在C#2.0的时候微软推出了泛型,可以说泛型在.net体系框架中应用到方方面面。
首先举一个小例子说一下泛型.
比如一个方法,我们既可以传string,又可以传int,还可以传DateTime,在.net framework 1.0时代是这样处理:
/// <summary> /// 1.0的写法 /// </summary> /// <param name="parameter"></param> public static void ShowObject(object parameter) { Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(Program), parameter.GetType().Name, parameter); }
泛型出来后的写法:
/// <summary> /// 2.0的写法 /// 延迟声明,把参数类型的声明推迟到调用 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="parameter"></param> public static void ShowT<T>(T parameter) { Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(Program), parameter.GetType().Name, parameter); }
调用:
ShowT<string>("hellow");
因为C#语言是强类型的,在编译的时候就要确定对象的类型。但是泛型这个地方是延迟声明,相当于dynamic.
对于泛型参数,编译的时候会以占位符来替代,只有在调用的时候才会确定其类型.
Console.WriteLine(typeof(List<>)); Console.WriteLine(typeof(Dictionary<,>));
如下:

泛型类:
/// <summary> /// 一个类来满足不同具体的类型 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class GenericT<T> { public GenericT(T _t) { val = _t; } public T val; }
调用:
int i = 0; var generic = new GenericT<int>(i);
泛型接口:
/// <summary> /// 一个接口来满足不同的具体实例的方法 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public interface InterfaceT<T> { T GetDataT(); }
public class Method : InterfaceT<List<int>> { public List<int> GetDataT() { return Enumerable.Range(0, 100).ToList(); } }
泛型委托:
public delegate List<T1> MyDelegate<T1, T>(T t);
public static class MethodWork { public static List<int> method(string t) { Console.WriteLine(t); return new List<int>(); } }
调用:
MyDelegate<int, string> del = MethodWork.method; del("Hello");
泛型约束:
/// <summary> /// 引用类型约束 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class GenericT<T> where T : class { public GenericT(T _t) { val = _t; } public T val; }
/// <summary> /// 接口约束 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="t"></param> public static void methods<T>(T t) where T:InterfaceT<T> { t.GetDataT(); }
/// <summary> /// 值类型约束 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="t"></param> public static T Methods<T>(T t) where T : struct { //会根据T的不同,赋予默认值 T _t = default(T); return t; }
/// <summary> /// 无参数构造函数约束
/// T必须包含一个无参数的构造函数 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="t"></param> public static T Methods<T>(T t) where T : new() { T _t = new T(); return t; }
协变与逆变(C#4.0推出的)
只能用在接口或委托中
out 协变covariant 修饰返回值
in 逆变contravariant 修饰传入参数
比如有两个类,A继承至B
/// <summary> /// 商品类 /// </summary> public class Products { /// <summary> /// 商品id /// </summary> public int id { get; set; } }
/// <summary> /// 零食类 /// </summary> public class snacks : Products { public string name { get; set; } }
//我们可以通过Snacks来实例化Products,任何父类出现的地方都可以使用子类来替代 Products data = new Snacks();
但是对象集合实例化就出错了
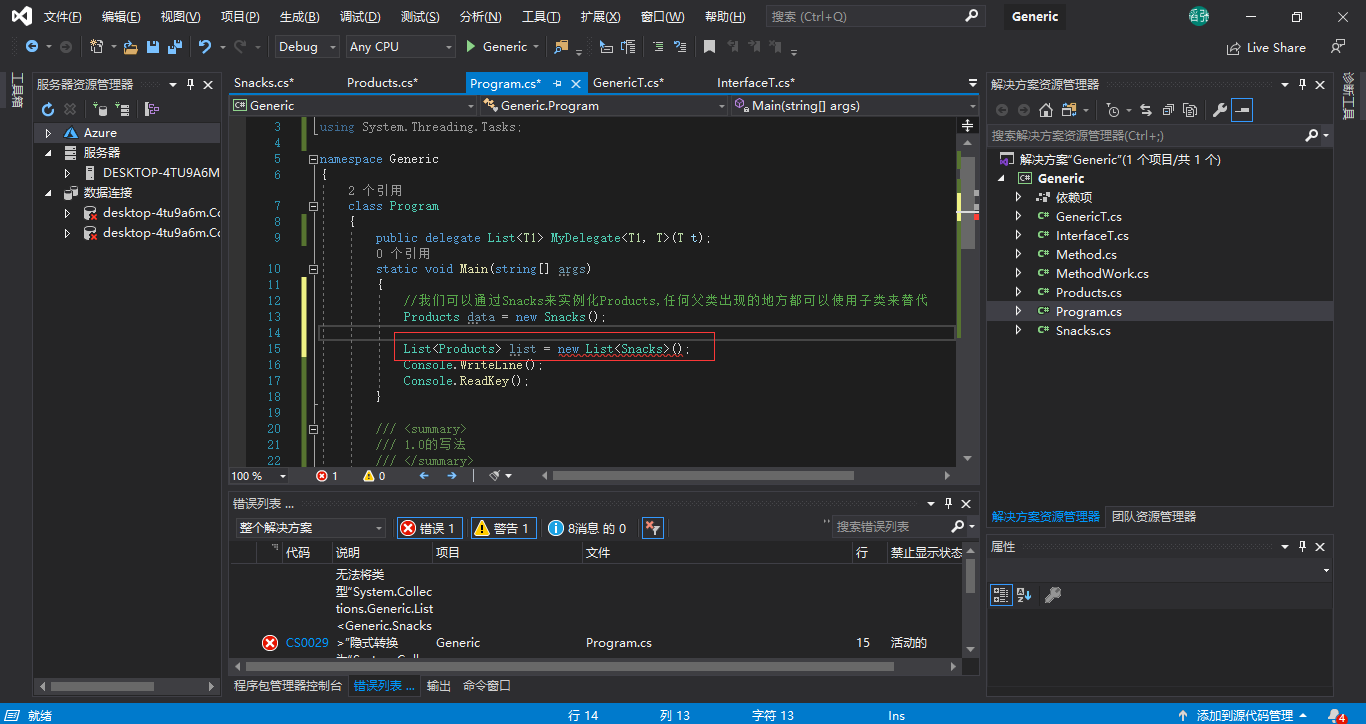
原因:
理论上是可以的,但是实际不行
因为两个List容器没有父子关系
我们可以把List<Products>()单独看成一个对象,List是没有继承关系的,所以两个List根本不对等
//我们可以这样写 List<Products> productsList = new List<Snacks>().Select(m => (Products)m).ToList();
//协变 IEnumerable<Products> products = new List<Snacks>();
Func<Products> func = new Func<Snacks>(() => { return new Snacks(); });
简单点说,一袋商品和一袋零食,两者根本不是继承的概念,继承必须是包括容器一起继承(这里容器是List<>)。因为容器和对象融为了一体,两者(List<Products>和List<Snacks>)就不再有继承的概念了。加了in、out之后,就是只判断内容(Products和Snacks)关系,忽略外面的容器(List<>)。
in(逆变)和out(协变)只能用在泛型参数申明前(肩括号里面).
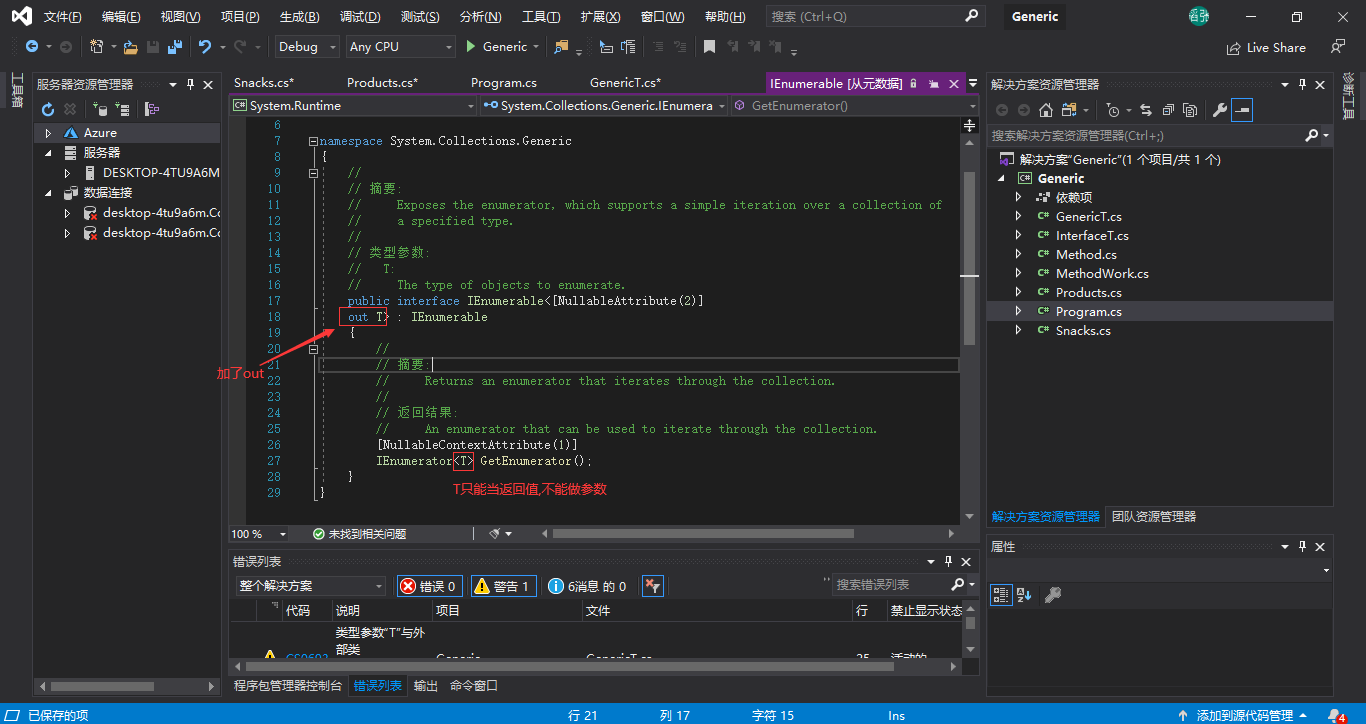
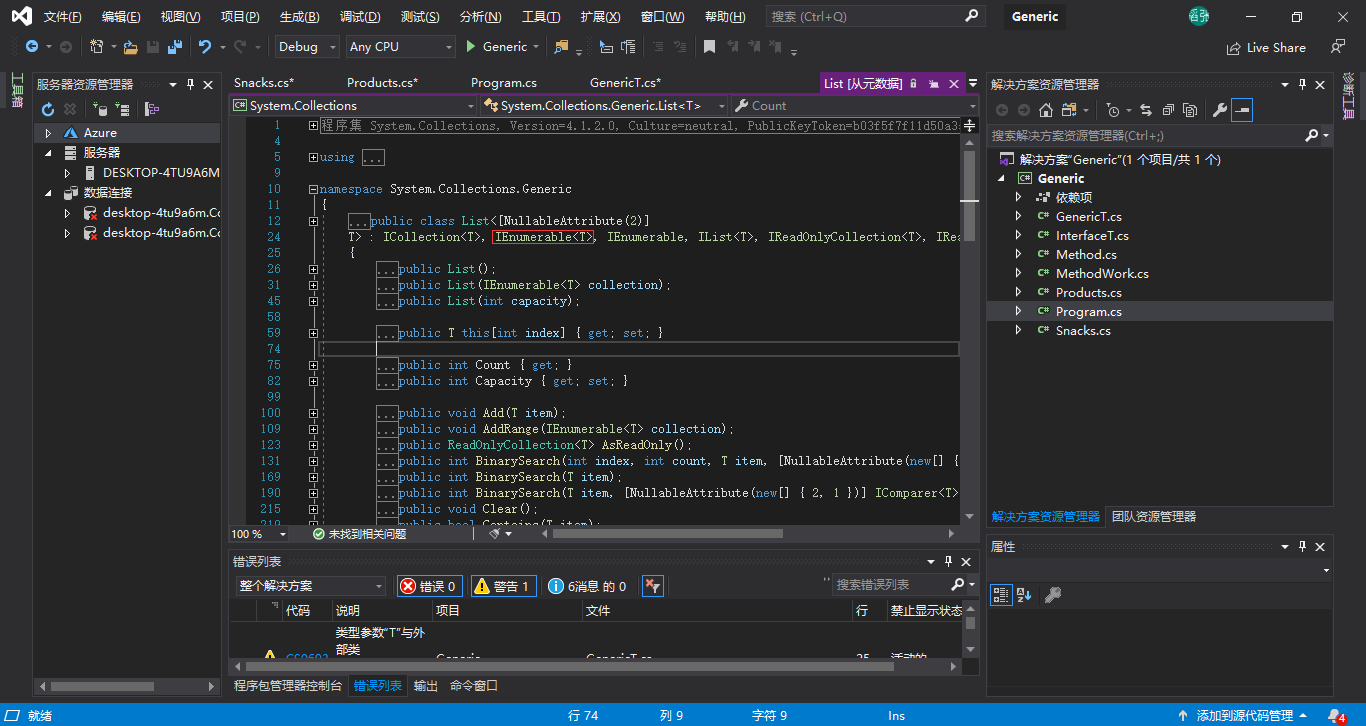
List继承了IEnumerable接口
逆变:
//泛型参数前是in
public interface ICustomerListIn<in T> {
//T只能当参数,不能当返回值 void Show(T t); } public class CustomerListIn<T> : ICustomerListIn<T> { public void Show(T t) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
//左边泛型对象是子类,右边是子类或父类都可以,反之亦然 ICustomerListIn<Snacks> products = new CustomerListIn<Products>(); Action<Snacks> func = new Action<Products>((Products data) => { });
协变逆变总结:1.协变.传入的泛型对象只能用在方法返回值上,逆变.传入的泛型对象只能用在方法参数上。
2.协变中实例化的对象或者传入的参数只能是对象本身或者子类,逆变中实例化的对象或者传入的参数可以是对象本身也可以是父类。
泛型缓存:
定义一个方法
public class CustomerCache<T> { /// <summary> /// 静态构造函数,程序启动后只会调用一次 /// </summary> static CustomerCache() { Console.WriteLine("调用了一次"); _val = DateTime.Now.Second; } /// <summary> /// 静态字段是不会被GC的 /// </summary> private static object _val = default(T); public static T GetData() { var typeName = typeof(T).FullName; string type = typeName.Substring(typeName.IndexOf('.') + 1); if (type.Contains("Int")) _val = Convert.ToInt32(_val.ToString()); if (type.Contains("String")) _val = _val.ToString(); return (T)_val; } }
调用:
Console.WriteLine(CustomerCache<int>.GetData()); Console.WriteLine(CustomerCache<string>.GetData());

当我们再次调用的时候,就不会再进入构造函数赋值,而是直接返回数据. 缓存就起作用了.
我们可以再封进行装一下
/// <summary> /// 自定义缓存,存进来,查出去 /// </summary> public class CustomCache { /// <summary> /// 静态构造函数,第一次使用CustomCache之前完成调用,且调用一次 /// </summary> static CustomCache() { //死循环,每隔十分钟检测过期的key,删除key,主动清理,保证过期数据不会常驻内存 Task.Run(() => { while (true) { var keyList = new List<string>(); //循环所有的key foreach (var key in CustomCacheDictionary.Keys) { var valueTime = CustomCacheDictionary[key]; if (DateTime.Now > valueTime.Value) { keyList.Add(key); } } //删除这些key keyList.ForEach(k => CustomCacheDictionary.Remove(k)); Thread.Sleep(1000 * 60 * 10);//休息十分钟 } }); } /// <summary> /// static是常驻内存,不会被GC(全局唯一的,共享的) /// private私有化,数据保证安全 /// KeyValuePair保存对象值与时间 /// 操作字典时要加锁,并发问题,因为只有一个字典容器,或者使用CocurrentDictionary=>线程安全字典,应对多线程 /// </summary> private static Dictionary<string, KeyValuePair<object, DateTime>> CustomCacheDictionary = new Dictionary<string, KeyValuePair<object, DateTime>>(); public static void Save(string key, object value, int timeoutSecond = 1800) { if (Exist(key)) Remove(key); //加上过期时间DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(timeoutSecond) CustomCacheDictionary.Add(key, new KeyValuePair<object, DateTime>(value, DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(timeoutSecond))); } public static void Remove(string key) { CustomCacheDictionary.Remove(key); } public static void RemoveAll() { CustomCacheDictionary.Clear(); } /// <summary> /// 只删除符合条件的key /// </summary> /// <param name="func"></param> public static void RemoveCondition(Func<string, bool> func) { var keyList = new List<string>(); //循环所有的key foreach (var key in CustomCacheDictionary.Keys) { //key带入判断是否符合条件 if (func.Invoke(key)) keyList.Add(key); } //删除这些key keyList.ForEach(k => CustomCacheDictionary.Remove(k)); } public static bool Exist(string key) { if (CustomCacheDictionary.ContainsKey(key)) { var valueTime = CustomCacheDictionary[key]; if (DateTime.Now > valueTime.Value) { //被动清理,查的时候才清理 CustomCacheDictionary.Remove(key); return false; } else return true; } else return false; } /// <summary> /// 获取数据 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <param name="func">方法:()=>Class.Method()</param> /// <returns></returns> public static T GetData<T>(string key, Func<T> func) { T result = default(T); if (!CustomCache.Exist(key)) { result = func.Invoke(); Save(key, result); } else //拿到value中的key就是得到value值 result = (T)CustomCacheDictionary[key].Key; return result; } }
上面的缓存方法只是一个简单的例子,实际项目中肯定会用到第三方缓存库。
the end!