从2018年Google提出BERT模型开始,transformer结构就在NLP领域大杀四方,使用transformer的BERT模型在当时横扫NLP领域的11项任务,取得SOTA成绩,包括一直到后来相继出现的XLNET,roBERT等,均采用transformer结构作为核心。在著名的SOTA机器翻译排行榜上,几乎所有排名靠前的模型都是用transformer。那么在transformer出现之前,占领市场的一直都是LSTM和GRU等模型,相比之下,transformer具有如下两个显著的优势:
1.transformer能够利用分布式GPU进行训练,从而提升模型的训练效率
2.在分析预测长序列文本时,transformer能够捕捉间隔较长的语义关联效果。
由于transformer在NLP领域的巨大成功,使得研究人员很自然的想到,如果将其应用于CV领域,又会取得怎样的效果呢,毕竟CV领域中的模型长期以来都是被CNNs主导,如果transformer能在CV领域进行适配和创新,是否能为CV模型的发展开辟一条新的道路。果然,近期transformer又在CV领域杀疯了,关于transformer的视觉模型在各大顶会论文中登场,其中又有不少模型实现了优于CNNs的效果。
今天我们就从最原始的transformer模型入手,来带大家彻底认识一下transformer。
transformer的架构
transformer的总体架构如下图:
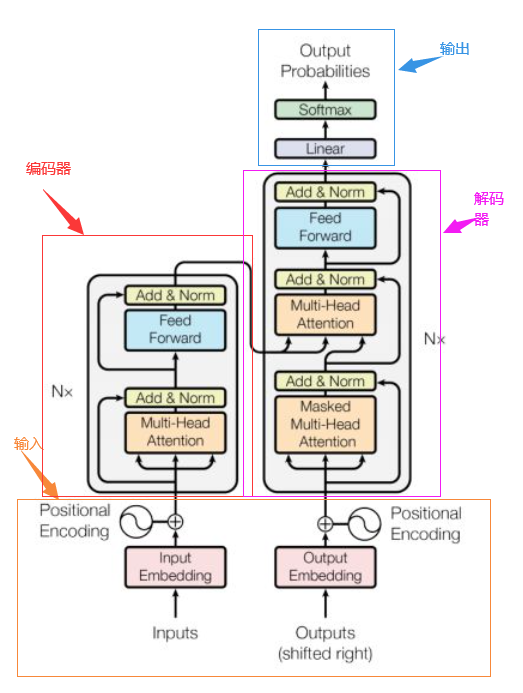
从上图可以看到,transformer的总体架构可以分为四个部分:输入、输出、编码器和解码器,以机器翻译任务为例,各个部分的组成如下:
输入部分(橙色区域)包含:
1.源文本的嵌入层以及位置编码器
2.目标文本的嵌入层以及位置编码器
输出部分(蓝色区域)包含:
1.线性层
2.softmax层
编码器部分(红色区域):
1.由N个编码器层堆叠而成
2.每个编码器层由两个子层连接结构组成
3.第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
4.第二个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
解码器部分(紫色区域):
1.由N个解码器层堆叠而成
2.每个解码器层由三个子层连接结构组成
3.第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
4.第二个子层连接结构包括一个多头注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
5.第三个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
输入部分:
文本嵌入层(Input Embedding)作用:无论是从源文本嵌入还是目标文本嵌入,都是为了将文本中的词汇的数字表示转变为向量表示,希望在这样的高维空间捕捉词汇间的关系。
Embedding代码实现:
1 # 文本嵌入层 2 class Embedding(Layer): 3 4 ''' 5 :param vocab:词表大小 6 :param dim_model:词嵌入的维度 7 ''' 8 def __init__(self,vocab,dim_model,**kwargs): 9 self._vocab = vocab 10 self._dim_model = dim_model 11 super(Embedding, self).__init__(**kwargs) 12 13 def build(self, input_shape, **kwargs): 14 self.embeddings = self.add_weight( 15 shape=(self._vocab,self._dim_model), 16 initializer='global_uniform', 17 name='embeddings' 18 ) 19 super(Embedding, self).build(input_shape) 20 21 def call(self, inputs): 22 if K.dtype(inputs) != 'int32': 23 inputs = K.cast(inputs,'int32') 24 embeddings = K.gather(self.embeddings,inputs) 25 embeddings *= self._dim_model**0.5 26 return embeddings 27 28 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 29 return input_shape + (self._dim_model)
位置编码层(Position Encoding)作用:因为在transformer编码器结构中并没有针对词汇位置信息的处理,因此需要在Embedding层后加入位置编码器,将词汇位置不同可能会产生不同语义的信息加入到词嵌入张量中,以弥补位置信息的缺失。
PE计算公式:
PE(pos,2i)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)
PE(pos,2i+1)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)
Position Encoding代码实现:
1 # 位置编码层 2 class PositionEncoding(Layer): 3 4 ''' 5 :param dim_model:词嵌入维度 6 ''' 7 def __init__(self,dim_model,**kwargs): 8 self._dim_model = dim_model 9 super(PositionEncoding, self).__init__(**kwargs) 10 11 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 12 seq_length = inputs.shape[1] 13 position_encodings = np.zeros((seq_length, self._model_dim)) 14 for pos in range(seq_length): 15 for i in range(self._model_dim): 16 position_encodings[pos, i] = pos / np.power(10000, (i - i % 2) / self._model_dim) 17 position_encodings[:, 0::2] = np.sin(position_encodings[:, 0::2]) # 2i 18 position_encodings[:, 1::2] = np.cos(position_encodings[:, 1::2]) # 2i+1 19 position_encodings = K.cast(position_encodings, 'float32') 20 return position_encodings 21 22 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 23 return input_shape
Embedding和Position Encoding相加层代码实现:
1 # Embeddings和Position Encodings相加层 2 class Add(Layer): 3 def __init__(self,**kwargs): 4 super(Add, self).__init__(**kwargs) 5 6 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 7 embeddings,positionEncodings = inputs 8 return embeddings + positionEncodings 9 10 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 11 return input_shape[0]
编码器解码器组件实现
相关概念:
- 掩码张量:掩代表遮掩,码就是张量中的数值,它的尺寸不定,里面一般只有0 和 1 元素,代表位置被遮掩或者不被遮掩,因此它的作用就是让另外一个张量中的一些数值被遮掩,也可以说是被替换,它的表现形式是一个张量。
- 掩码张量的作用:在transformer中,掩码张量的主要作用在应用attention,有一些生成的attention张量中的值计算有可能已知了未来信息而得到的,未来信息被看到是因为训练时会把整个输出结果都一次性进行Embedding,但是理论上解码器的输出却不是一次就能产生最终结果的,而是一次次的通过上一次结果综合得到的,因此,未来的信息可能被提前利用,这个时候就需要对未来信息进行遮掩。
- Multi-Head Attention 是由多个Self-Attention 组成。从多头注意力的结构图中,我们看到貌似这个所谓的多头指的就是多组线性变变换层,其实并不是,这里其实仅使用了一组线性变换层,即三个变换张量对Q,K,V进行线性变换,这些变换并不会改变原有张量的尺度,因此每个变换张量都是方阵,得到结果后多头作用才开始体现,每个头从词义层面分割输出张量,但是句子中的每个词的表示只取得一部分,也就是只分割了最后一维的词嵌入向量(words embedding)。
- self-attention和multi-head attention的结构如下图。在计算中需要用到矩阵Q(query),K(key),V(value),实际接收的输入是单词的表示向量组成的矩阵X或上一个编码器的输出,Q,K,V通过将输入进行线性变换得到。
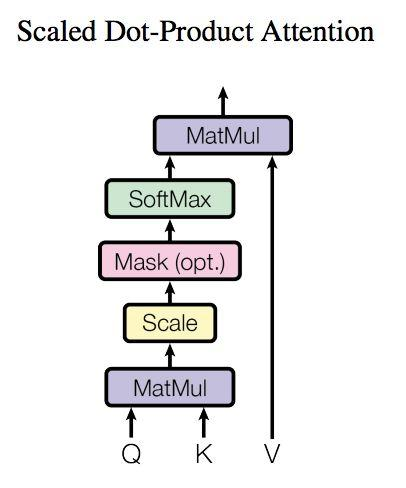
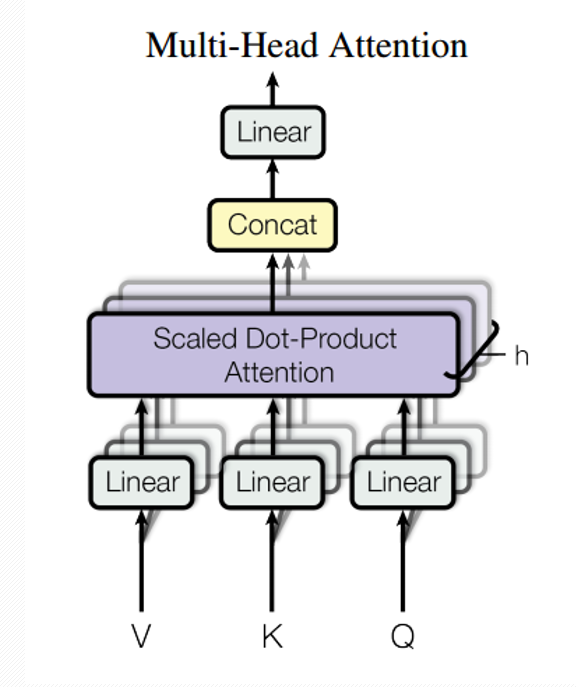
Self-Attention 层代码实现:
1 # 自注意力层 2 class ScaledDotProductAttention(Layer): 3 def __init__(self, masking=True, future=False, dropout_rate=0., **kwargs): 4 self._masking = masking 5 self._future = future 6 self._dropout_rate = dropout_rate 7 self._masking_num = -2 ** 32 + 1 8 super(ScaledDotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs) 9 10 def mask(self, inputs, masks): 11 masks = K.cast(masks, 'float32') 12 masks = K.tile(masks, [K.shape(inputs)[0] // K.shape(masks)[0], 1]) 13 masks = K.expand_dims(masks, 1) 14 outputs = inputs + masks * self._masking_num 15 return outputs 16 17 def future_mask(self, inputs): 18 diag_vals = tf.ones_like(inputs[0, :, :]) 19 tril = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorLowerTriangular(diag_vals).to_dense() 20 future_masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tril, 0), [tf.shape(inputs)[0], 1, 1]) 21 paddings = tf.ones_like(future_masks) * self._masking_num 22 outputs = tf.where(tf.equal(future_masks, 0), paddings, inputs) 23 return outputs 24 25 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 26 if self._masking: 27 assert len(inputs) == 4, "inputs should be set [queries, keys, values, masks]." 28 queries, keys, values, masks = inputs 29 else: 30 assert len(inputs) == 3, "inputs should be set [queries, keys, values]." 31 queries, keys, values = inputs 32 33 if K.dtype(queries) != 'float32': queries = K.cast(queries, 'float32') 34 if K.dtype(keys) != 'float32': keys = K.cast(keys, 'float32') 35 if K.dtype(values) != 'float32': values = K.cast(values, 'float32') 36 37 matmul = K.batch_dot(queries, tf.transpose(keys, [0, 2, 1])) # MatMul 38 scaled_matmul = matmul / int(queries.shape[-1]) ** 0.5 # Scale 39 if self._masking: 40 scaled_matmul = self.mask(scaled_matmul, masks) # Mask(opt.) 41 42 if self._future: 43 scaled_matmul = self.future_mask(scaled_matmul) 44 45 softmax_out = K.softmax(scaled_matmul) # SoftMax 46 # Dropout 47 out = K.dropout(softmax_out, self._dropout_rate) 48 49 outputs = K.batch_dot(out, values) 50 51 return outputs 52 53 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 54 return input_shape
Multi-Head Attention层代码实现:
1 # 多头自注意力层 2 class MultiHeadAttention(Layer): 3 4 def __init__(self, n_heads, head_dim, dropout_rate=.1, masking=True, future=False, trainable=True, **kwargs): 5 self._n_heads = n_heads 6 self._head_dim = head_dim 7 self._dropout_rate = dropout_rate 8 self._masking = masking 9 self._future = future 10 self._trainable = trainable 11 super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs) 12 13 # 用方阵做Q,K,V的权重矩阵进行线性变换,维度不变 14 def build(self, input_shape): 15 self._weights_queries = self.add_weight( 16 shape=(input_shape[0][-1], self._n_heads * self._head_dim), 17 initializer='glorot_uniform', 18 trainable=self._trainable, 19 name='weights_queries') 20 self._weights_keys = self.add_weight( 21 shape=(input_shape[1][-1], self._n_heads * self._head_dim), 22 initializer='glorot_uniform', 23 trainable=self._trainable, 24 name='weights_keys') 25 self._weights_values = self.add_weight( 26 shape=(input_shape[2][-1], self._n_heads * self._head_dim), 27 initializer='glorot_uniform', 28 trainable=self._trainable, 29 name='weights_values') 30 super(MultiHeadAttention, self).build(input_shape) 31 32 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 33 if self._masking: 34 assert len(inputs) == 4, "inputs should be set [queries, keys, values, masks]." 35 queries, keys, values, masks = inputs 36 else: 37 assert len(inputs) == 3, "inputs should be set [queries, keys, values]." 38 queries, keys, values = inputs 39 40 queries_linear = K.dot(queries, self._weights_queries) 41 keys_linear = K.dot(keys, self._weights_keys) 42 values_linear = K.dot(values, self._weights_values) 43 44 # 将变换后的Q,K,V在embedding words的维度上进行切分 45 queries_multi_heads = tf.concat(tf.split(queries_linear, self._n_heads, axis=2), axis=0) 46 keys_multi_heads = tf.concat(tf.split(keys_linear, self._n_heads, axis=2), axis=0) 47 values_multi_heads = tf.concat(tf.split(values_linear, self._n_heads, axis=2), axis=0) 48 49 if self._masking: 50 att_inputs = [queries_multi_heads, keys_multi_heads, values_multi_heads, masks] 51 else: 52 att_inputs = [queries_multi_heads, keys_multi_heads, values_multi_heads] 53 54 attention = ScaledDotProductAttention( 55 masking=self._masking, future=self._future, dropout_rate=self._dropout_rate) 56 att_out = attention(att_inputs) 57 58 outputs = tf.concat(tf.split(att_out, self._n_heads, axis=0), axis=2) 59 60 return outputs 61 62 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 63 return input_shape
Position-wise Feed Forward代码实现:
1 # Position-wise Feed Forward层 2 # out = (relu(xW1+b1))W2+b2 3 class PositionWiseFeedForward(Layer): 4 5 def __init__(self, model_dim, inner_dim, trainable=True, **kwargs): 6 self._model_dim = model_dim 7 self._inner_dim = inner_dim 8 self._trainable = trainable 9 super(PositionWiseFeedForward, self).__init__(**kwargs) 10 11 def build(self, input_shape): 12 self.weights_inner = self.add_weight( 13 shape=(input_shape[-1], self._inner_dim), 14 initializer='glorot_uniform', 15 trainable=self._trainable, 16 name="weights_inner") 17 self.weights_out = self.add_weight( 18 shape=(self._inner_dim, self._model_dim), 19 initializer='glorot_uniform', 20 trainable=self._trainable, 21 name="weights_out") 22 self.bais_inner = self.add_weight( 23 shape=(self._inner_dim,), 24 initializer='uniform', 25 trainable=self._trainable, 26 name="bais_inner") 27 self.bais_out = self.add_weight( 28 shape=(self._model_dim,), 29 initializer='uniform', 30 trainable=self._trainable, 31 name="bais_out") 32 super(PositionWiseFeedForward, self).build(input_shape) 33 34 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 35 if K.dtype(inputs) != 'float32': 36 inputs = K.cast(inputs, 'float32') 37 inner_out = K.relu(K.dot(inputs, self.weights_inner) + self.bais_inner) 38 outputs = K.dot(inner_out, self.weights_out) + self.bais_out 39 return outputs 40 41 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 42 return self._model_dim
Normalization代码实现:
1 # Normalization层 2 class LayerNormalization(Layer): 3 4 def __init__(self, epsilon=1e-8, **kwargs): 5 self._epsilon = epsilon 6 super(LayerNormalization, self).__init__(**kwargs) 7 8 def build(self, input_shape): 9 self.beta = self.add_weight( 10 shape=(input_shape[-1],), 11 initializer='zero', 12 name='beta') 13 self.gamma = self.add_weight( 14 shape=(input_shape[-1],), 15 initializer='one', 16 name='gamma') 17 super(LayerNormalization, self).build(input_shape) 18 19 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 20 mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(inputs, [-1], keepdims=True) 21 normalized = (inputs - mean) / ((variance + self._epsilon) ** 0.5) 22 outputs = self.gamma * normalized + self.beta 23 return outputs 24 25 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 26 return input_shape
Transformer整体架构实现:
1 class Transformer(Layer): 2 def __init__(self, vocab_size, model_dim, n_heads=8, encoder_stack=6, decoder_stack=6, feed_forward_size=2048, dropout=0.1, **kwargs): 3 self._vocab_size = vocab_size 4 self._model_dim = model_dim 5 self._n_heads = n_heads 6 self._encoder_stack = encoder_stack 7 self._decoder_stack = decoder_stack 8 self._feed_forward_size = feed_forward_size 9 self._dropout_rate = dropout 10 super(Transformer, self).__init__(**kwargs) 11 12 def build(self, input_shape): 13 self.embeddings = self.add_weight( 14 shape=(self._vocab_size, self._model_dim), 15 initializer='glorot_uniform', 16 trainable=True, 17 name="embeddings") 18 super(Transformer, self).build(input_shape) 19 20 def encoder(self,inputs): 21 if K.dtype(inputs) != 'int32': 22 inputs = K.cast(inputs, 'int32') 23 24 masks = K.equal(inputs,0) 25 # Embeddings 26 embeddings = Embedding(self._vocab_size,self._model_dim)(inputs) 27 # Position Encodings 28 position_encodings = PositionEncoding(self._model_dim)(embeddings) 29 # Embeddings + Position Encodings 30 encodings = embeddings + position_encodings 31 # Dropout 32 encodings = K.dropout(encodings,self._dropout_rate) 33 34 # Encoder 35 for i in range(self._encoder_stack): 36 # Multi-head Attention 37 attention = MultiHeadAttention(self._n_heads,self._model_dim // self._n_heads) 38 attention_input = [encodings,encodings,encodings,masks] 39 attention_out = attention(attention_input) 40 # Add & Norm 41 attention_out += encodings 42 attention_out = LayerNormalization()(attention_out) 43 # Feed-Forward 44 pwff = PositionWiseFeedForward(self._model_dim,self._feed_forward_size) 45 pwff_out = pwff(attention_out) 46 # Add & Norm 47 pwff_out += attention_out 48 encodings = LayerNormalization()(pwff_out) 49 50 return encodings,masks 51 52 def decoder(self,inputs): 53 decoder_inputs, encoder_encodings, encoder_masks = inputs 54 if K.dtype(decoder_inputs) != 'int32': 55 decoder_inputs = K.cast(decoder_inputs, 'int32') 56 decoder_masks = K.equal(decoder_inputs,0) 57 # Embeddings 58 embeddings = Embedding(self._vocab_size,self._model_dim)(decoder_inputs) 59 # Position Encodings 60 position_encodings = PositionEncoding(self._model_dim)(embeddings) 61 # Embeddings + Position Encodings 62 encodings = embeddings + position_encodings 63 # Dropout 64 encodings = K.dropout(encodings,self._dropout_rate) 65 66 for i in range(self._decoder_stack): 67 # Masked-Multi-head-Attention 68 masked_attention = MultiHeadAttention(self._n_heads, self._model_dim // self._n_heads, future=True) 69 masked_attention_input = [encodings, encodings, encodings, decoder_masks] 70 masked_attention_out = masked_attention(masked_attention_input) 71 # Add & Norm 72 masked_attention_out += encodings 73 masked_attention_out = LayerNormalization()(masked_attention_out) 74 75 # Multi-head-Attention 76 attention = MultiHeadAttention(self._n_heads, self._model_dim // self._n_heads) 77 attention_input = [masked_attention_out, encoder_encodings, encoder_encodings, encoder_masks] 78 attention_out = attention(attention_input) 79 # Add & Norm 80 attention_out += masked_attention_out 81 attention_out = LayerNormalization()(attention_out) 82 83 # Feed-Forward 84 pwff = PositionWiseFeedForward(self._model_dim, self._feed_forward_size) 85 pwff_out = pwff(attention_out) 86 # Add & Norm 87 pwff_out += attention_out 88 encodings = LayerNormalization()(pwff_out) 89 90 # Pre-Softmax 与 Embeddings 共享参数 91 linear_projection = K.dot(encodings, K.transpose(self.embeddings)) 92 outputs = K.softmax(linear_projection) 93 return outputs 94 95 def call(self, inputs, **kwargs): 96 encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs = inputs 97 encoder_encodings, encoder_masks = self.encoder(encoder_inputs) 98 encoder_outputs = self.decoder([decoder_inputs, encoder_encodings, encoder_masks]) 99 return encoder_outputs 100 101 def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape): 102 return (input_shape[0][0], input_shape[0][1], self._vocab_size)
下一篇将使用transformer构建BERT网络进行文本情感分类实战。