一、统计数据频率
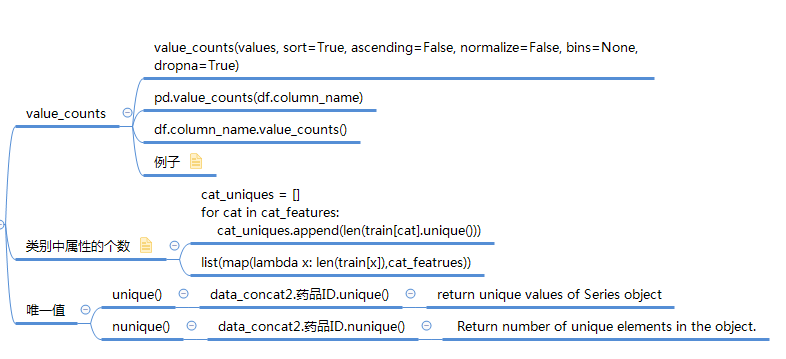
1. values_counts
pd.value_counts(df.column_name) df.column_name.value_counts() Series.value_counts(normalize=False, sort=True, ascending=False, bins=None, dropna=True)[source] Return a Series containing counts of unique values.
参数详解
normalize : boolean, default False If True then the object returned will contain the relative frequencies of the unique values. sort : boolean, default True Sort by values. ascending : boolean, default False Sort in ascending order. bins : integer, optional Rather than count values, group them into half-open bins, a convenience for pd.cut, only works with numeric data. dropna : boolean, default True Don’t include counts of NaN.
参数示例讲解
index = pd.Index([3, 1, 2, 3, 4, np.nan]) index.value_counts() Out[144]: 3.0 2 4.0 1 2.0 1 1.0 1 dtype: int64 index.value_counts(normalize=True) Out[145]: 3.0 0.4 4.0 0.2 2.0 0.2 1.0 0.2 dtype: float64 index.value_counts(bins=3) Out[146]: (2.0, 3.0] 2 (0.996, 2.0] 2 (3.0, 4.0] 1 dtype: int64 index.value_counts(dropna=False) Out[148]: 3.0 2 NaN 1 4.0 1 2.0 1 1.0 1 dtype: int64

In [21]: data=pd.DataFrame(pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6,11,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,3]).values.reshape(4,4),columns=['a','b','c','d']) In [22]: data Out[22]: a b c d 0 1 2 3 4 1 5 6 11 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 In [23]: pd.value_counts(data.a) Out[23]: 1 2 2 1 5 1 Name: a, dtype: int64 In [26]: pd.value_counts(data.a).sort_index() Out[26]: 1 2 2 1 5 1 Name: a, dtype: int64 In [27]: pd.value_counts(data.a).sort_index().index Out[27]: Int64Index([1, 2, 5], dtype='int64') In [28]: pd.value_counts(data.a).sort_index().values Out[28]: array([2, 1, 1], dtype=int64)
2.类别中属性的个数
# 方式一
cat_uniques = []
for cat in cat_features:
cat_uniques.append(len(train[cat].unique()))
uniq_values_in_categories = pd.DataFrame.from_items([('cat_name', cat_features), ('unique_values', cat_uniques)])
# 方式二
list(map(lambda x: len(train[x]),cat_featrues))
3.唯一值

二、数据去重
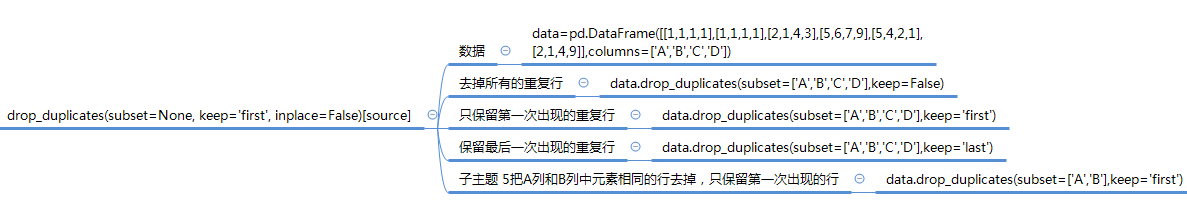
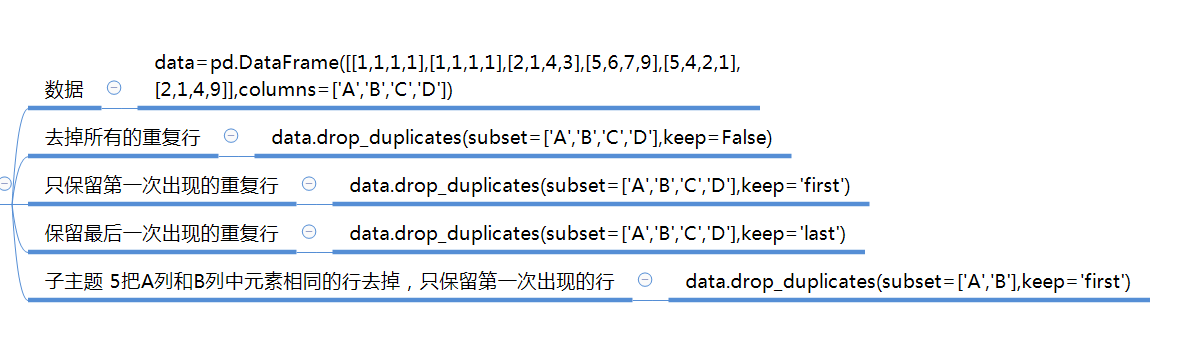
def drop_duplicates(self, subset=None, keep='first', inplace=False):
"""
Return DataFrame with duplicate rows removed, optionally only
considering certain columns
Parameters
----------
subset : column label or sequence of labels, optional
Only consider certain columns for identifying duplicates, by
default use all of the columns
keep : {'first', 'last', False}, default 'first'
- ``first`` : Drop duplicates except for the first occurrence.
- ``last`` : Drop duplicates except for the last occurrence.
- False : Drop all duplicates.
inplace : boolean, default False
Whether to drop duplicates in place or to return a copy
Returns
-------
deduplicated : DataFrame
"""
- duplicated()方法
- 查看列是否重复
dataframe.colname.duplicated()
- 查看整行是否重复
dataframe.duplicated()
- 查看subset是否重复
dataframe.duplicated(subset = [])
- drop_duplicats()方法
用于丢弃重复项
dataframe.drop_duplicats()
- 参数keep
keep可以为first和last,表示是选择最前一项还是最后一项保留。
dataframe.duplicated(keep = "first") dataframe.duplicated(keep = "last")
也可以设置布尔类型,当设为False时候,重复项将都被显示。
dataframe.duplicated(keep = "False")
三、数据类型转换

四、聚合方法


import pandas as pd from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import numpy as np pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None) df = pd.read_csv('911.csv') print(df.head(1)) lat lng desc 0 40.297876 -75.581294 REINDEER CT & DEAD END; NEW HANOVER; Station ... zip title timeStamp twp 0 19525.0 EMS: BACK PAINS/INJURY 2015-12-10 17:10:52 NEW HANOVER addr e 0 REINDEER CT & DEAD END 1 df.info() <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 249737 entries, 0 to 249736 Data columns (total 9 columns): lat 249737 non-null float64 lng 249737 non-null float64 desc 249737 non-null object zip 219391 non-null float64 title 249737 non-null object timeStamp 249737 non-null object twp 249644 non-null object addr 249737 non-null object e 249737 non-null int64 dtypes: float64(3), int64(1), object(5) memory usage: 17.1+ MB #获取分类 temp_list = df.title.str.split(':').tolist() cate_list = list(set([i[0] for i in temp_list])) cate_list Out[152]: ['Fire', 'Traffic', 'EMS'] #构造全为0的数组 zeros_df = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0],len(cate_list))),columns=cate_list) #赋值 for cate in cate_list: zeros_df[cate][df.title.str.contains(cate)] = 1 print(zeros_df) Fire Traffic EMS 0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1 0.0 0.0 1.0 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 3 0.0 0.0 1.0 4 0.0 0.0 1.0 5 0.0 0.0 1.0 6 0.0 0.0 1.0 7 0.0 0.0 1.0 8 0.0 0.0 1.0 9 0.0 1.0 0.0 10 0.0 1.0 0.0 11 0.0 1.0 0.0 12 0.0 1.0 0.0 13 0.0 1.0 0.0 14 0.0 1.0 0.0 15 0.0 1.0 0.0 16 0.0 0.0 1.0 17 0.0 0.0 1.0 18 0.0 0.0 1.0 19 0.0 1.0 0.0 20 0.0 1.0 0.0 21 0.0 1.0 0.0 22 1.0 0.0 0.0 23 0.0 1.0 0.0 24 0.0 1.0 0.0 25 0.0 0.0 1.0 26 0.0 0.0 1.0 27 1.0 0.0 0.0 28 0.0 1.0 0.0 29 0.0 1.0 0.0 ... ... ... 249707 0.0 1.0 0.0 249708 1.0 0.0 0.0 249709 0.0 0.0 1.0 249710 0.0 1.0 0.0 249711 0.0 1.0 0.0 249712 0.0 0.0 1.0 249713 1.0 0.0 0.0 249714 1.0 0.0 0.0 249715 0.0 1.0 0.0 249716 0.0 0.0 1.0 249717 0.0 0.0 1.0 249718 1.0 0.0 0.0 249719 0.0 0.0 1.0 249720 0.0 0.0 1.0 249721 0.0 0.0 1.0 249722 0.0 1.0 0.0 249723 0.0 0.0 1.0 249724 0.0 0.0 1.0 249725 0.0 0.0 1.0 249726 1.0 0.0 0.0 249727 1.0 0.0 0.0 249728 0.0 1.0 0.0 249729 0.0 0.0 1.0 249730 0.0 0.0 1.0 249731 0.0 1.0 0.0 249732 0.0 0.0 1.0 249733 0.0 0.0 1.0 249734 0.0 0.0 1.0 249735 1.0 0.0 0.0 249736 0.0 1.0 0.0 [249737 rows x 3 columns] sum_ret = zeros_df.sum(axis=0) print(sum_ret) Fire 37432.0 Traffic 87465.0 EMS 124844.0 dtype: float64

df = pd.read_csv('911.csv') # print(df.head(1)) # print(df.info()) #获取分类 temp_list = df.title.str.split(':').tolist() cate_list = [i[0] for i in temp_list] df['cate'] = pd.DataFrame(np.array(cate_list).reshape(df.shape[0],1)) print(df.groupby(by='cate').count()['title']) cate EMS 124840 Fire 37432 Traffic 87465 Name: title, dtype: int64
五、分布分析
pd.cut(data['col_names'], bins, labels=None)
实例
import numpy
import pandas
from pandas import read_csv
data = read_csv('E:/python/data_analysis/data/dis-cut.csv')
bins = [data['年龄'].min()-1,20,30,40,max(data.年龄)+1]
labels = ['20岁及以下','21岁到30岁','31岁到40岁','41岁以上']
age_cut = pandas.cut(data.年龄,bins,labels=labels)
data['年龄分层'] = age_cut
result = data.groupby(by=['年龄分层'])['年龄'].agg(['size','mean'])
result.rename(columns= {'size': '人数','mean': '平均年龄'})
Out[171]:
人数 平均年龄
年龄分层
20岁及以下 2061 19.302280
21岁到30岁 46858 25.759081
31岁到40岁 8729 33.095773
41岁以上 1453 50.625602
六、交叉分析


import pandas from pandas import read_csv data = read_csv('E:/python/data_analysis/data/pivot_table.csv') bins = [data['年龄'].min() - 1, 20, 30, 40, max(data.年龄) + 1] labels = ['20岁及以下', '21岁到30岁', '31岁到40岁', '41岁以上'] age_cut = pandas.cut(data.年龄, bins, labels=labels) data['年龄分层'] = age_cut r1 = data.pivot_table( values=['年龄'], index=['年龄分层'], columns=['性别'], aggfunc=[numpy.size, numpy.mean] ) r2 = data.pivot_table( values=['年龄'], index=['年龄分层'], columns=['性别'], aggfunc=[numpy.std], ) print(r1.index) print(r1['size']['年龄']['女']) print(r1.join(r2)) CategoricalIndex(['41岁以上', '21岁到30岁', '31岁到40岁', '20岁及以下'], categories=['20岁及以下', '21岁到30岁', '31岁到40岁', '41岁以上'], ordered=True, name='年龄分层', dtype='category') 年龄分层 41岁以上 111 21岁到30岁 2903 31岁到40岁 735 20岁及以下 567 Name: 女, dtype: int64 size mean std 年龄 年龄 年龄 性别 女 男 女 男 女 男 年龄分层 41岁以上 111 1950 18.972973 19.321026 1.708053 1.044185 21岁到30岁 2903 43955 25.954874 25.746149 2.453642 2.361298 31岁到40岁 735 7994 33.213605 33.084939 2.316704 2.200319 20岁及以下 567 886 51.691358 49.943567 6.761848 7.914171

import pandas as pd import numpy as np data = pd.DataFrame({'Sample': range(1, 11), 'Gender': ['Female', 'Male', 'Female', 'Male', 'Male', 'Male', 'Female', 'Female', 'Male', 'Female'], 'Handedness': ['Right-handed', 'Left-handed', 'Right-handed', 'Right-handed', 'Left-handed', 'Right-handed', 'Right-handed', 'Left-handed', 'Right-handed', 'Right-handed']}) #假设我们想要根据性别和用手习惯对这段数据进行#统计汇总。虽然可以用pivot_table()实现该功#能,但是pandas.crosstab()函数会更方便: # 方法一:用pivot_table # 其实我觉的一点都不麻烦ε=(´ο`*)))唉 data.pivot_table(index=['Gender'], columns='Handedness', aggfunc=len, margins=True) Out[173]: Sample Handedness Left-handed Right-handed All Gender Female 1 4 5 Male 2 3 5 All 3 7 10 # 方法二:用crosstab pd.crosstab(data.Gender, data.Handedness, margins=True) Out[174]: Handedness Left-handed Right-handed All Gender Female 1 4 5 Male 2 3 5 All 3 7 10
- 透视表pivot_table()是一种进行分组统计的函数,参数aggfunc决定统计类型;
- 交叉表crosstab()是一种特殊的pivot_table(),专用于计算分组频率。
具体使用参照 https://www.cnblogs.com/onemorepoint/p/8425300.html
七、格式化输出
pandas dataframe数据全部输出,数据太多也不用省略号表示。
pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
或者
with option_context('display.max_rows', 10, 'display.max_columns', 5):
代码逻辑
八、索引

