一、 CORS 预请求
允许方法:
GET、 HEAD、 POST 这三个方法 不需要预请求。
允许 Content-Type
text/plain、 multipart/form-data、 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 这三个不需要预请求
其他限制
请求头限制、 XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象均没有注册任何事件监听器
请求中没有使用 ReadableStream 对象
server.js 代码
const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') http.createServer(function (request, response) { console.log('request come', request.url) const html = fs.readFileSync('test.html', 'utf8') response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' }) response.end(html) }).listen(8888) console.log('server listening on 8888')
server2.js 代码
const http = require('http') http.createServer(function (request, response) { console.log('request come', request.url) response.writeHead(200, { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': 'http://127.0.0.1:8888', 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'X-Test-Cors', //预请求头 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'POST, PUT, DELETE',//请求方式 'Access-Control-Max-Age': '1000' //多长事件内不需要预请求来验证 }) response.end('123') }).listen(8887) console.log('server listening on 8887')
test.html 代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <!-- cors1 --> <!-- <script> var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest() xhr.open('GET', 'http://127.0.0.1:8887/') xhr.send() </script> --> <script> fetch('http://localhost:8887', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'X-Test-Cors': '123' } }) </script> </html>
用nodejs 去运行 server.js 和 server2.js
node server.js
node server2.js
结果:
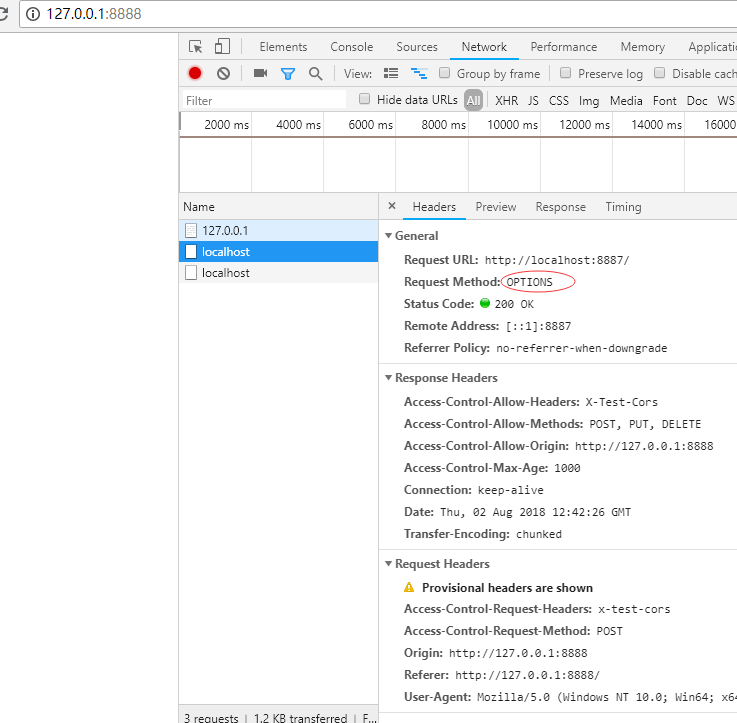
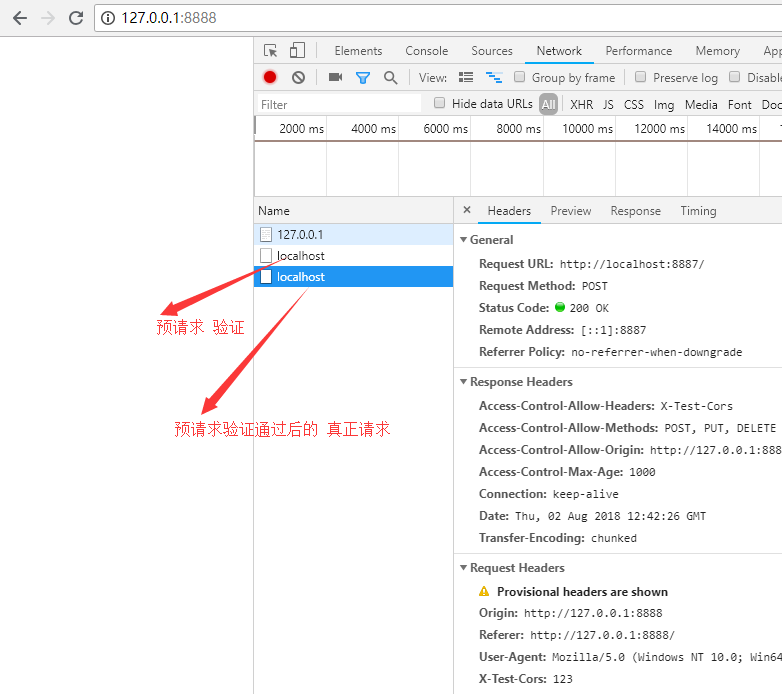
二、 缓存头 Cache-Control 的含义和使用
缓存 Cache-Control
可缓存性
public:表示(发送,请求,以及中间代理)任何地方 都可以对我返回内容的缓存的操控。
private:表示 只有发起请求的浏览器 才可以进行缓存。
no-cache:任何一个节点 都不可以缓存(你可以去缓存,但是你需要去服务器去验证一下。才可以使用本地的缓存。)
到期
max-age = <seconds> : 多少秒以后 缓存过期。
s-maxage = <seconds> :代理服务器 会优先选择这个 到期的时间。
max-stale = <seconds> : 在这个时间内, 即使缓存过期了,也会使用这个过期的缓存。
重新验证
must-revalidate :重新去服务器获取数据 验证缓存是否到期。而不能直接使用本地的缓存。
proxy-revalidate:代理缓存服务器重新去获取数据验证魂村是否到期,而不能直接使用本地缓存。
其他
no-store:本地和代理服务器 都不可以存缓存。
no-traansform:告诉代理服务器不要随便改动 请求返回的内容。
server.js 代码
const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') http.createServer(function (request, response) { console.log('request come', request.url) if (request.url === '/') { const html = fs.readFileSync('test.html', 'utf8') response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' }) response.end(html) } if (request.url === '/script.js') { response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/javascript', 'Cache-Control': 'max-age=20' }) response.end('console.log("script loaded")') } }).listen(8888) console.log('server listening on 8888')
test.html 代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <script src="/script.js"></script> </html>
第一次访问返回结果:
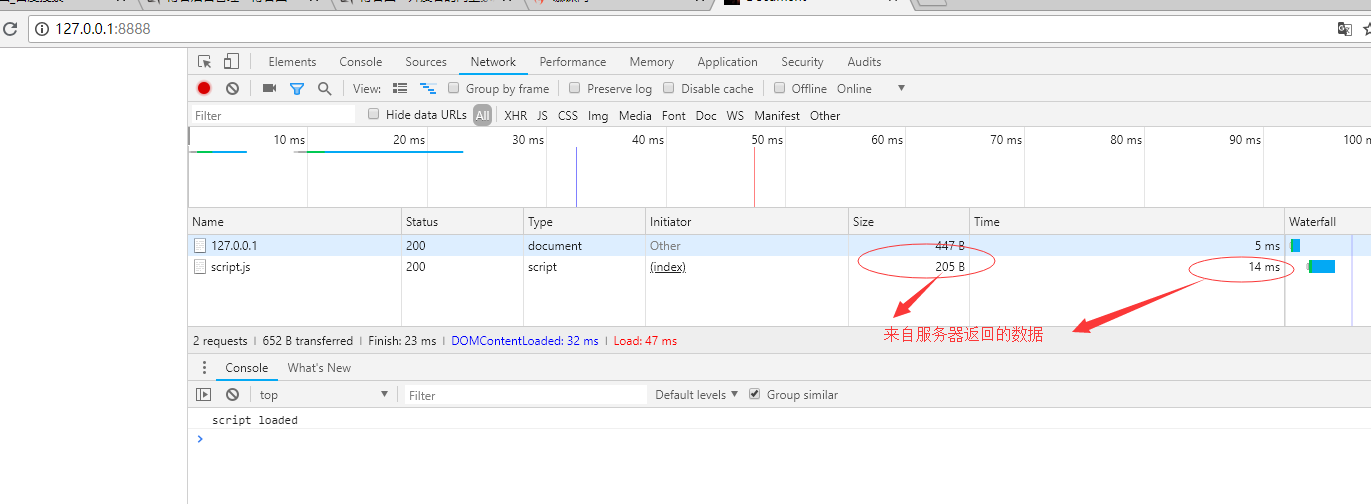
在到期缓存时间之内再一次访问:
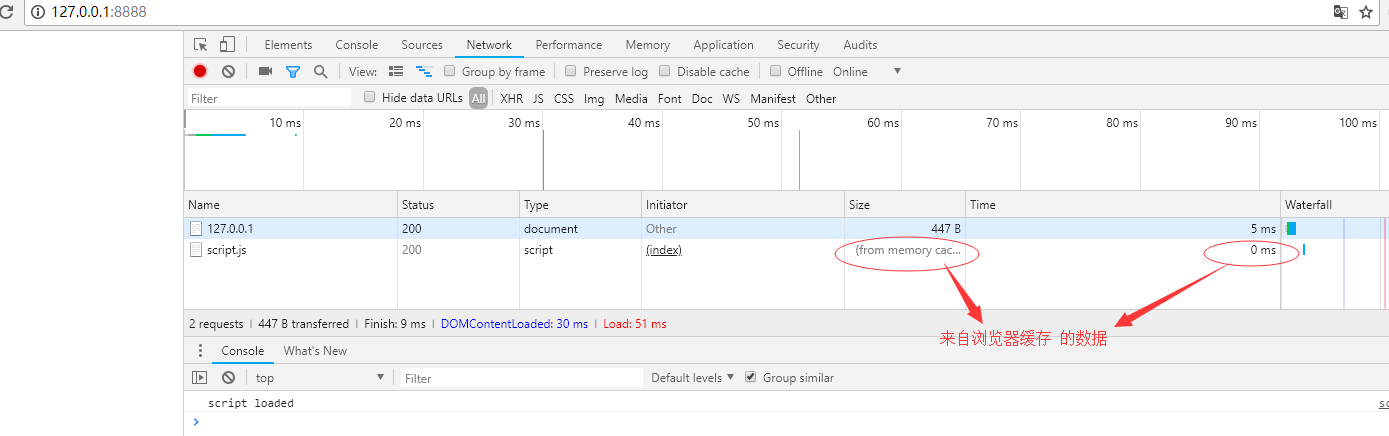
三、缓存验证 Last-Modified 和 Etag 的使用
资源验证

验证头
Last-Modified:上次修改时间
配合if-Modified-Since 或者 if-Unmodified-Since 使用,对比上次修改时间来验证资源是否需要更新。
Etag:数据签名
配合if-Match 或者 if-Non-Match 使用,对比资源的签名判断是否使用缓存。
server.js 代码
const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') http.createServer(function (request, response) { console.log('request come', request.url) if (request.url === '/') { const html = fs.readFileSync('test.html', 'utf8') response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' }) response.end(html) } if (request.url === '/script.js') { const etag = request.headers['if-none-match'] if (etag === '777') { response.writeHead(304, { //状态码304 表示资源没有被修改可以用本地缓存 'Content-Type': 'text/javascript', 'Cache-Control': 'max-age=2000000, no-cache', 'Last-Modified': '123', 'Etag': '777' }) response.end() } else { response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/javascript', 'Cache-Control': 'max-age=2000000, no-cache', 'Last-Modified': '123', 'Etag': '777' }) response.end('console.log("script loaded twice")') } } }).listen(8888) console.log('server listening on 8888')
test.html 代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <script src="/script.js"></script> </html>
第一次发送请求结果:
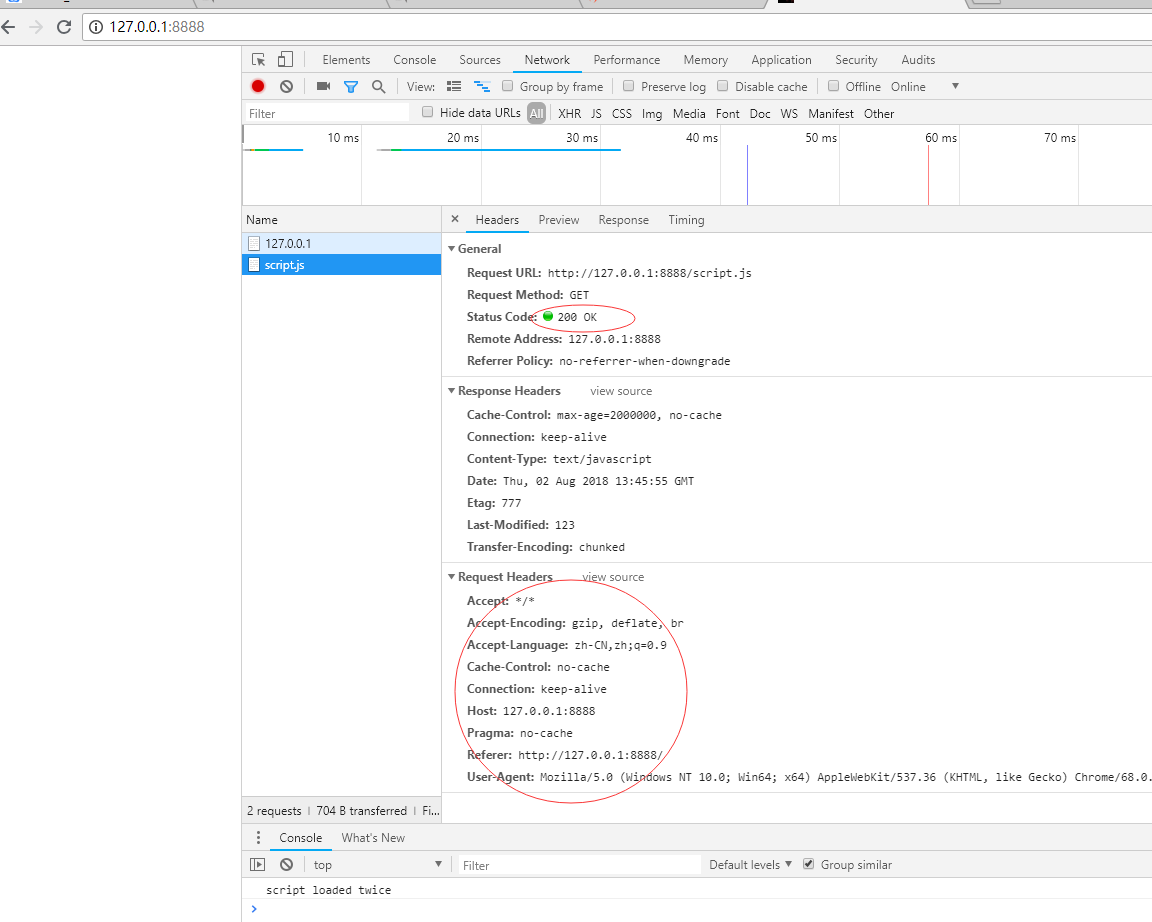
第二次发送请求结果:
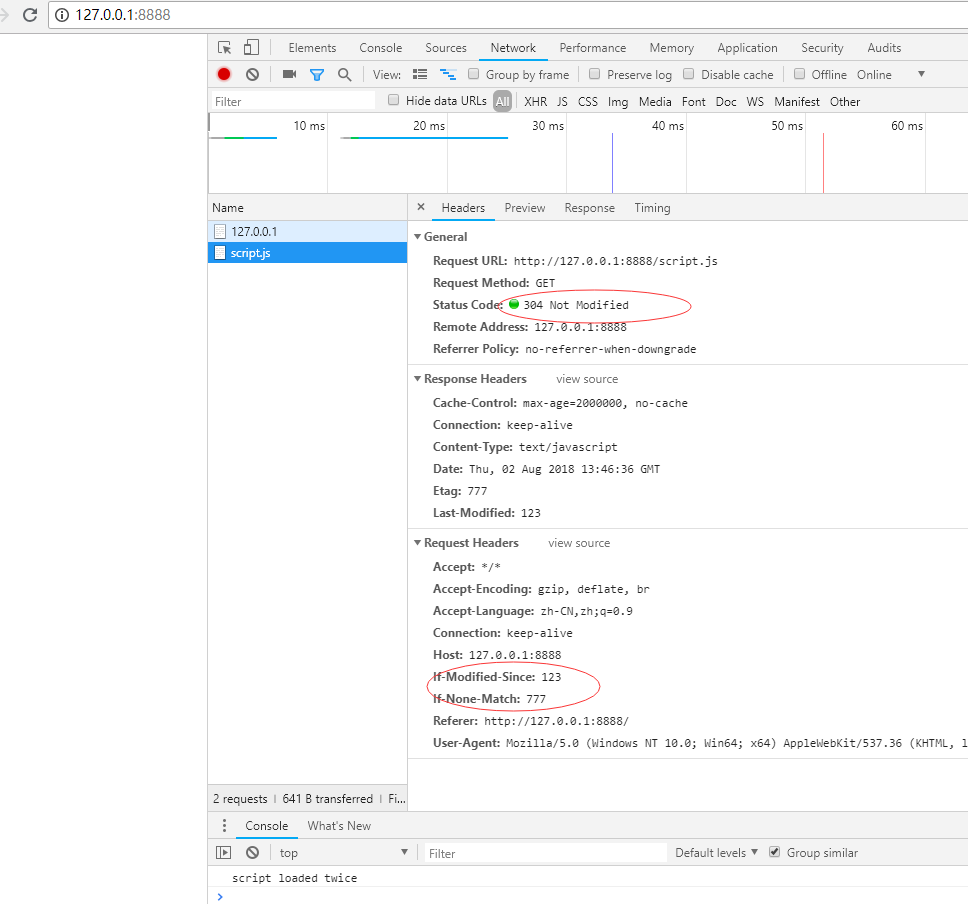
总结:第一次发送请求时候,响应头返回服务器的数字签名 Etag,浏览器存入缓存头if-None-Match中,第二次发送请求的时候,服务器验证if-None-Match 与 服务器的 Etag 是否一致,一致使用浏览器本地的缓存,不一致则使用从服务器重新返回新数据。