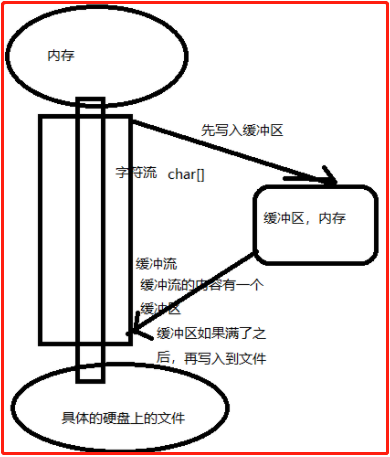
什么是缓冲流:
缓冲流的基本原理,是在创建流对象时,会创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
图解:
1、字节缓冲流BufferedInputStream;BufferedOutputStream:
- public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) :创建一个 新的缓冲输入流。
- public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) : 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
案例对比:
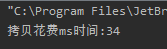
使用缓冲流,拷贝文件每次拷贝1024字节
import java.io.*; /** * @ClassName FileCopyTryCatchBuffer * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/17. */ public class FileCopyTryCatchBuffer { public static void main(String[] args) { String srcPath = "C:\Users\ZHANGMINGDA\Pictures\康熙北巡.jpg"; String dstpath = "C:\Users\ZHANGMINGDA\Pictures\康熙北巡bak.jpg"; byte[] tmpbytes = new byte[1024]; int copyLength; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try(InputStream bfis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath)); OutputStream bfos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dstpath))){ while ((copyLength = bfis.read(tmpbytes)) != -1){ bfos.write(tmpbytes,0,copyLength); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("拷贝花费ms时间:" + (endTime - startTime)); } }
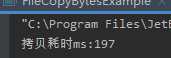
不使用缓冲流,拷贝文件每次拷贝1024字节
import java.io.*; /** * @ClassName FileCopyBytesExample * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/17. */ public class FileCopyBytesExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\Users\ZHANGMINGDA\Pictures\康熙北巡.jpg"; String dstpath = "C:\Users\ZHANGMINGDA\Pictures\康熙北巡bak.jpg"; InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcPath); OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dstpath); byte[] tmpBytes = new byte[1024]; int length ; while ((length = fis.read(tmpBytes)) != -1) { fos.write(tmpBytes,0,length); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); fis.close(); fos.close(); System.out.println("拷贝耗时ms:" + (endTime -startTime)); } }
2、字符缓冲流BufferedReader(Reader in);BufferedWriter(Writer out) :
构造方法:
- public BufferedReader(Reader in) :创建一个新的缓冲输入流。
- public BufferedWriter(Writer out) : 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
看它们具备的特有方法:
- BufferedReader: public String readLine() : 读一行文字。读到最后一行返回null。
- BufferedWriter: public void newLine() : 写一行行分隔符,由系统属性定义符号。
练习:打乱的诗词排序
1->独立寒秋,湘江北去,橘子洲头。 2->看万山红遍,层林尽染; 3->漫江碧透,百舸争流。 4->鹰击长空,鱼翔浅底, 5->万类霜天竞自由。
使用treeSet 对诗词语句排序:
import java.io.*; import java.sql.SQLOutput; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.TreeSet; /** * @ClassName TextCopyTryCatchExample * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/18. */ public class TextCopyTryCatchExample { public static void main(String[] args){ String srcpath = "输入输出文件读写/src/test/output/沁园春雪-长沙.txt"; String dstpath = "输入输出文件读写/src/test/output/沁园春雪-长沙-sort.txt"; try (BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcpath)); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dstpath))) { String tmpStringLine ; //存放临时的每行文本 Map<Integer,String> tmpMap = new HashMap<>(); //存放诗词语句和顺序序号的对应 TreeSet<Integer> indexSet = new TreeSet(); //对数字排序 while ((tmpStringLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ String[] tmpLineArr = tmpStringLine.split("->"); int indexKey = Integer.parseInt(tmpLineArr[0]); indexSet.add(indexKey); //TreeSet 集合插入元素按数字大小进行自动排序1,2,3... tmpMap.put(indexKey,tmpLineArr[1]); //Map集合 } //按顺序遍历,写入到新文件 for(Integer index : indexSet){ System.out.println(index); bufferedWriter.write(index + "->" + tmpMap.get(index)); bufferedWriter.newLine(); } }catch (FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e ){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { } } }
排序需求其实可以不用TreeSet也行。
HashMap具体的数据要存放在某个位置,是不是通过key的hashCode()来计算的。其实,HashMap会根据这个key的hashCode来对我们的数据进行排序。为什么HashMap的key又是无序的,这个是因为hashCode是通过对应的变量在内存里面的地址计算出来。但是Integer的hashCode就是它自己。所以说,我们加入了Integer的key之后,HashMap会通过key从小到大给我们排序。
import java.io.*; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** * @ClassName TextCopyHashMap * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/18. */ public class TextCopyBufferWriterHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { String srcPath = "输入输出文件读写/src/test/output/沁园春雪-长沙.txt"; String dstPath = "输入输出文件读写/src/test/output/沁园春雪-长沙-HashMapSort.txt"; try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcPath)); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dstPath))) { String tmpLine ; Map<Integer,String> textMap = new HashMap<>(); while ((tmpLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ String[] tmpLineArr = tmpLine.split("->"); Integer lineIndex = Integer.parseInt(tmpLineArr[0]); textMap.put(lineIndex,tmpLineArr[1]); } System.out.println(textMap); //{1=独立寒秋,湘江北去,橘子洲头。, 2=看万山红遍,层林尽染;, 3=漫江碧透,百舸争流。, 4=鹰击长空,鱼翔浅底,, 5=万类霜天竞自由。} for(Integer index : textMap.keySet()){ bufferedWriter.write(textMap.get(index)); bufferedWriter.newLine(); } /** * 独立寒秋,湘江北去,橘子洲头。 * 看万山红遍,层林尽染; * 漫江碧透,百舸争流。 * 鹰击长空,鱼翔浅底, * 万类霜天竞自由。 */ //复习Map.entrySet() 取值 Set entrySet = textMap.entrySet(); for(Object o : entrySet){ Map.Entry<Integer,String> a = (Map.Entry<Integer,String>)o; System.out.println(a.getKey() + a.getValue()); /** * 1独立寒秋,湘江北去,橘子洲头。 * 2看万山红遍,层林尽染; * 3漫江碧透,百舸争流。 * 4鹰击长空,鱼翔浅底, * 5万类霜天竞自由。 */ } }catch (FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }