1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程概念;
(2) 掌握线程创建的两种技术;
(3) 理解和掌握线程的优先级属性及调度方法;
(4) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握线程概念;
l 掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
l 利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
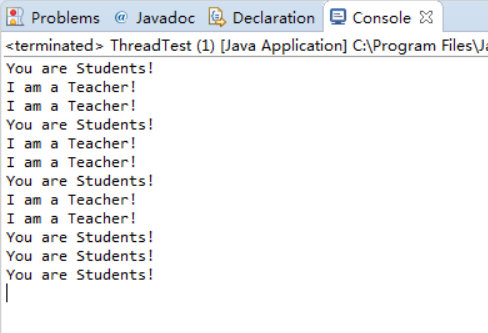
class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left=new Lefthand(); right=new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } }
利用Runnable接口改造程序修改后。
class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable left = new Lefthand(); Thread a = new Thread(left); Runnable right = new Righthand(); Thread b = new Thread(right); a.start(); b.start(); } } ThreadTest
测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
l 掌握线程创建的两种技术。
(1) 在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
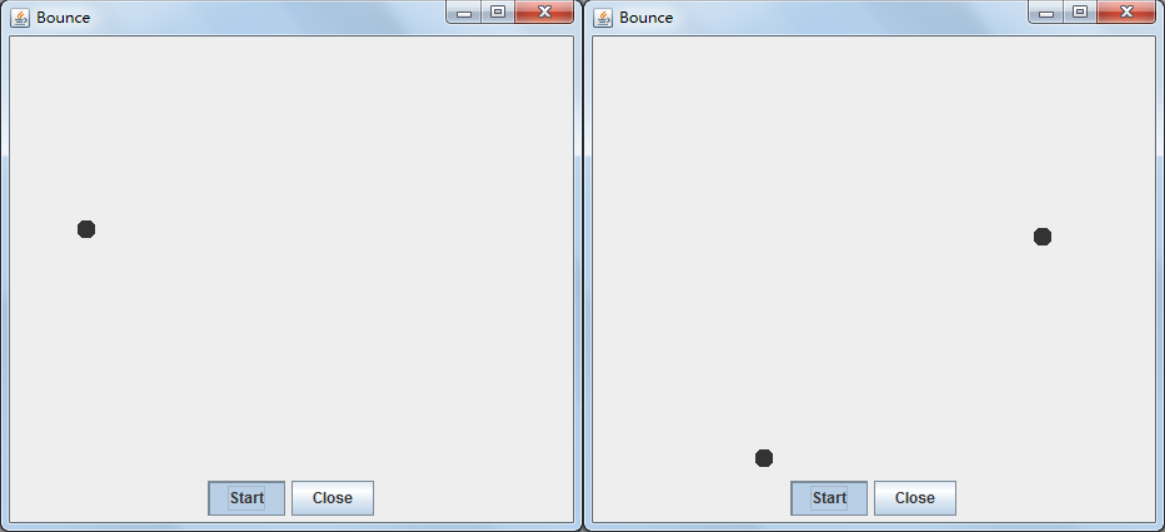
package bounceThread; import java.awt.geom.*; /** A ball that moves and bounces off the edges of a rectangle * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Ball { private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** Moves the ball to the next position, reversing direction if it hits one of the edges */ //定义了移动方法 public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** Gets the shape of the ball at its current position. */ //定义球外形 public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); } } Ball Ball
package bounce; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * The component that draws the balls. * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BallComponent extends JPanel { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /** * Add a ball to the component. * @param b the ball to add */ public void add(Ball b) { balls.add(b); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); // erase background Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; for (Ball b : balls) { g2.fill(b.getShape()); } } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } } BallComponent BallComponent
package bounce; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * Shows an animated bouncing ball. * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bounce { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * The frame with ball component and buttons. */ class BounceFrame extends JFrame { private BallComponent comp; public static final int STEPS = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 3; /** * Constructs the frame with the component for showing the bouncing ball and * Start and Close buttons */ public BounceFrame() { setTitle("Bounce"); comp = new BallComponent(); add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());//将按钮放入buttonPanel addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);//将buttonPanel放入边界管理器的南端 pack(); } /** * Adds a button to a container. * @param c the container * @param title the button title * @param listener the action listener for the button */ public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) { //生成按钮对象 JButton button = new JButton(title); c.add(button); button.addActionListener(listener);//注册监听器事件 } /** * Adds a bouncing ball to the panel and makes it bounce 1,000 times. */ public void addBall() { try { Ball ball = new Ball(); comp.add(ball); for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) { ball.move(comp.getBounds()); comp.paint(comp.getGraphics()); Thread.sleep(DELAY);//在两个球显示之间有延迟 } } catch (InterruptedException e)//中断异常 { } } } Bounce Bounce
(2)在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
package bounceThread; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * 显示动画弹跳球 * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BounceThread { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setTitle("BounceThread"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * 框架与球组件和按钮 */ class BounceFrame extends JFrame { private BallComponent comp; public static final int STEPS = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 5; /** * 用显示弹跳球以及开始和关闭按钮的组件构建框架 */ public BounceFrame() { comp = new BallComponent(); add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * 向容器添加按钮 * * @param c * the container * @param title * the button title * @param listener * the action listener for the button */ public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(title); c.add(button); button.addActionListener(listener); } /** * 在画布上添加一个弹跳球,并启动一个线程使其弹跳 */ public void addBall() { Ball ball = new Ball(); comp.add(ball); Runnable r = () -> { try { for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) { ball.move(comp.getBounds());//将球移动到下一个位置,如果碰到其中一个边缘则反转方向 comp.repaint();//重绘此组件。 Thread.sleep(DELAY);//在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠 } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } BounceThread BounceThread
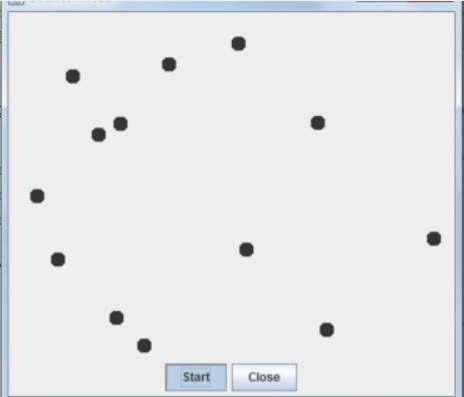
测试程序3:分析以下程序运行结果并理解程序。
class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner=new Race[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( ); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( ); runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY); runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);} public void run( ) { for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++); System.out.println(getName()+"线程的优先级是"+getPriority()+"已计算完毕!"); } }

测试程序4
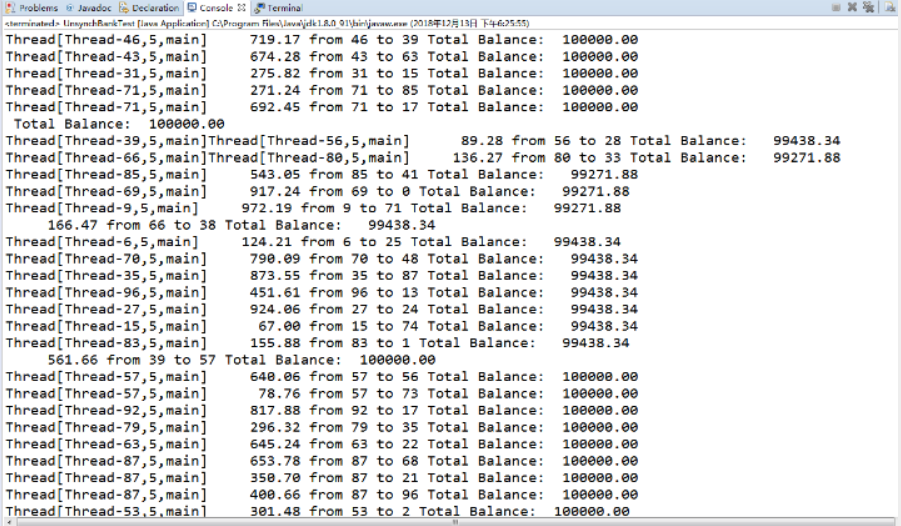
l 教材642页程序模拟一个有若干账户的银行,随机地生成在这些账户之间转移钱款的交易。每一个账户有一个线程。在每一笔交易中,会从线程所服务的账户中随机转移一定数目的钱款到另一个随机账户。
在Elipse环境下调试教材642页程序14-5、14-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
package unsynch; import java.util.*; /** * 有许多银行账户的银行 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bank { private final double[] accounts; /** * 建设银行 * @param n 账号 * @param initialBalance 每个账户的初始余额 */ public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) { accounts = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); } /** * 把钱从一个账户转到另一个账户 * @param from 转账账户从 * @param to 转账账户到 * @param amount 转让的数额 */ public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) { if (accounts[from] < amount) return; System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); accounts[from] -= amount; System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); accounts[to] += amount; System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); } /** * 获取所有帐户余额的总和 * @return 总余额 */ public double getTotalBalance() { double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts) sum += a; return sum; } /** * 获取银行中的帐户数量 * @return 账号 */ public int size() { return accounts.length; } } Bank ank
package unsynch; /** * 此程序显示多个线程访问数据结构时的数据损坏 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class UnsynchBankTest { public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) { int fromAccount = i; Runnable r = () -> { try { while (true) { int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } } UnsynchBankTest UnsynchBankTest
综合编程练习
编程练习1
1.设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:

(1) 用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(2) 用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(3) 点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
package AA; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { DemoJFrame page = new DemoJFrame(); }); } } Main Main
package AA; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Toolkit; import java.awt.Window; public class WinCenter { public static void center(Window win){ Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize(); Dimension wSize = win.getSize(); if(wSize.height > sSize.height){ wSize.height = sSize.height; } if(wSize.width > sSize.width){ wSize.width = sSize.width; } win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width)/ 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height)/ 2); } } WinCenter WinCenter
package o; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.BorderFactory; import javax.swing.ButtonGroup; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JCheckBox; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JRadioButton; import javax.swing.JTextField; public class DemoJFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel jPanel1; private JPanel jPanel2; private JPanel jPanel3; private JPanel jPanel4; private JTextField fieldname; private JComboBox comboBox; private JTextField fieldadress; private ButtonGroup bg; private JRadioButton Male; private JRadioButton Female; private JCheckBox read; private JCheckBox sing; private JCheckBox dance; public DemoJFrame() { // 设置窗口大小 this.setSize(800, 400); // 设置可见性 this.setVisible(true); // 设置标题 this.setTitle("编程练习一"); // 设置关闭操作 this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 设置窗口居中 WinCenter.center(this); // 创建四个面板对象 jPanel1 = new JPanel(); setJPanel1(jPanel1); jPanel2 = new JPanel(); setJPanel2(jPanel2); jPanel3 = new JPanel(); setJPanel3(jPanel3); jPanel4 = new JPanel(); setJPanel4(jPanel4); // 设置容器的为流布局 FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(); this.setLayout(flowLayout); // 将四个面板添加到容器中 this.add(jPanel1); this.add(jPanel2); this.add(jPanel3); this.add(jPanel4); } /* * 设置面一 */ private void setJPanel1(JPanel jPanel) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45)); // 给面板的布局设置为网格布局 一行4列 jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel name = new JLabel("name:"); name.setSize(100, 50); fieldname = new JTextField(""); fieldname.setSize(80, 20); JLabel study = new JLabel("qualification:"); comboBox = new JComboBox(); comboBox.addItem("初中"); comboBox.addItem("高中"); comboBox.addItem("本科"); jPanel.add(name); jPanel.add(fieldname); jPanel.add(study); jPanel.add(comboBox); } /* * 设置面板二 */ private void setJPanel2(JPanel jPanel) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50)); // 给面板的布局设置为网格布局 一行4列 jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel name = new JLabel("address:"); fieldadress = new JTextField(); fieldadress.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(150, 50)); JLabel study = new JLabel("hobby:"); JPanel selectBox = new JPanel(); selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("")); selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); read = new JCheckBox("reading"); sing = new JCheckBox("singing"); dance = new JCheckBox("danceing"); selectBox.add(read); selectBox.add(sing); selectBox.add(dance); jPanel.add(name); jPanel.add(fieldadress); jPanel.add(study); jPanel.add(selectBox); } /* * 设置面板三 */ private void setJPanel3(JPanel jPanel) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT); jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout); JLabel sex = new JLabel("性别:"); JPanel selectBox = new JPanel(); selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("")); selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1)); bg = new ButtonGroup(); Male = new JRadioButton("male"); Female = new JRadioButton("female"); bg.add(Male ); bg.add(Female); selectBox.add(Male); selectBox.add(Female); jPanel.add(sex); jPanel.add(selectBox); } /* * 设置面板四 */ private void setJPanel4(JPanel jPanel) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 50, 10); jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout); jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout); JButton sublite = new JButton("提交"); JButton reset = new JButton("重置"); sublite.addActionListener((e) -> valiData()); reset.addActionListener((e) -> Reset()); jPanel.add(sublite); jPanel.add(reset); } /* * 提交数据 */ private void valiData() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 // 拿到数据 String name = fieldname.getText().toString().trim(); String xueli = comboBox.getSelectedItem().toString().trim(); String address = fieldadress.getText().toString().trim(); System.out.println(name); System.out.println(xueli); String hobbystring=""; if (read.isSelected()) { hobbystring+="reading "; } if (sing.isSelected()) { hobbystring+="singing "; } if (dance.isSelected()) { hobbystring+="dancing "; } System.out.println(address); if (Male.isSelected()) { System.out.println("male"); } if (Female.isSelected()) { System.out.println("female"); } System.out.println(hobbystring); } /* * 重置 */ private void Reset() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 fieldadress.setText(null); fieldname.setText(null); comboBox.setSelectedIndex(0); read.setSelected(false); sing.setSelected(false); dance.setSelected(false); bg.clearSelection(); } } DemoJFrame DemoJFrame


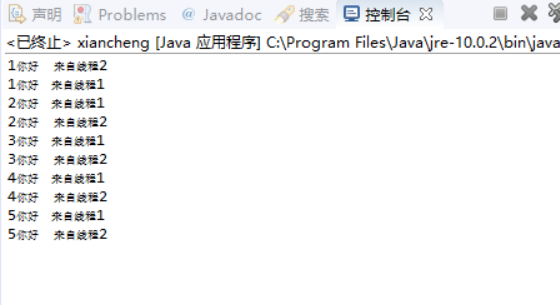
2.创建两个线程,每个线程按顺序输出5次“你好”,每个“你好”要标明来自哪个线程及其顺序号。
package BB; class xian1 extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println( i+ "你好"+" 来自线程1"); try{ sleep(200); } catch(InterruptedException e)//异常捕获 { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class xian2 extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println( i+ "你好"+" 来自线程2"); try{ sleep(200); } catch(InterruptedException e)//异常捕获 { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } public class xiancheng { //属性 static xian1 xian11; static xian2 xian22; public static void main(String[] args) { xian11=new xian1(); xian22=new xian2(); //用start()方法启动线程 xian11.start(); xian22.start(); } }
实验总结 :通过本周的学习我学到了线程的概念,并且掌握了线程创建的两种技术,(1)用Thread类的子类创建线程(2)用Runnable()接口实现线程;理解和掌握了线程的优先级属性及调度方法,学到了线程的七种状态。