序运行时的活动的日志记录。该文件在struts2文件中app目录下的struts2-showcase.war包目录下的WEB-INF下的lib中

3>我们还需要加入struts2中的一个插件包struts2-spring-plugin-2.3.30.jar(经常容易忘记)
4>由于本例我们还需要操作mySql数据库因此还需加入数据库驱动包mysql-connector-java-5.1.39-bin.jar
第2步:由于本例用到了struts所以还是需要先配置strtus.xml文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> 2 <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC 3 "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" 4 "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> 5 6 <struts> 7 <!-- 告知Struts2运行时使用Spring来创建对象 --> 8 <constant name="struts.objectFactory" value="spring" /> 9 <package name="001pck" extends="struts-default"> 10 <action name="Index" class="myIndexAction"> 11 <result name="success">/WEB-INF/jsp/index.jsp</result> 12 </action> 13 14 </package> 15 </struts>
注意:这里的class并没有引用一个具体的类而是取了一个别名,接下来再由spring给它注入
第3步:配置applicationContext.xml文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 6 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 7 xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" 8 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" 9 xsi:schemaLocation=" 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd 13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-4.2.xsd 14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd"> 15 <!-- 类似于财务部门一样,类就是钱,所有需要类的实例都由srping去管理, pojo除外--> 16 <bean id="myIndexAction" class="action.IndexAction" scope="prototype"> 17 <property name="index" ref="myService1"></property> 18 </bean> 19 <!-- index = new IndexServiceImpl() --> 20 <bean id="myDao1" class="dao.BookCardDaoImpl" scope="prototype"> 21 <property name="c" ref="myConnection1"></property> 22 </bean> 23 24 <bean id="myService1" class="service.IndexServiceImpl" scope="prototype"> 25 <property name="bcd" ref="myDao1"></property> 26 </bean> 27 28 <bean id="myConnection1" class="util.MyConnection_mysql" scope="prototype"></bean> 29 30 <bean id="myConnection2" class="util.MyConnection_sqlserver" scope="prototype"></bean> 31 32 </beans>
在这里我介绍一下这份配置文件的相关信息吧
1 头文件我们一般从官方模板中拷贝过来,需要注意一下版本号
2 bean标记就是我们需要给项目中的每一个实例配置一个bean(pojo除外),当哪一层需要调用时,spring会帮我们注入。
3 bean标记中id属性为在本文件中起一标识作用用来区分其他bean,class属性的值便是当前bean引用了哪一个类 ,scope属性的值为prototype为非单例的意思
4 bean标记中的子标记property便是当前这个类中需要注入的属性,name属性值为我们java类中的属性名,ref属性值为当前类需要引用哪一个实现类。
本例中我们可以看到dao中引用了myConnection1也就是引用了mysql的连接,如此一来便可以轻松切换mySQL和sqlServer两个数据库,而并不需要改动我们的任何逻辑代码。
下面我给出一个dao的样例代码
1 public class BookCardDaoImpl implements BookCardDao {
2
3 //只做属性的申明,不写死具体的实现
4 private MyConnection c;
5
6 //提供一个set方法spring会自动注入
7 public void setC(MyConnection c) {
8 this.c = c;
9 }
10
11 @Override
12 public List<BookCard> getAllCardInfo() {
13
14 // 第一步:获取数据库连接
15 Connection conn = c.getConnection();
16
17 // 第二步:查询数据库
18 // (操作JDBC,需要sql语句,需要执行sql语句对象,需要执行sql语句后结果集合)
19 String sql = "select * from BookCard";// 需要执行的sql语句
20 PreparedStatement stmt = null;// 执行sql语句对象
21 ResultSet rs = null;// 执行sql语句后的结果集
22 try {
23 stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
24 rs = stmt.executeQuery();
25 } catch (Exception e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 }
28
29 // 第三步
30 // 拿到rs后,执行一个遍历以及封装
31 List<BookCard> myBookCardList = new ArrayList<BookCard>();
32 try {
33 while (rs.next()) {
34 // 风格:实体类是一个pojo对象,一般直接new就行
35 BookCard bc = new BookCard();
36 // 进行数据库封装
37 bc.setCid(rs.getInt("cid"));
38 bc.setName(rs.getString("name"));
39 bc.setSex(rs.getString("sex"));
40 bc.setCardDate(rs.getDate("cardDate"));
41 bc.setDeposit(rs.getBigDecimal("deposit"));
42 myBookCardList.add(bc);
43 }
44 } catch (Exception e1) {
45 e1.printStackTrace();
46 }
47
48 //关闭资源
49 try {
50 rs.close();
51 stmt.close();
52 conn.close();
53 } catch (Exception e) {
54 e.printStackTrace();
55 }
56
57 // 第5步返回结果集List给客户端
58 return myBookCardList;
59 }
spring的环境在这一步已经是搭建完成了,我再来介绍一下spring的注入。
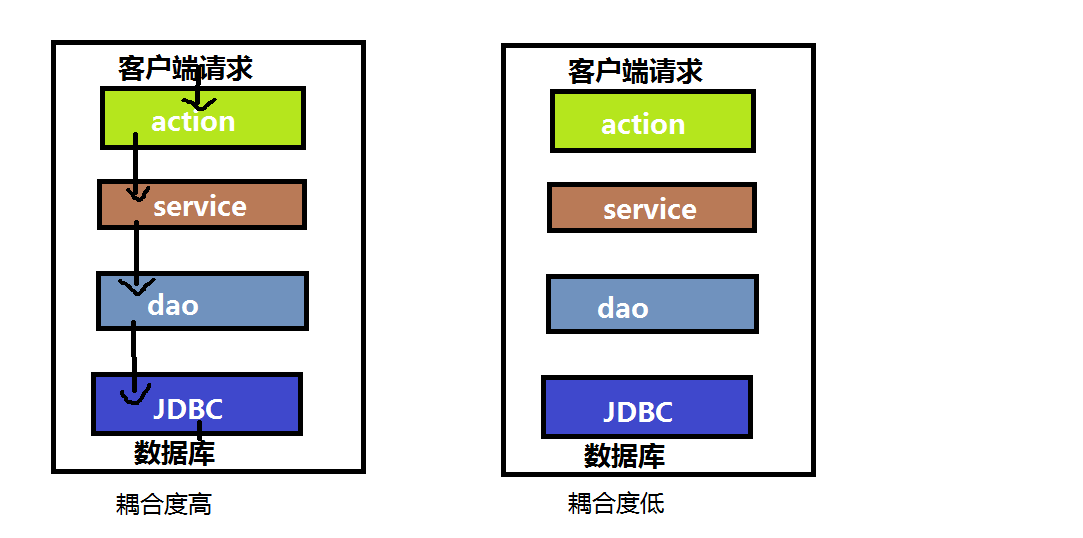
大家可以清晰的看到左边这幅图呢是传统的面向对象编程的写法,每一层都与另外一层紧密耦合,当一层出现问题,层层都需要变动,在软件工程中是大忌
右图中,层与层之间都已经分离出来了,这里具体实现是通过在每一层都定义一个接口,层与层之间调用的都是接口并不关心是哪一个实现类,真正的实现类是谁不在代码中出现而是交给spring让他给我们注入。
