ConditionObject是AQS中的内部类,提供了条件锁的同步实现,实现了Condition接口,并且实现了其中的await(),signal(),signalALL()等方法。
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)的分析点此
ConditionObject主要是为并发编程中的同步提供了等待通知的实现方式,可以在不满足某个条件的时候挂起线程等待。直到满足某个条件的时候在唤醒线程。
使用方式如下:
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition condition = lock.newCondition();//创建和该锁关联的条件锁 public void conditionWait() throws InterruptedException{ lock.lock(); try { condition.await(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void ConditionSignal() throws InterruptedException{ lock.lock(); try { condition.signal(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } }
lock()和unlock()在AQS一文中已经分析过其实现方式了,这里主要分析ConditionObject中的await()和signal()的实现分析。
在一个AQS同步器中,可以定义多个Condition,只需要多次lock.newCondition(),每次都会返回一个新的ConditionObject对象。
在ConditionObject中,通过一个等待队列来维护条线等待的线程。所以在一个同步器中可以有多个等待队列,他们等待的条件是不一样的。
等待队列
等待队列是一个FIFO的队列,在队列的每个节点都包含了一个线程引用。该线程就是在Condition对象上等待的线程。这里的节点和AQS中的同步队列中的节点一样,使用的都是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node类。每个调用了condition.await()的线程都会进入到等待队列中去。
在Condition中包含了firstWaiter和lastWaiter,每次加入到等待队列中的线程都会加入到等待队列的尾部,来构成一个FIFO的等待队列。

下面看看await()方法的具体实现
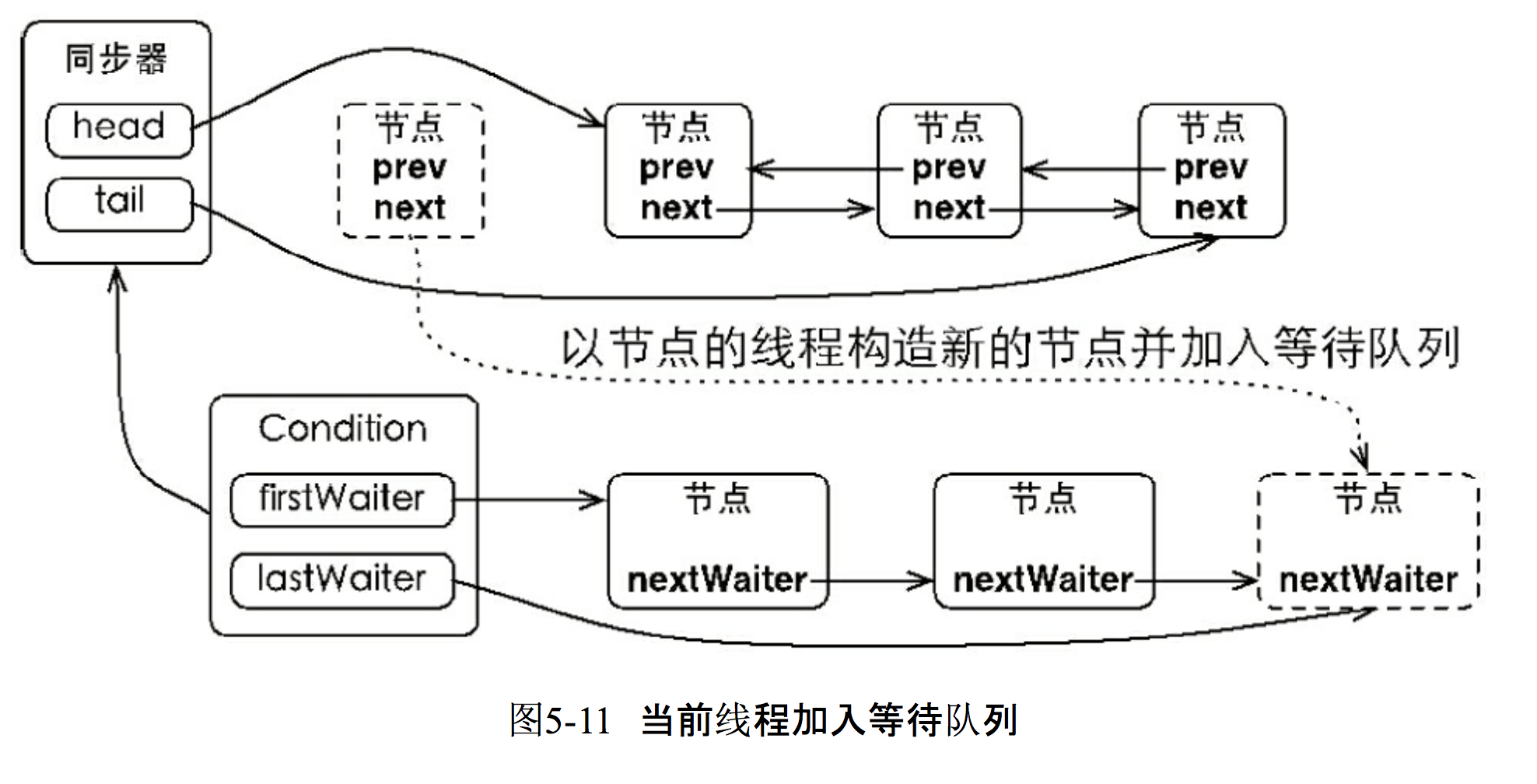
public final void await() throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); //把当前线程的节点加入到等待队列中 int savedState = fullyRelease(node); //由于调用await()方法的线程是已经获取了锁的,所以在加入到等待队列之后,需要去释放锁,并且唤醒后继节点线程 int interruptMode = 0; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this); //挂起当前线程,当别的线程调用了signal(),并且是当前线程被唤醒的时候才从park()方法返回 if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0) break; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) //当被唤醒后,该线程会尝试去获取锁,只有获取到了才会从await()方法返回,否则的话,会挂起自己 interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); }
可以看到这个方法是会响应中断的。
private Node addConditionWaiter() { Node t = lastWaiter; // If lastWaiter is cancelled, clean out. if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { //首先判断lastWaiter节点是否为空,或者是否是处于条件等待,如果不是的话则把它从等待队列中删除。 unlinkCancelledWaiters(); t = lastWaiter; } Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION); if (t == null) //把当前线程构建的节点加入到等待队列中去,并且返回当前节点 firstWaiter = node; else t.nextWaiter = node; lastWaiter = node; return node; }
final int fullyRelease(Node node) { boolean failed = true; try { int savedState = getState(); if (release(savedState)) { failed = false; return savedState; } else { throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); } } finally { if (failed) node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; } }
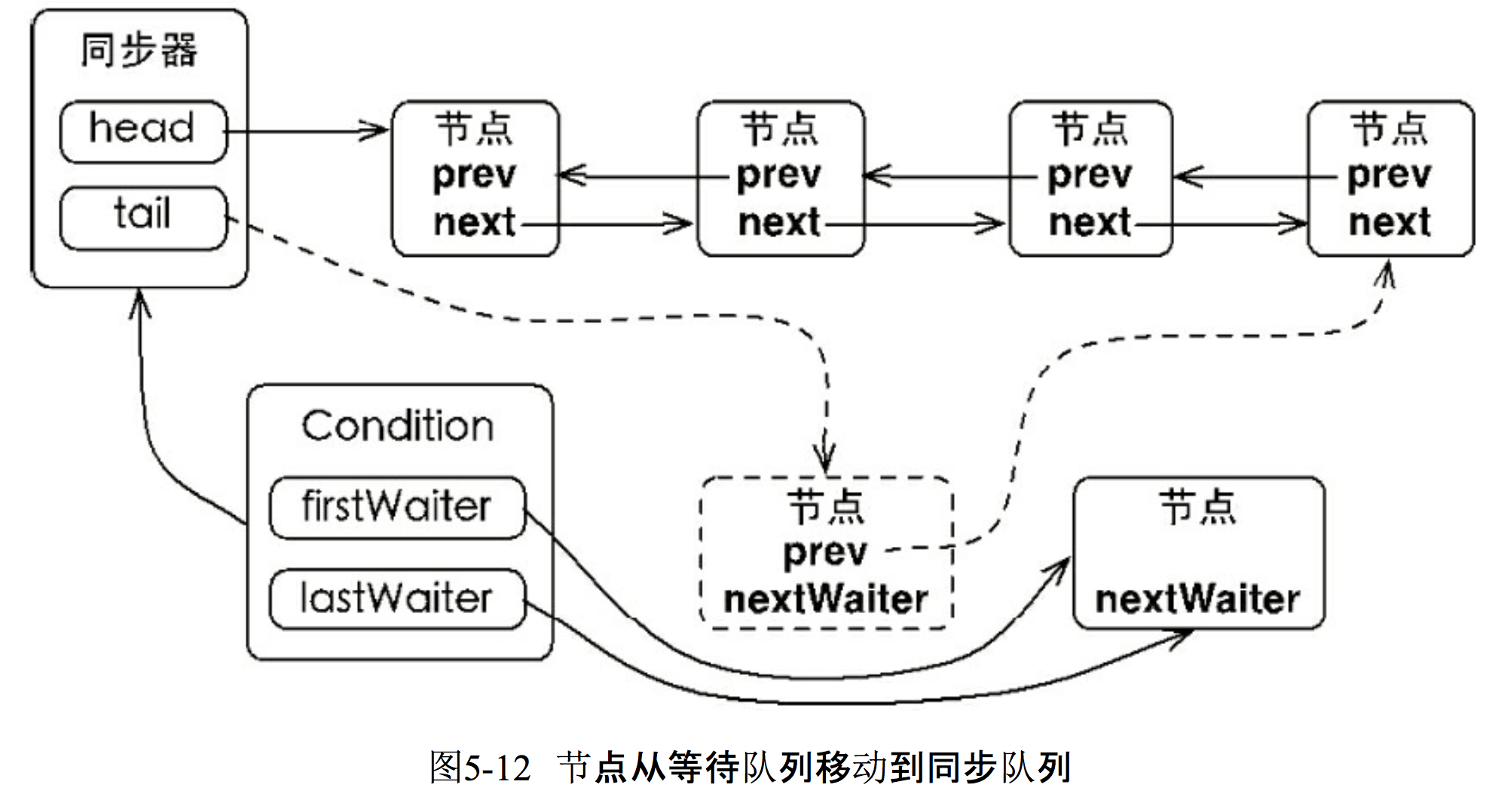
在看看signal()方法的具体实现:
private void doSignal(Node first) { do { if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null) lastWaiter = null; first.nextWaiter = null; } while (!transferForSignal(first) && //从first开始遍历等待队列,把第一个非空、没取消的节点transfer到同步队列 (first = firstWaiter) != null); } public final void signal() { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null) doSignal(first); }
signal()方法首先会判断当前线程是不是独占的持有锁,然后唤醒等待队列中的第一个等待线程。
/** * Transfers a node from a condition queue onto sync queue. * Returns true if successful. * @param node the node * @return true if successfully transferred (else the node was * cancelled before signal) */ final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) { /* * If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled. */ if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) return false; /* * Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to * indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or * attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which * case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong). */ Node p = enq(node); //返回的是node的前一个节点 int ws = p.waitStatus; if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL)) LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); //唤醒刚加入到同步队列的线程,被唤醒之后,该线程才能从await()方法的park()中返回。 return true; }