SELECT INTO 语句:表示从一个表中选取数据,然后把数据插入另一个表中,常用来备份一张表
1.全表结构备份:
SELECT * INTO new_table_name
FROM old_tablename;
示例:备份student表,备份表取名为student_backup
select * into student_backup
from student ;
则会生成一张与student表结构及数据一样的备份表。
只是将表A表中的数据插入到B表中:(数据同步/迁移)
insert into table_2(字段1,字段2,字段3) select 字段1,字段2,字段3from table_1 -- table_1 相当于A表 table_2 相当于B表 字段类型对应
--insert语句中的Values不能带Select语句
2.如果只备份表中的某些列:
SELECT column_name1,column_name2...
INTO new_table_name
FROM old_tablename
示例:只备份student表中的sno,name列入新表student_backup
select sno,name into student_backup
from student ;
3.如果需要将表中满足一定条件的记录进行备份,则可以使用where字句配套使用
示例:将所有性别为男的学生记录备份到新表student_backup
select * into student_backup
from student
where sex='男';
注:但是在mysql中使用SELECT INTO语句是无法进行备份操作,执行命令时会提示新表未定义

所以,我们应该使用下列语句进行数据表的备份操作。
1.只复制表结构到新表 :(只有结构无数据)
create table 新表 select * from 旧表 where1=2
或create table 新表 like 旧表
此两种方法的区别:使用第一条语句,备份的新表并没有旧表的primary key 、auto_increment等属性,需要重新对新表进行设置
示例:create table newstudent select * from student where 1=2;
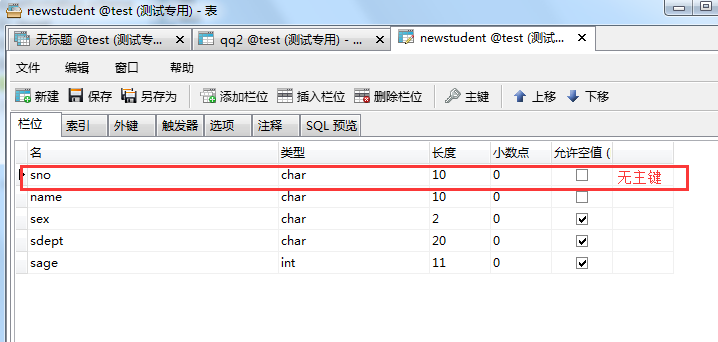
或者 create table newstudent like sutdent;

2.复制表结构及数据到新表
create table 新表 select * from 旧表;---这种方法会将oldtable中所有的内容都拷贝过来,同时也存在备份的新表不具备旧表 primary key、auto_increment等属性,需要对新表再次设置。
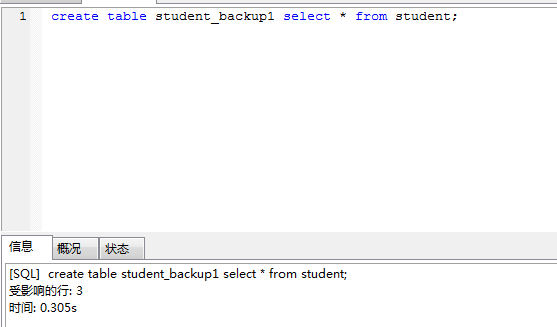
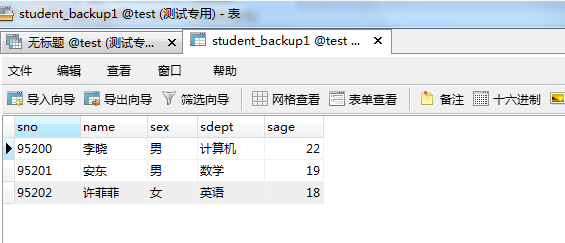
示例:复制student表中所有数据到新表student_backup1;
create table student_backup1 select * from student;
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yhitest/p/5807655.html