In some country there are exactly n cities and m bidirectional roads connecting the cities. Cities are numbered with integers from 1 to n. If cities a and b are connected by a road, then in an hour you can go along this road either from city a to city b, or from city b to city a. The road network is such that from any city you can get to any other one by moving along the roads.
You want to destroy the largest possible number of roads in the country so that the remaining roads would allow you to get from city s1 to city t1 in at most l1 hours and get from city s2 to city t2 in at most l2 hours.
Determine what maximum number of roads you need to destroy in order to meet the condition of your plan. If it is impossible to reach the desired result, print -1.
The first line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000, 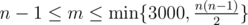 ) — the number of cities and roads in the country, respectively.
) — the number of cities and roads in the country, respectively.
Next m lines contain the descriptions of the roads as pairs of integers ai, bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n, ai ≠ bi). It is guaranteed that the roads that are given in the description can transport you from any city to any other one. It is guaranteed that each pair of cities has at most one road between them.
The last two lines contains three integers each, s1, t1, l1 and s2, t2, l2, respectively (1 ≤ si, ti ≤ n, 0 ≤ li ≤ n).
Print a single number — the answer to the problem. If the it is impossible to meet the conditions, print -1.
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
3 5 2
0
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
2 4 2
1
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
3 5 1
-1
题目大意:给定一张边权均为1的无向图。 问至少需要保留多少边,使得s1到t1的最短路不超过l1,s2到t2的最短路不超过l2。
分析:其实就是求最后s1到t1最短路和s2到t2最短路的路径并嘛.
画几个图会发现最后路径的形式一定是分叉的四段加上重叠的一段(每一段都可能为空).只需要保留这些边,也就是保证了只有一条路可达.那么枚举这个重叠部分的两端,计算一下两端分别到s1,t1,s2,t2的最短路,最后更新答案即可.这一步可以预处理得到.
坑点:重叠部分可能为一个点;做一次后s1,t1要交换!
#include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 3010,inf = 0x7ffffff; int n,m,head[maxn],to[maxn * maxn],nextt[maxn * maxn],tot = 1,d[maxn][maxn],vis[maxn]; int s1,t1,l1,s2,t2,l2,ans; void add(int x,int y) { to[tot] = y; nextt[tot] = head[x]; head[x] = tot++; } void bfs(int x) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[x][i] = inf; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); queue <int> q; q.push(x); vis[x] = 1; d[x][x] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); vis[u] = 0; for (int i = head[u]; i; i = nextt[i]) { int v = to[i]; if (d[x][v] > d[x][u] + 1) { d[x][v] = d[x][u] + 1; if (!vis[v]) { vis[v] = 1; q.push(v); } } } } } int main() { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); add(x,y); add(y,x); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) bfs(i); scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&s1,&t1,&l1,&s2,&t2,&l2); if (d[s1][t1] > l1 || d[s2][t2] > l2) puts("-1"); else { ans = d[s1][t1] + d[s2][t2]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if (d[i][j] >= inf) continue; int temp1 = d[s1][i] + d[i][j] + d[j][t1]; int temp2 = d[s2][i] + d[i][j] + d[j][t2]; if (temp1 > l1 || temp2 > l2) continue; int temp = temp1 + temp2 - d[i][j]; ans = min(temp,ans); } } swap(s1,t1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if (d[i][j] >= inf) continue; int temp1 = d[s1][i] + d[i][j] + d[j][t1]; int temp2 = d[s2][i] + d[i][j] + d[j][t2]; if (temp1 > l1 || temp2 > l2) continue; int temp = temp1 + temp2 - d[i][j]; ans = min(temp,ans); } } printf("%d ",m - ans); } return 0; }