前面在mnist中使用了三个非线性层来增加模型复杂度,并通过最小化损失函数来更新参数,下面实用最底层的方式即张量进行前向传播(暂不采用层的概念)。
主要注意点如下:
· 进行梯度运算时,tensorflow只对tf.Variable类型的变量进行记录,而不对tf.Tensor或者其他类型的变量记录
· 进行梯度更新时,如果采用赋值方法更新即w1=w1+x的形式,那么所得的w1是tf.Tensor类型的变量,所以要采用原地更新的方式即assign_sub函数,或者再次使用tf.Variable包起来(不推荐)
代码如下:
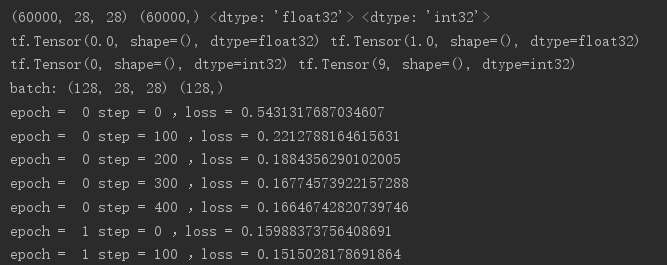
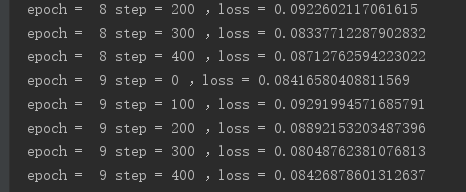
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import datasets import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2' # x:[60k,28,28] # y:[60k] (x,y),_=datasets.mnist.load_data() x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x,dtype=tf.float32)/255.0 y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y,dtype=tf.int32) print(x.shape,y.shape,x.dtype,y.dtype) print(tf.reduce_min(x),tf.reduce_max(x)) print(tf.reduce_min(y),tf.reduce_max(y)) train_db=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)).batch(128) train_iter=iter(train_db) sample=next(train_iter) print('batch:',sample[0].shape,sample[1].shape) # [b,784]=>[b,256]=>[b,128]=>[b,10] # w shape[dim_in,dim_out] b shape[dim_out] w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784,256],stddev=0.1)) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])) w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256,128],stddev=0.1)) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])) w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128,10],stddev=0.1)) b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 设置学习率 lr = 0.001 for epoch in range(10): # 对数据集迭代 for step,(x,y) in enumerate(train_db): # x:[128,28,28] y:[128] x = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28*28]) with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # tape只会跟踪tf.Variable # x:[b,28*28] # [b,784]@[784,256]+[256]=>[b,256]+[256] h1 = x@w1 + b1 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) # 去线性化 h2 = h1@w2 + b2 h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) # 去线性化 out = h2@w3 + b3 # 计算损失 y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y,depth=10) # mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2) loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out) # mean:scalar loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) # 计算梯度 grads = tape.gradient(loss,[w1,b1,w2,b2,w3,b3]) # w1 = w1 -lr * w1_grad w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0]) # 原地更新 b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1]) w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2]) b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3]) w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4]) b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5]) if step % 100 == 0: print('epoch = ',epoch,'step =',step,',loss =',float(loss))
效果如下: