注意布尔逻辑运行:
&&(短路与) 各 &的区别:
&&只要判断到一项为0,则后面不判断。&,两项都要判断
||(短路或)和 |的区别:
public class BoolTest{
||和 |的区别:
public static void main(String args[]){
if((1/1==1)||(1/0==1)){
System.out.println("True");
}
if((1/1!=1)&&(1/0==1)){
System.out.println("True");
}
}
}
1.条件判断:
if---else-----
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 31 ;
if(x==30){ // 条件满足
System.out.println("年龄是30岁!") ;
}else if(x<30){
System.out.println("年龄小于30岁!") ;
}else{
System.out.println("年龄大于30岁!") ;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 31 ;
if(x==30){ // 条件满足
System.out.println("年龄是30岁!") ;
}else if(x<30){
System.out.println("年龄小于30岁!") ;
}else{
System.out.println("年龄大于30岁!") ;
}
}
}
2.switch------case--
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
int ch = 6 ;
switch(ch){
case 1:{
System.out.println("结果是1") ;
break ;
}
case 2:{
System.out.println("结果是2") ;
break ;
}
case 3:{
System.out.println("结果是3") ;
break ;
}
default:{
System.out.println("没有此结果") ;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int ch = 6 ;
switch(ch){
case 1:{
System.out.println("结果是1") ;
break ;
}
case 2:{
System.out.println("结果是2") ;
break ;
}
case 3:{
System.out.println("结果是3") ;
break ;
}
default:{
System.out.println("没有此结果") ;
}
}
}
}
3.循环while
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 1 ;
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
while(x<=100){ // 如果最后x的内容变成了大于100,则此循环退出
sum += x ; // 进行加法操作
x++ ; // 修改循环条件
}
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 1 ;
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
while(x<=100){ // 如果最后x的内容变成了大于100,则此循环退出
sum += x ; // 进行加法操作
x++ ; // 修改循环条件
}
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
4.do----while
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 1 ;
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
do{ // 如果最后x的内容变成了大于100,则此循环退出
sum += x ; // 进行加法操作
x++ ; // 修改循环条件
}while(x<=100) ;
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 1 ;
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
do{ // 如果最后x的内容变成了大于100,则此循环退出
sum += x ; // 进行加法操作
x++ ; // 修改循环条件
}while(x<=100) ;
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
5.for
public class TestDemo39 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
for(int x=0;x<=100;x++){
sum += x ;
}
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int sum = 0 ; // 接收最终的计算结果
for(int x=0;x<=100;x++){
sum += x ;
}
System.out.println(sum) ;
}
}
注意:
public class MethodArrayDemo05{
public static void main(String args[]){
int t1[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9} ;
for(int x:t1){
System.out.print(x + "、") ;
}
}
};
6.break:public static void main(String args[]){
int t1[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9} ;
for(int x:t1){
System.out.print(x + "、") ;
}
}
};
public class TestDemo40 {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=0;x<10;x++){
if(x==3){
break ; // 退出整个循环
}
System.out.println("x = " + x) ;
}
}
}
7.continue:public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=0;x<10;x++){
if(x==3){
break ; // 退出整个循环
}
System.out.println("x = " + x) ;
}
}
}
public class TestDemo41 {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=0;x<10;x++){
if(x==3){
continue ; // 退出一个循环
}
System.out.println("x = " + x) ;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=0;x<10;x++){
if(x==3){
continue ; // 退出一个循环
}
System.out.println("x = " + x) ;
}
}
}
8.换行
public class TestDemo42 {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=1;x<10;x++){
for(int y=1;y<=x;y++){
System.out.print(x + "*" + y + "=" + x*y +" ") ;
}
System.out.println() ; // 换行
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=1;x<10;x++){
for(int y=1;y<=x;y++){
System.out.print(x + "*" + y + "=" + x*y +" ") ;
}
System.out.println() ; // 换行
}
}
}
9.嵌套
public class TestDemo43 {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=1;x<=3000;x++){
if(x%3==0&&x%5==0&&x%7==0){
System.out.println(x + " ") ;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int x=1;x<=3000;x++){
if(x%3==0&&x%5==0&&x%7==0){
System.out.println(x + " ") ;
}
}
}
}
10.双目运算:
public class TestDemo46 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 10 ;
int y = 20 ;
int z = 50 ;
int max = x<y?y:x ;
max = max<z?z:max ;
System.out.println(max) ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 10 ;
int y = 20 ;
int z = 50 ;
int max = x<y?y:x ;
max = max<z?z:max ;
System.out.println(max) ;
}
}
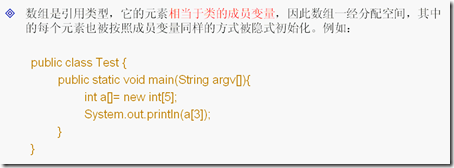
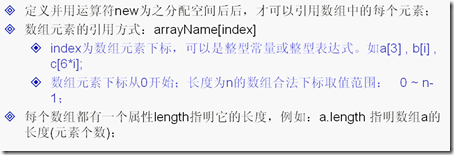
11.数组
在JDK中也有一个对应的数组排序方法:java.util.Arrays.sort(数组名称) ;
定义:
int arr[][]= new int[2][3];
int arr[][] = new int[2][];
arr[0] = new int[3];
arr[1] = new int[4];
错误:
int arr[2][3] = {......};
int arr[][] = new int[][5];
不定参数:
public class MethodArrayDemo06{
public static void main(String args[]){
int temp[] = {2,4,6,8} ;
fun() ; // 没有参数
fun(1) ; // 一个参数
fun(1,3,5,7,9) ; // 一个参数
fun(temp) ;
}
public static void fun(int ... arg){
for(int x:arg){
System.out.print(x + "、") ;
}
System.out.println() ;
}
};
public static void main(String args[]){
int temp[] = {2,4,6,8} ;
fun() ; // 没有参数
fun(1) ; // 一个参数
fun(1,3,5,7,9) ; // 一个参数
fun(temp) ;
}
public static void fun(int ... arg){
for(int x:arg){
System.out.print(x + "、") ;
}
System.out.println() ;
}
};
2函数的重载
如果是函数返回值不同,刚不是函数的重载。public class MethodDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
int x[] = init() ; // 通过方法取得内容
print(x) ; // 接收数组
}
public static void print(int temp[]){ // 此方法接收数组
for(int i=0;i<temp.length;i++){
System.out.println("temp["+i+"] = " + temp[i]) ;
}
}
public static int[] init(){
int y[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6} ;
return y ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x[] = init() ; // 通过方法取得内容
print(x) ; // 接收数组
}
public static void print(int temp[]){ // 此方法接收数组
for(int i=0;i<temp.length;i++){
System.out.println("temp["+i+"] = " + temp[i]) ;
}
}
public static int[] init(){
int y[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6} ;
return y ;
}
}