(一)Spring IOC容器---对象循环依赖
1. 什么是循环依赖? what?
(1)循环依赖-->循环引用。--->即2个或以上bean 互相持有对方,最终形成闭环。
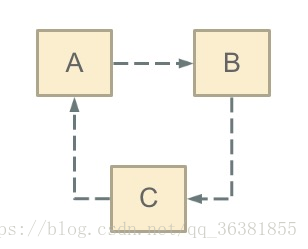
eg:A依赖B,B依赖C,C又依赖A。【注意:这里不是函数的循环调用【是个死循环,除非有终结条件】,是对象相互依赖关系】
2. Spring中循环依赖的场景?where?
①:构造器的循环依赖。【这个Spring解决不了】
StudentA有参构造是StudentB。StudentB的有参构造是StudentC,StudentC的有参构造是StudentA ,这样就产生了一个循环依赖的情况,
我们都把这三个Bean交给Spring管理,并用有参构造实例化
public class StudentA {
private StudentB studentB ;
public void setStudentB(StudentB studentB) {
this.studentB = studentB;
}
public StudentA() {
}
public StudentA(StudentB studentB) {
this.studentB = studentB;
}
}
public class StudentB {
private StudentC studentC ;
public void setStudentC(StudentC studentC) {
this.studentC = studentC;
}
public StudentB() {
}
public StudentB(StudentC studentC) {
this.studentC = studentC;
}
}
public class StudentC {
private StudentA studentA ;
public void setStudentA(StudentA studentA) {
this.studentA = studentA;
}
public StudentC() {
}
public StudentC(StudentA studentA) {
this.studentA = studentA;
}
}
<bean id="a" class="com.zfx.student.StudentA">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="b"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="com.zfx.student.StudentB">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="c"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="c" class="com.zfx.student.StudentC">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="a"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
下面是测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/zfx/student/applicationContext.xml");
//System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class));
}
}
执行结果报错信息为:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'a': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
②【setter循环依赖】field属性的循环依赖【setter方式 单例,默认方式-->通过递归方法找出当前Bean所依赖的Bean,然后提前缓存【会放入Cach中】起来。通过提前暴露 -->暴露一个exposedObject用于返回提前暴露的Bean。】
setter方式注入:
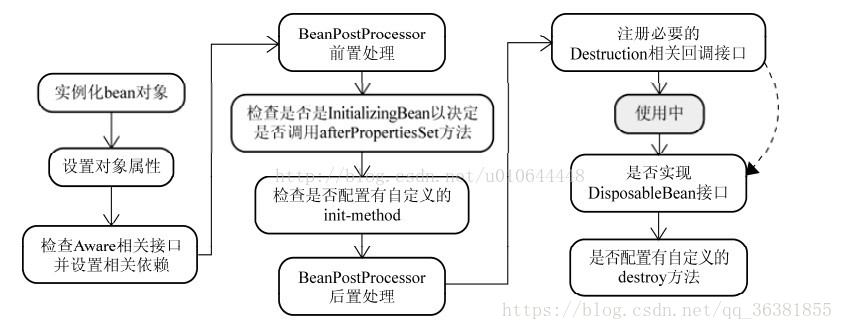
图中前两步骤得知:Spring是先将Bean对象实例化【依赖无参构造函数】--->再设置对象属性的
这就不会报错了:
原因:Spring先用构造器实例化Bean对象----->将实例化结束的对象放到一个Map中,并且Spring提供获取这个未设置属性的实例化对象的引用方法。结合我们的实例来看,,当Spring实例化了StudentA、StudentB、StudentC后,紧接着会去设置对象的属性,此时StudentA依赖StudentB,就会去Map中取出存在里面的单例StudentB对象,以此类推,不会出来循环的问题喽。
3. 如何检测是否有循环依赖?how to find?
可以 Bean在创建的时候给其打个标记,如果递归调用回来发现正在创建中的话--->即可说明循环依赖。
4.怎么解决的? todo what?
Spring的循环依赖的理论依据其实是基于Java的引用传递,当我们获取到对象的引用时,对象的field或zh属性是可以延后设置的(但是构造器必须是在获取引用之前)。
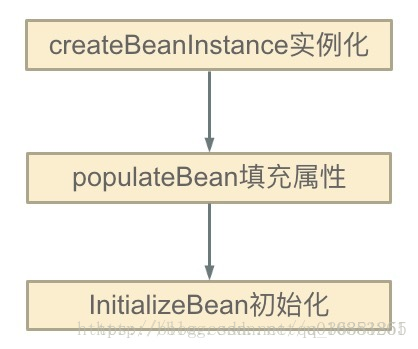
Spring的单例对象的初始化主要分为三步:
①:createBeanInstance:实例化,其实也就是 调用对象的构造方法实例化对象
②:populateBean:填充属性,这一步主要是多bean的依赖属性进行填充
③:initializeBean:调用spring xml中的init() 方法。
从上面讲述的单例bean初始化步骤我们可以知道,循环依赖主要发生在第一、第二步。也就是构造器循环依赖和field循环依赖。
那么我们要解决循环引用也应该从初始化过程着手,对于单例来说,在Spring容器整个生命周期内,有且只有一个对象,所以很容易想到这个对象应该存在Cache中,Spring为了解决单例的循环依赖问题,使用了三级缓存。
调整配置文件,将构造函数注入方式改为 属性注入方式 即可
3.源码怎么实现的? how?
(1)三级缓存源码主要 指:
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */ private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256); /** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */ private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<String, ObjectFactory<?>>(16); /** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */ private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>(16);
这三级缓存分别指:
singletonFactories : 单例对象工厂的cache
earlySingletonObjects :提前暴光的单例对象的Cache 。【用于检测循环引用,与singletonFactories互斥】
singletonObjects:单例对象的cache
我们在创建bean的时候,首先想到的是从cache中获取这个单例的bean,这个缓存就是singletonObjects。主要调用方法就就是:
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
上面的代码需要解释两个参数:
- isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation()判断当前单例bean是否正在创建中,也就是没有初始化完成(比如A的构造器依赖了B对象所以得先去创建B对象, 或则在A的populateBean过程中依赖了B对象,得先去创建B对象,这时的A就是处于创建中的状态。)
- allowEarlyReference 是否允许从singletonFactories中通过getObject拿到对象
分析getSingleton()的整个过程,Spring首先从一级缓存singletonObjects中获取。如果获取不到,并且对象正在创建中,就再从二级缓存earlySingletonObjects中获取。如果还是获取不到且允许singletonFactories通过getObject()获取,就从三级缓存singletonFactory.getObject()(三级缓存)获取,如果获取到了则:
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
从singletonFactories中移除,并放入earlySingletonObjects中。其实也就是从三级缓存移动到了二级缓存。
从上面三级缓存的分析,我们可以知道,Spring解决循环依赖的诀窍就在于singletonFactories这个三级cache。这个cache的类型是ObjectFactory,定义如下:
public interface ObjectFactory<T> {
T getObject() throws BeansException;
}
这个接口在下面被引用
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
这里就是解决循环依赖的关键,这段代码发生在createBeanInstance之后,也就是说单例对象此时已经被创建出来(调用了构造器)。这个对象已经被生产出来了,虽然还不完美(还没有进行初始化的第二步和第三步),但是已经能被人认出来了(根据对象引用能定位到堆中的对象),所以Spring此时将这个对象提前曝光出来让大家认识,让大家使用。
这样做有什么好处呢?让我们来分析一下“A的某个field或者setter依赖了B的实例对象,同时B的某个field或者setter依赖了A的实例对象”这种循环依赖的情况。A首先完成了初始化的第一步,并且将自己提前曝光到singletonFactories中,此时进行初始化的第二步,发现自己依赖对象B,此时就尝试去get(B),发现B还没有被create,所以走create流程,B在初始化第一步的时候发现自己依赖了对象A,于是尝试get(A),尝试一级缓存singletonObjects(肯定没有,因为A还没初始化完全),尝试二级缓存earlySingletonObjects(也没有),尝试三级缓存singletonFactories,由于A通过ObjectFactory将自己提前曝光了,所以B能够通过ObjectFactory.getObject拿到A对象(虽然A还没有初始化完全,但是总比没有好呀),B拿到A对象后顺利完成了初始化阶段1、2、3,完全初始化之后将自己放入到一级缓存singletonObjects中。此时返回A中,A此时能拿到B的对象顺利完成自己的初始化阶段2、3,最终A也完成了初始化,进去了一级缓存singletonObjects中,而且更加幸运的是,由于B拿到了A的对象引用,所以B现在hold住的A对象完成了初始化。
知道了这个原理时候,肯定就知道为啥Spring不能解决“A的构造方法中依赖了B的实例对象,同时B的构造方法中依赖了A的实例对象”这类问题了!因为加入singletonFactories三级缓存的前提是执行了构造器,所以构造器的循环依赖没法解决
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36381855/article/details/79752689 https://blog.csdn.net/u010644448/article/details/59108799#