一、前言
大多数的情况下,只要不涉及线程安全问题,map都可以使用hashMap,不过hashMap有一个问题,hashMap的迭代顺序不是hashMap的存储顺序,即hashMap中的元素是无序的。但是有些场景下,我们需要使用一个有序的map。这种情况下,我们就需要使用linkedHashMap,它虽然增加了时间和空间上的开销,但是通过维护一个运行于所有条目的双向链表,linkedHashMap保证了元素的迭代顺序。
四个关注点在linkedHashMap上的答案
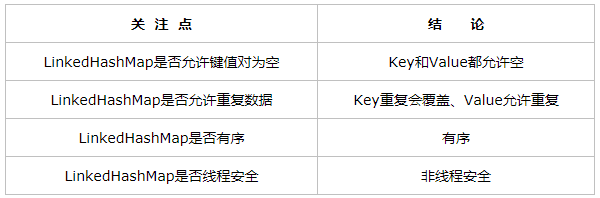
二、linkedHashMap的数据结构
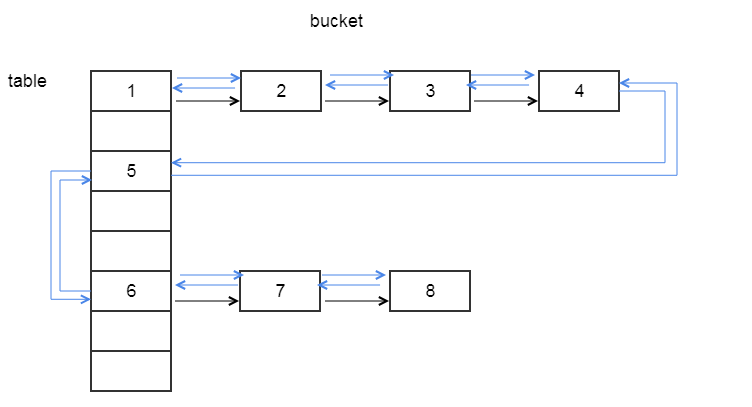
说明:上图说明了linkedHashMap的数据结构,和hashMap一样,linkedHashMap也使用了数组+链表(单向链表)+红黑树的方式来存储元素,所不同的是,因为需要维护元素的存储顺序,linkedHashMap还使用了双向链表来将前后元素串起来。所以linkedHashMap的数据结构为:数组+单向链表+红黑树+双向链表。
三、linkedHashMap源码分析-属性及构造函数
3.1 类的继承关系
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>extends HashMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>
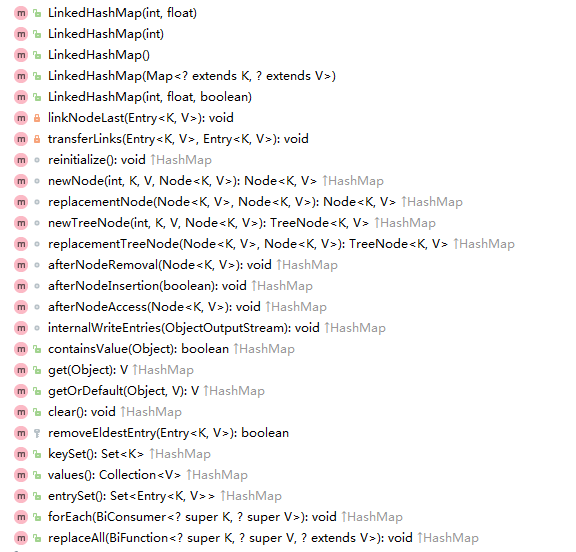
说明:linkedHashMap继承自hashMap,所以hashMap中非私有的属性和方法,linkedHashMap都可以使用,而且从下图linkedHashMap的方法中可以看出,linkedHashMap中并没有直接操作数据结构的方法(比如对元素的增删改查的函数,除了get函数),其对元素的增删改查等操作都是基于其父类hashMap中的方法,所不同的只是细节上的实现有所区别罢了。
linkedHashMap中的方法:
3.2 类的属性
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> { static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } } // 版本序列号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L; // 链表头结点 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; // 链表尾结点 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; // 访问顺序 final boolean accessOrder; }
说明:其中静态内部类Entry就是存储元素的地方,类似于hashMap中的Node,只是多了个before,after属性用于维护双向链表。accessOrder为true的时候,linkedHashMap中的元素是以访问的顺序存储,accessOrder为false的时候,linkedHashMap中的元素是以插入的顺序存储,一般我们使用的都是accessOrder为false的情况,即元素以插入的顺序排序,关于accessOrder为true的用法下面会提到。
3.3 类的构造函数
1、LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)型
/** * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance * with the specified initial capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); accessOrder = false; }
说明:调用父类hashMap中对应的构造方法,并将accessOrder置为false,通过指定的初始容量和加载因子实例化一个空的、以插入顺序来存储的linkedHashMap。
2、LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity)型
/** * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance * with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative */ public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) { super(initialCapacity); accessOrder = false; }
说明:调用父类hashMap中对应的构造方法,并将accessOrder置为false,通过指定的初始容量和默认的加载因子实例化一个空的、以插入顺序来存储的linkedHashMap。
3、LinkedHashMap()型
/** * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance * with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public LinkedHashMap() { super(); accessOrder = false; }
说明:调用父类hashMap中对应的构造方法,并将accessOrder置为false,通过默认的初始容量和加载因子实例化一个空的、以插入顺序来存储的linkedHashMap。
4、LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)型
/** * Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with * the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> * instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial * capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map. * * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { super(); accessOrder = false; putMapEntries(m, false); }
说明:调用父类hashMap中对应的构造方法,并将accessOrder置为false,通过默认的初始容量和加载因子实例化一个以插入顺序来存储的linkedHashMap(已存储参数map中的元素)。
5、LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder)型
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the * specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for * access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); this.accessOrder = accessOrder; }
说明:调用父类hashMap中对应的构造方法,并将accessOrder置为true或false,通过指定的初始容量、指定的加载因子、指定的accessOrder实例化一个空的linkedHashMap。
四、linkedHashMap源码分析-核心函数
linkedHashMap对元素的增删改查等操作大多基于其父类hashMap中的方法,只是实现的细节有所不同,而linkedHashMap所做的是维护元素的插入顺序(双向链表)。
4.1 增:put和putVal函数----存储元素
所使用的是hashMap中的put和putVal函数
1 /** 2 * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. 3 * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old 4 * value is replaced. 5 * 6 * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated 7 * @param value value to be associated with the specified key 8 * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or 9 * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. 10 * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map 11 * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) 12 */ 13 public V put(K key, V value) { 14 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 15 }
但是在putVal中的实现有所不同
1 /** 2 * Implements Map.put and related methods 3 * 4 * @param hash hash for key 5 * @param key the key 6 * @param value the value to put 7 * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value 8 * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. 9 * @return previous value, or null if none 10 */ 11 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 12 boolean evict) { 13 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 14 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 15 n = (tab = resize()).length; 16 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 17 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 18 else { 19 Node<K,V> e; K k; 20 if (p.hash == hash && 21 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 22 e = p; 23 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 24 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 25 else { 26 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 27 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 28 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 29 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 30 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 31 break; 32 } 33 if (e.hash == hash && 34 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 35 break; 36 p = e; 37 } 38 } 39 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 40 V oldValue = e.value; 41 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 42 e.value = value; 43 afterNodeAccess(e); 44 return oldValue; 45 } 46 } 47 ++modCount; 48 if (++size > threshold) 49 resize(); 50 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 51 return null; 52 }
说明1:注意位于第17、28行的newNode方法,因为linkedHashMap中重写了这个方法,所以在虽然存储元素用的是hashMap中的putVal方法,但到newNode时调用的是linkedHashMap的newNode方法,这是多态的概念。
linkedHashMap中的newNode方法:
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); linkNodeLast(p); return p; }
linkNodeLast方法:维护确保元素存储顺序的双向链表:
// link at the end of list private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail; tail = p; if (last == null) head = p; else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } }
其中LinkedHashMap.Entry继承自HashMap.Node,在HashMap.Node基础上增加了前后两个指针域,注意,HashMap.Node中的next域也存在。
/** * HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries. */ static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } }
同理,newTreeNode也一样,调用的是linkedHashMap中的newTreeNode方法
TreeNode<K,V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(hash, key, value, next); linkNodeLast(p); return p; }
说明2:注意位于第43、50行的afterNodeAccess和afterNodeInsertion,因为linkedHashMap中重写了这两个方法,所以实际中调动的是linkedHashMap中的这两个方法,和上述的newNode一样,也是多态的概念。
afterNodeAccess:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last; if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.after = null; if (b == null) head = a; else b.after = a; if (a != null) a.before = b; else last = b; if (last == null) head = p; else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } tail = p; ++modCount; } }
说明:此函数在很多函数(如put时key已经存在,get等)中都会被回调,若访问顺序为true,且访问的对象不是尾结点,则下面的图展示了访问前和访问后的状态,假设访问的结点为结点3
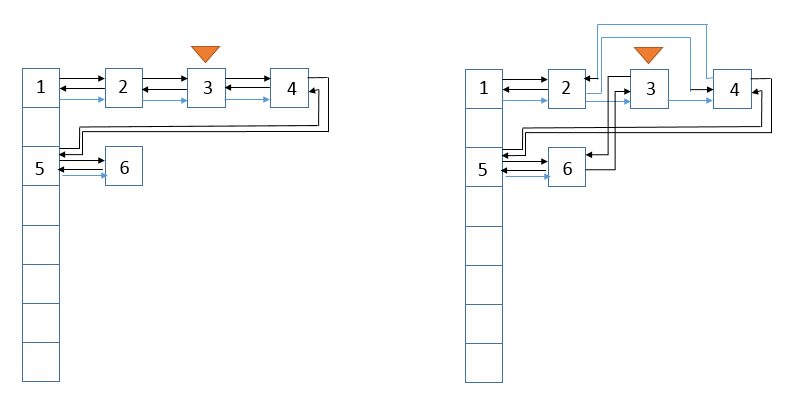
说明:从图中可以看到,结点3链接到了双向链表原尾结点后面,变成了新的尾节点。
afterNodeInsertion:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first; if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { K key = first.key; removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true); } }
removeEldestEntry:
1 /** 2 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map should remove its eldest entry. 3 * This method is invoked by <tt>put</tt> and <tt>putAll</tt> after 4 * inserting a new entry into the map. It provides the implementor 5 * with the opportunity to remove the eldest entry each time a new one 6 * is added. This is useful if the map represents a cache: it allows 7 * the map to reduce memory consumption by deleting stale entries. 8 * 9 * <p>Sample use: this override will allow the map to grow up to 100 10 * entries and then delete the eldest entry each time a new entry is 11 * added, maintaining a steady state of 100 entries. 12 * <pre> 13 * private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 100; 14 * 15 * protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) { 16 * return size() > MAX_ENTRIES; 17 * } 18 * </pre> 19 * 20 * <p>This method typically does not modify the map in any way, 21 * instead allowing the map to modify itself as directed by its 22 * return value. It <i>is</i> permitted for this method to modify 23 * the map directly, but if it does so, it <i>must</i> return 24 * <tt>false</tt> (indicating that the map should not attempt any 25 * further modification). The effects of returning <tt>true</tt> 26 * after modifying the map from within this method are unspecified. 27 * 28 * <p>This implementation merely returns <tt>false</tt> (so that this 29 * map acts like a normal map - the eldest element is never removed). 30 * 31 * @param eldest The least recently inserted entry in the map, or if 32 * this is an access-ordered map, the least recently accessed 33 * entry. This is the entry that will be removed it this 34 * method returns <tt>true</tt>. If the map was empty prior 35 * to the <tt>put</tt> or <tt>putAll</tt> invocation resulting 36 * in this invocation, this will be the entry that was just 37 * inserted; in other words, if the map contains a single 38 * entry, the eldest entry is also the newest. 39 * @return <tt>true</tt> if the eldest entry should be removed 40 * from the map; <tt>false</tt> if it should be retained. 41 */ 42 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) { 43 return false; 44 }
说一下这个方法的使用:
afterNodeInsertion方法会在使用put和putAll方法的时候被调用。removeEldestEntry()方法返回true会删除map中的eldest entry(accessOrder为false:least recently inserted entry,accessOrder为true:least recently accessed entry),返回false不做任何操作。
该方法给其子类定义了一个功能:返回true,每次有元素被added的时候,都会remove the eldest entry。这在linkedHashMap被用作缓存的时候是有用的,可以减少内存的消耗,不会无限制的存储元素。
注释中也给了一个linkedHashMap用作缓存的例子:linkedHashMap只存储100个元素,当超过100个元素的时候,就会进行remove。
无特别定义的情况下,afterNodeAccess(accessOrder为true)和afterNodeInsertion(重写该方法,返回true值)都不会执行里面的操作。所以linkedHashMap中存储元素时和hashMap是一样的,只是多了一个维护元素顺序的双向链表。
4.2 删:remove和removeNode函数----删除元素
所使用的是hashMap中的remove和removeNode函数
/** * Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present. * * @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */ public V remove(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value; }
removeNode方法
1 /** 2 * Implements Map.remove and related methods 3 * 4 * @param hash hash for key 5 * @param key the key 6 * @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored 7 * @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal 8 * @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing 9 * @return the node, or null if none 10 */ 11 final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, 12 boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { 13 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; 14 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 15 (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 16 Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; 17 if (p.hash == hash && 18 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 19 node = p; 20 else if ((e = p.next) != null) { 21 if (p instanceof TreeNode) 22 node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); 23 else { 24 do { 25 if (e.hash == hash && 26 ((k = e.key) == key || 27 (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { 28 node = e; 29 break; 30 } 31 p = e; 32 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 33 } 34 } 35 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || 36 (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { 37 if (node instanceof TreeNode) 38 ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); 39 else if (node == p) 40 tab[index] = node.next; 41 else 42 p.next = node.next; 43 ++modCount; 44 --size; 45 afterNodeRemoval(node); 46 return node; 47 } 48 } 49 return null; 50 }
注意第45行的afterNodeRemoval方法,该方法在linkedHashMap中被重写,所以实际调用的是linkedHashMap中的afterNodeRemoval方法
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.before = p.after = null; if (b == null) head = a; else b.after = a; if (a == null) tail = b; else a.before = b; }
说明:该方法就是重新维护双向链表中元素的前后联系。
4.3 改:putVal函数----修改元素
详见4.1,与添加元素是同一个操作。
4.4 查:get和getNode方法----查找元素
linkedHashMap中重写了get方法,但其中的getNod方法使用的还是hashMap中的getNode方法
/** * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : * key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise * it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> * indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also * possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. * The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to * distinguish these two cases. */ public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null) return null; if (accessOrder) afterNodeAccess(e); return e.value; }
与hashMap中的get方法不同的是,linkedHashMap中根据accessOrder的真假来调用afterNodeAccess方法,为true,get查询元素的时候就会重新进行双向链表的维护,将最近一次访问的元素置于双向链表的尾部,为false,不做下一步操作。参见4.1中的afterNodeAccess方法。
举例(accessOrder为true):
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedHashMap<String,String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(16,0.75f,true); linkedHashMap.put("111","111"); linkedHashMap.put("222","222"); linkedHashMap.put("333","333"); linkedHashMap.put("444","444"); System.out.println("未进行访问之前=========" + linkedHashMap); linkedHashMap.get("222"); System.out.println("进行访问之后===========" + linkedHashMap); } }
结果:
未进行访问之前========={111=111, 222=222, 333=333, 444=444}
进行访问之后==========={111=111, 333=333, 444=444, 222=222}
4.5 containsValue函数----map是否存在该value
/** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the * specified value. * * @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the * specified value */ public boolean containsValue(Object value) { for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) { V v = e.value; if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v))) return true; } return false; }
说明:containsValue函数根据双链表结构来查找是否包含value,是按照插入顺序进行查找的,与HashMap中的此函数查找方式不同,HashMap是使用按照桶遍历,没有考虑插入顺序。
hashMap中的containsValue函数
/** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the * specified value. * * @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the * specified value */ public boolean containsValue(Object value) { Node<K,V>[] tab; V v; if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) { for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { if ((v = e.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v))) return true; } } } return false; }
五、总结
总得来看,LinkedHashMap的实现就是HashMap+LinkedList的实现方式,以HashMap维护数据结构,以LinkList的方式维护数据插入顺序。
最后说一下利用linkedHashMap实现LRUCache(LRU算法缓存)
LRUCache源码如下:
public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private final int maxSize; public LRUCache(int maxSize){ this(maxSize, 16, 0.75f, false); } public LRUCache(int maxSize, int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder){ super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, accessOrder); this.maxSize = maxSize; } protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) { return this.size() > this.maxSize; } }
顾名思义,LRUCache就是基于LRU算法的Cache(缓存),这个类继承自LinkedHashMap,而类中看到没有什么特别的方法,这说明LRUCache实现缓存功能都是源自LinkedHashMap的。LinkedHashMap可以实现LRU算法的缓存基于两点:
1、LinkedList首先它是一个Map,Map是基于K-V的,和缓存一致
2、LinkedList提供了一个boolean值可以让用户指定是否实现LRU
那么,首先我们了解一下什么是LRU:LRU即Least Recently Used,最近最少使用,也就是说,当缓存满了,会优先淘汰那些最近最不常访问的数据。比方说数据a,1天前访问了;数据b,2天前访问了,缓存满了,优先会淘汰数据b。
上述linkedHashMap的构造函数中有个带布尔值的:
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); this.accessOrder = accessOrder; }
这个accessOrder,它表示:
(1)false,所有的Entry按照插入的顺序排列
(2)true,所有的Entry按照访问的顺序排列
第二点的意思就是,如果有1 2 3这3个Entry,那么访问了1,就把1移到尾部去,即2 3 1。每次访问都把访问的那个数据移到双向队列的尾部去,那么每次要淘汰数据的时候,双向队列最头的那个数据不就是最不常访问的那个数据了吗?换句话说,双向链表最头的那个数据就是要淘汰的数据。
"访问",这个词有两层意思:
1、根据Key拿到Value,也就是get方法
2、修改Key对应的Value,也就是put方法
根据linkedHashMap的源码也可以看到,在调用get方法和put方法的时候,都会调用afterNodeAccess方法,accessOrder为true就会重新进行元素的排序。
至于如何淘汰掉最近最少使用的元素,当我们在linkedHashMap中增加元素(put)的时候,都会调用afterNodeInsertion函数,当我们重写afterNodeInsertion函数中的removeEldestEntry函数并返回true时,就会进行删除最近最少使用的元素了。
举例说明:
public class LRULinkedHashMap { //定义缓存的容量 private int cacheSize; private LinkedHashMap<String,String> cacheMap; public LRULinkedHashMap(int cacheSize){ this.cacheSize = cacheSize; cacheMap = new LinkedHashMap(16, 0.75F, true){ //重写linkedHashMap中的removeEldestEntry方法, @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) { //当linkedHashMap中元素的个数大于缓存的个数时,返回true,删除最近最少使用的元素 if(cacheMap.size() > cacheSize){ return true; }else{ return false; } } }; } public void put(String key, String value){ cacheMap.put(key, value); } public String get(String key){ return cacheMap.get(key); } public Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> getAll(){ return cacheMap.entrySet(); } public static void main(String[] args) { LRULinkedHashMap map = new LRULinkedHashMap(3); map.put("key1", "1"); map.put("key2", "2"); map.put("key3", "3"); for (Map.Entry<String, String> e : map.getAll()){ System.out.println(e.getKey()+"====>"+e.getValue()); } System.out.println(" "); map.get("key2"); for (Map.Entry<String, String> e : map.getAll()){ System.out.println(e.getKey()+"====>"+e.getValue()); } System.out.println(" "); map.put("key4", "4"); for (Map.Entry<String, String> e : map.getAll()){ System.out.println(e.getKey()+"====>"+e.getValue()); } } }
结果:
key1====>1 key2====>2 key3====>3 key1====>1 key3====>3 key2====>2 key3====>3 key2====>2 key4====>4
说明:自定义一个基于linkedHashMap实现的缓存类,缓存容量为3,当添加了三个元素后进行get访问,再put第四个元素,根据结果来看,符合上面的分析。
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/5052323.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/5248868.html