List
添加方法(添加到末尾):.add(str)
.add(index, str) 将新的str 值存入 index索引,原来索引index 和值往后移一位。
根据索引将元素值改变:.set(index,str)
根据索引获取元素: .get(index)
得到list 中元素数的和 .size()
根据索引删除元素: .remove(index)
根据元素对象删除内容:.remove(str)
根据元素从前后往查找: .indexOf(str) 找到即返回索引,未找到返回 -1
根据元素从后往前查找: .lastIndexOf(str) 找到即返回索引,未找到返回 -1
list 是否包含某个元素 .contains(str) ,返回true 或 false
.equals() 和 .hashcode()
equals 判断两个对象元素是否相同,
ArrayList 和 LinkedList
相同点: 都是List接口实现类 ;线程不安全;
异:
ArrayList 是线性表,是基于动态数组实现,查询快,增删慢; 可自动扩容;
LinkedList 链表数据实现,查询慢,增删快;
HashTabe 和 HashMap
添加方法 .put(index,str)
根据索引获取元素:.get(index)
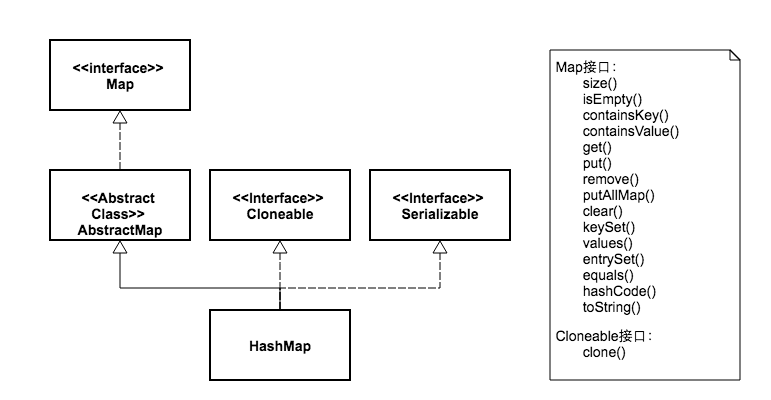
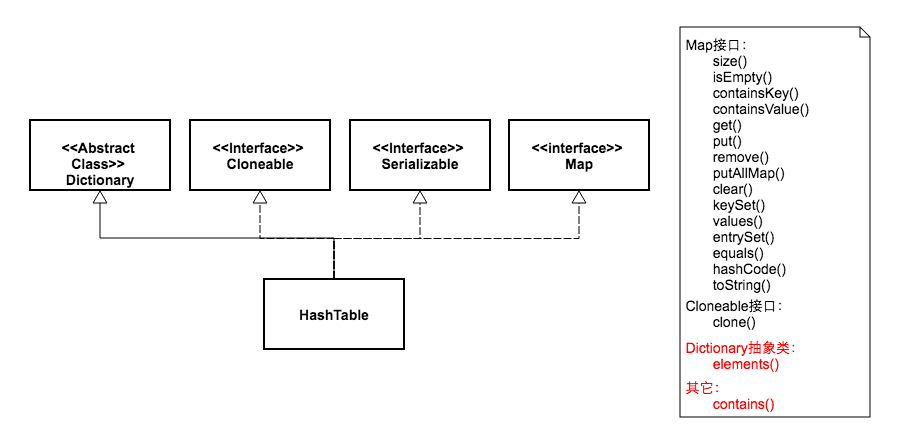
相同点: 都是Map接口实现类 ;
异:
1. 线程安全性不同: HashTable 是线程安全;添加里synchronized 关键字, HashMap 是非线程安全。
2. 存储不同: HashTable 不允许null 作为key; HashMap 允许null 作为key 值,且总是存储在数组第一个节点。
3. 继承父类不同:HashTale 继承Dictionary 抽象类; HashMap 继承类AbtractMap。
4. hash值不同: HashTable 直接使用对象的hashCode; HashMap 重新计算hash值。
5. 提供contains方法: HashTable 保留了contains,containsKey 和 containsValue 三个方法; HashMap去除了contains 方法,改成containsKey 和 containsValue。
TreeMap 根据key, 从小到大自然排序
List<String> listOne = new ArrayList<String>();
listOne.add("apple");
listOne.add("pear");
listOne.add("banana");
listOne.add("peach");
listOne.add("apple");
System.out.println("banana"+listOne.indexOf("apple"));//从前往后搜索
System.out.println("banana"+listOne.lastIndexOf("apple"));//从 后往前搜索
for(int i=0;i<listOne.size();i++){
System.out.println("value:"+listOne.get(i));
}
Iterator it = listOne.iterator();//返回listOne 集合对象
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println("==value:"+it.next()); //ArrayList从前往后输出值
}
Hashtable<Integer,String> ht=new Hashtable<Integer,String>();
ht.put(1,"Anna");
ht.put(2,"Bill");
ht.put(3,"Cindy");
ht.put(4,"Dell");
ht.put(5,"Felex");
ht.put(6,"Elsa");
Iterator it1 = ht.values().iterator();//获取值的集合对象
while (it1.hasNext()){
System.out.println("value:"+it1.next()); //从后往前输出
}
Iterator itKey= ht.keySet().iterator();//获取健的集合对象
while (itKey.hasNext()){
System.out.println("====key:"+itKey.next()); //从后往前输出
}