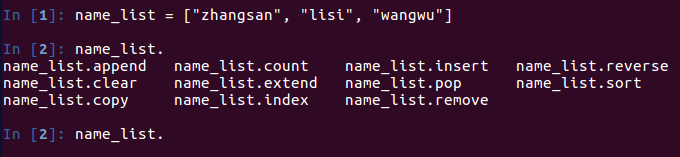
列表的定义
- 列表的取值操作:list[index]、list.index(obj)
# 1. 取值和取索引 # 取值 print(name_list[1]) # 取索引 print(name_list.index("lisi"))
- 列表的添加操作的方法有:list.insert、list.append、list.extend
# 2. 增加操作 # 向列表末尾追加数据 name_list.append("zhangfengxian") # 向指定索引插入数据 name_list.insert(1, "zq") # 把其他列表的数据追加到末尾 temp_list = ["Jake", "Rory", "Rose"] name_list.extend(temp_list)
- 列表的修改操作:list[index] = xxxx
# 3. 修改 name_list[0] = "pipi"
- 列表的删除操作:list.remove、list.pop、list.clear
# 4. 删除 # 删除指定的数据 name_list.remove("wangwu") # 删除末尾的数据 name_list.pop() # 删除指定位置的数据 name_list.pop(1) # 清楚所有数据 name_list.clear()
del关键同样也可以删除列表中的数据,它还是删除某一个定义的变量:
name_list = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu"] # del删除列表中的数据 del name_list[1] name = "wangsan" # 删除name这个变量 del name # 后续使用name这个变量会报错:NameError: name 'name' is not defined print(name) print(name_list)
- 列表的统计:len,list.count
# 5. 统计 name_list = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu", "lisi"] # 列表的长度 print("列表的长度为:%d" % len(name_list)) # 数据在列表中出现的次数 print("lisi出现的次数为:%d" % name_list.count("lisi"))
- 列表排序:list.sort、list.reverse
name_list = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu"] num_list = [11, 2, 5, 66, 12, 3] # 升序 # name_list.sort() # num_list.sort() # 降序 # name_list.sort(reverse=True) # num_list.sort(reverse=True) # 反转 name_list.reverse() num_list.reverse() print(name_list) print(num_list)
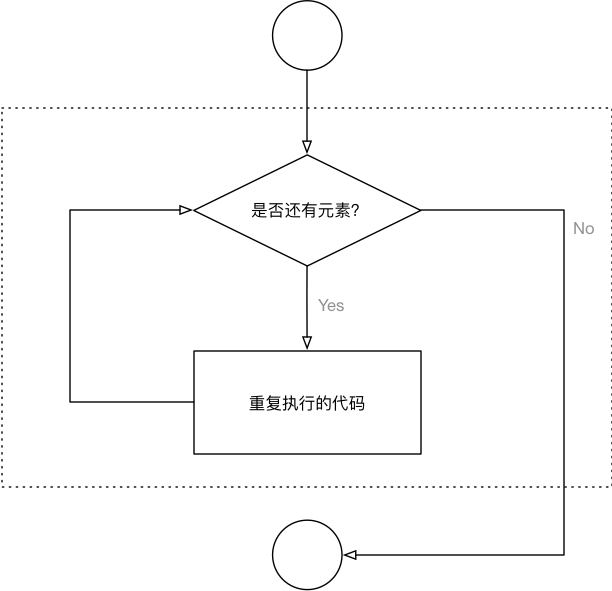
循环遍历
-
-
遍历列表的简单例子如下:
name_list = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu"] for name in name_list: print("My name is %s" % name)
--本文完--