原型模式用于创建重复的对象,同时又能保证性能。
这种模式是实现了一个原型接口,该接口用于创建当前对象的克隆。当直接创建对象的代价比较大时,则采用这种模式。例如,一个对象需要在一个高代价的数据库操作之后被创建。我们可以缓存该对象,在下一个请求时返回它的克隆,在需要的时候更新数据库,以此来减少数据库调用。(Django ORM)
实现克隆操作,在 JAVA 继承 Cloneable,重写 clone()方法。
使用场景:
1、资源优化场景。
2、类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等。
3、性能和安全要求的场景。
4、通过 new 产生一个对象需要非常繁琐的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模式。
5、一个对象多个修改者的场景。
6、一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以考虑使用原型模式拷贝多个对象供调用者使用。
7、在实际项目中,原型模式很少单独出现,一般是和工厂方法模式一起出现,通过 clone 的方法创建一个对象,然后由工厂方法提供给调用者。
来看UML图:
Shape类实现Cloneable接口,实现了clone方法。
ShapeCache缓存了三个Shape对象,当请求获取该对象时,返回对象的clone。
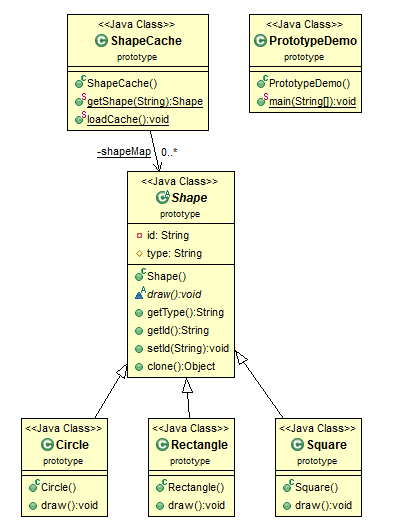
来看代码:
Shape及其子类:
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getType(){
return type;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(){
type = "Rectangle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Square extends Shape {
public Square(){
type = "Square";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(){
type = "Circle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
主要就是Shape类实现了clone方法,各个子类实现了draw方法。
ShapeCache类:
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class ShapeCache {
private static Hashtable<String, Shape> shapeMap
= new Hashtable<String, Shape>();
public static Shape getShape(String shapeId) {
Shape cachedShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId);
return (Shape) cachedShape.clone();
}
public static void loadCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeMap.put(circle.getId(),circle);
Square square = new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeMap.put(square.getId(),square);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(),rectangle);
}
}
loadCache方法创建了三个Shape对象,保存在HashMap中。
当调用getShape时,返回该对象的clone。
Demo:
public class PrototypeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeCache.loadCache();
Shape clonedShape = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("1");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape.getType());
Shape clonedShape2 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("2");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape2.getType());
Shape clonedShape3 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("3");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape3.getType());
}
}