本节介绍软件光栅器的OBJ和MTL文件加载,转载请注明出处。
在管线的应用程序阶段,我们需要设置光栅器所渲染的模型数据。这些模型数据包括模型顶点的坐标、纹理、法线和材质等等,可以由我们手动编写,也可以通过文件读取。OBJ文件就是一种常用的存储模型数据的文件格式,它内部包含有所有渲染所需的信息。
比如:
mtllib myteapot.mtl 表示模型的材质文件名
v 7.0000 12.0000 -0.0000 顶点位置
vn 0.9667 -0.2557 0.0105 法线向量
vt 0.5000 1.9000 0.0000 纹理坐标
f 1/1/1 2/2/2 3/3/3 f开头的行,表示一个三角面的三个顶点信息索引值,比如1/1/1表示顶点索引1的点,法线信息取vn的第1个,纹理信息取vt的第1个。
在模型加载时调用相关方法,从设定的路径读取obj文件即可:
GeometryGenerator::GetInstance()->LoadOBJModel(m_box, "Models/myteapot.obj"); //从obj文件加载茶壶模型 Models/myteapot.obj Models/probeColor.obj
其中m_box为自定义的网格数据结构GeometryGenerator::MeshData* :
class GeometryGenerator { private: GeometryGenerator() {} public: static GeometryGenerator* GetInstance()//饿汉 { static GeometryGenerator instance; return &instance; } //基本网络结构:顶点集合+索引集合 struct MeshData { std::vector<VertexIn> vertices; std::vector<UINT> indices; }; //创建一个立方体:指定宽(X方向)、高(Y方向)、深(Z方向) void CreateBox(float width, float height, float depth, MeshData &mesh); void LoadOBJModel(MeshData &mesh, char* filename); };
LoadOBJModel()方法就是用于加载OBJ文件的核心方法:
void GeometryGenerator::LoadOBJModel(MeshData &mesh,char* filename){ //载入obj文件,获取顶点纹理法线数据 ObjParser* pObjParser = new ObjParser(); pObjParser->SetFileName(filename);//myteapot.obj probeColor pObjParser->ReadFileCounts();//统计顶点纹理和法线数mVertexCount、mTexcoordCount等等 //将数据传入顶点、纹理、法线和面数组 // After get enough memory, clear these counts to 0, use it as index VertexType* vertices = new VertexType[pObjParser->mVertexCount]; VertexType* texcoords = new VertexType[pObjParser->mTexcoordCount]; VertexType* normals = new VertexType[pObjParser->mNormalCount]; FaceType* faces = new FaceType[pObjParser->mFaceCount]; std::ifstream fin; fin.open(pObjParser->mInFile); if (fin.fail()) { pObjParser->mErr << "Open input file : Failed." << std::endl; return; } char input; char ignore; int iver = 0, itex = 0, inor = 0, ifac = 0; fin.get(input); while (!fin.eof()) { if (input == 'v') { fin.get(input); switch (input) { case ' ': { fin >> vertices[iver].x >> vertices[iver].y >> vertices[iver].z;//写入顶点数组 //vertices[iver].z *= -1.0f; // RH->LH iver++; break; } case 't': { fin >> texcoords[itex].x >> texcoords[itex].y >>texcoords[itex].z;//写入纹理数组 //texcoords[itex].y = 1.0f - texcoords[itex].y; // RH->LH itex++; break; } case 'n': { fin >> normals[inor].x >> normals[inor].y >> normals[inor].z;//写入法线数组 //normals[inor].z *= -1.0f; // RH->LH inor++; break; } } } if (input == 'f') { fin.get(input); if (input == ' ') {//写入三角面的数组,换个旋转方向,要不然会被背面剔除 fin >> faces[ifac].vIndex1 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].tIndex1 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].nIndex1; fin >> faces[ifac].vIndex2 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].tIndex2 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].nIndex2; fin >> faces[ifac].vIndex3 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].tIndex3 >> ignore >> faces[ifac].nIndex3; ifac++; } } while (input != ' ') fin.get(input); fin.get(input); } fin.close(); //以上代码将数据读取到vertices、texcoords、normals和faces数组中 mesh.vertices.clear(); mesh.indices.clear(); mesh.vertices.resize(pObjParser->mFaceCount * 3); //一共36个索引(每面6个) mesh.indices.resize(pObjParser->mFaceCount * 3); int i = 0, j = 0; for (; i < pObjParser->mFaceCount * 3;){ mesh.indices[i] = i; mesh.indices[i + 1] = i + 1; mesh.indices[i + 2] = i + 2; mesh.vertices[i].pos.x = vertices[faces[j].vIndex1 - 1].x;//绑定顶点坐标 mesh.vertices[i].pos.y = vertices[faces[j].vIndex1 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i].pos.z = vertices[faces[j].vIndex1 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i].pos.w = 1; ZCVector tmp1 = mesh.vertices[i].pos; mesh.vertices[i].tex.u = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex1 - 1].x;//绑定纹理坐标 mesh.vertices[i].tex.v = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex1 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i].normal.x = normals[faces[j].nIndex1 - 1].x;//绑定法线 mesh.vertices[i].normal.y = normals[faces[j].nIndex1 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i].normal.z = normals[faces[j].nIndex1 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i].normal.w = 0; mesh.vertices[i].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f);//绑定颜色 mesh.vertices[i].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 1].pos.x = vertices[faces[j].vIndex2 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 1].pos.y = vertices[faces[j].vIndex2 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 1].pos.z = vertices[faces[j].vIndex2 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i + 1].pos.w = 1; ZCVector tmp2 = mesh.vertices[i+1].pos; mesh.vertices[i + 1].tex.u = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex2 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 1].tex.v = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex2 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 1].normal.x = normals[faces[j].nIndex2 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 1].normal.y = normals[faces[j].nIndex2 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 1].normal.z = normals[faces[j].nIndex2 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i + 1].normal.w = 0; mesh.vertices[i + 1].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 1].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 1].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 2].pos.x = vertices[faces[j].vIndex3 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 2].pos.y = vertices[faces[j].vIndex3 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 2].pos.z = vertices[faces[j].vIndex3 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i + 2].pos.w = 1; ZCVector tmp3 = mesh.vertices[i+2].pos; mesh.vertices[i + 2].tex.u = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex3 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 2].tex.v = texcoords[faces[j].tIndex3 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 2].normal.x = normals[faces[j].nIndex3 - 1].x; mesh.vertices[i + 2].normal.y = normals[faces[j].nIndex3 - 1].y; mesh.vertices[i + 2].normal.z = normals[faces[j].nIndex3 - 1].z; mesh.vertices[i + 2].normal.w = 0; mesh.vertices[i + 2].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 2].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); mesh.vertices[i + 2].color = ZCVector(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f); i += 3; j++; } }
以上代码,先遍历一遍,将该obj文件的顶点数量、纹理数量等等计算出来,确定各属性数组的大小;然后再遍历一遍obj文件的索引,将将数据读取到vertices、texcoords、normals和faces数组中;然后第三次遍历时,根据f开头的行表示的索引,将顶点信息组装成mesh网格信息。
其中ReadFileCounts()方法用于遍历一遍顶点,记录下该obj文件的顶点数量、纹理数量等等:
bool ObjParser::ReadFileCounts() { char input; std::ifstream fin; fin.open(mInFile); if (fin.fail()) { mErr << "Open input file : Failed." << std::endl; return false; } fin.get(input); while (!fin.eof()) { if (input == 'v') { fin.get(input); switch (input) { case ' ': { mVertexCount++; break; } case 't': { mTexcoordCount++; break; } case 'n': { mNormalCount++; break; } } } if (input == 'f') { fin.get(input); if (input == ' ') mFaceCount++; } // otherwise read in the remainder of the line. while (input != ' ') fin.get(input); // start reading the beginning of the next line. fin.get(input); } fin.close(); return true; }
在导入OBJ模型后,还可以导入mtl材质文件,mtl文件一般可以通过3dsMax生成模型时设置附带生成,记录了模型的材质信息。光栅器中通过该方法导入:
LoadMaterial("Models/myteapot.mtl");//从mtl文件获得bmp纹理贴图的位置,获取模型的材质 3dsmax导出myteapot.mtl
LoadMaterial()方法的实现:
void BoxDemo::LoadMaterial(char* fileName){ std::stringstream ss; string mtlfile; ss << fileName; ss >> mtlfile; std::ifstream fin; std::ofstream mErr; fin.open(mtlfile); if (fin.fail()) { mErr << "Open input file : Failed." << std::endl; } char input; fin.get(input); while (!fin.eof()) { if (input == ' '){ fin.get(input); } if (input == 'K') { fin.get(input); switch (input) { case 'a': { //fin >> vertices[mVertexCount].x >> vertices[mVertexCount].y >> vertices[mVertexCount].z; fin >> m_material.ambient.x >> m_material.ambient.y >> m_material.ambient.z; break; } case 'd': { fin >> m_material.diffuse.x >> m_material.diffuse.y >> m_material.diffuse.z; break; } case 's': { fin >> m_material.specular.x >> m_material.specular.y >> m_material.specular.z; m_material.specular.w = 1.f; break; } } } if (input == 'm'){ fin.get(input); fin.get(input); fin.get(input); fin.get(input); fin.get(input); if (input == 'd'){//获得漫反射贴图 fin.get(input); fin.get(input); stringstream ss2; while (input != ' '){ ss2 << input; fin.get(input); } ss2 >> bmplocation; } } // otherwise read in the remainder of the line. while (input != ' ') fin.get(input); // start reading the beginning of the next line. fin.get(input); } }
以上代码通过遍历mtl材质文件,将指向该模型的环境光系数、漫反射系数、镜面反射系数、高光系数和纹理、法线贴图等路径加载到光栅器维护的数据容器中,供之后的PS像素着色器阶段使用。
myteapot.obj和myteapot.mtl文件最终的渲染效果:
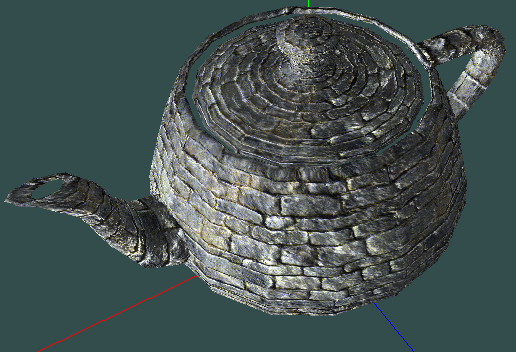
(完)