当系统中有多个进程到时候,哪个进程先执行,哪个进程后执行是由进程的优先级决定的。进程的优先级是由nice值决定的、nice值越小,优先级越高。可以看做越友好那么调度优先级越低。进程可以通过nice函数获取更改它的nice值,进程只能影响自己的nice值,不能影响其他进程的nice值
#include <unistd.h>
int nice(int incr)
incr参数被增加到调用进程的nice值上,如果nice值太大,系统直接将它降到最大合法值。
可以通过nice命令来查看系统的默认nice值。一般都是为0
root@zhf-maple:/home/zhf/桌面# nice
0
使用ps -l也可以查看当前进程的nice值。NI就是nice值
root@zhf-maple:/home/zhf/桌面# ps -l
F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD
4 S 0 6678 6668 0 80 0 - 15612 wait pts/0 00:00:00 su
4 S 0 6679 6678 0 80 0 - 5850 wait pts/0 00:00:00 bash
4 R 0 6900 6679 0 80 0 - 8809 - pts/0 00:00:00 p
下面的这个程序我们通过改变2个并行运行进程的nice值,运行程序10秒,期间对各个进程进行计数。最后统计进程的计数值
unsigned long long count; #设置全局变量进行进程的计数
struct timeval end;
#checktime判断进程的运行时间
void checktime(char *str){
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
if (tv.tv_sec > end.tv_sec && tv.tv_sec >= end.tv_usec){
printf("%s count =%lld ",str,count);
exit(0);
}
}
void schedule_try(){
pid_t pid;
char *s;
int adj=0;
int ret;
int nzero=20;
gettimeofday(&end,NULL);
end.tv_sec+=10;
if((pid=fork()) == 0){
s="child";
printf("current nice value in child is %d,adjusting by %d ",nice(0)+nzero,adj);
ret=nice(adj);
printf("now child nice value is %d ",ret+nzero);
}
else{
s="parent";
printf("current nice value in parent is %d ",nice(0)+nzero);
}
for(;;){
if (++count == 0)
printf("error occured");
checktime(s);
}
}
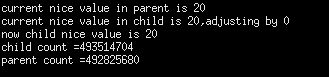
首先设置adj也就是nice值的调整量为0.此时父子进程的nice值都为20.
运行结果如下:可以看到由于父子进程的nice都为20.因此在10秒内父子进程的计算基本上差不多。可以认为父子进程占用了相同的CPU资源。
除了nice函数,我们还可以通过getpriority/setpriority函数来获取和设置进程的优先级
#include <sys/resource.h>
int getpriority(int which, int who);
int setpriority(int which,int who,int value);
1、PRIO_PROCESS,一个特定的进程,此时who的取值为进程ID
2、PRIO_PGRP,一个进程组的所有进程,此时who的取值为进程组的ID
3、PRIO_USER,一个用户拥有的所有进程,此时who的取值为实际用户ID
getpriority的用法:
void schedule_try2(){
pid_t pid;
int prio;
pid=fork();
if (pid == 0){
prio=getpriority(PRIO_PROCESS,getpid());
printf("The priority of child is %d ",prio);
}
}
所以nice函数也可以用getpriority和setpriority来实现
int nice( int increment)
{
int oldprio = getpriority( PRIO_PROCESS, getpid());
return setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, getpid(), oldprio + increment);
}