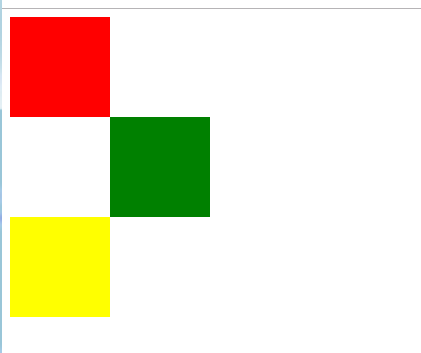
########################总结###############
块级标签能够嵌套某些块级标签和内敛标签
内敛标签不能块级标签,只能嵌套内敛标签
嵌套就是:
<div> <span> ffff </span> </div>
####p标签比较特殊,不能包含块级标签,p标签也不能包含p标签
<p> <div>xxxxxxxxxxx</div> </p>
字体
.c2{ font-family: '华文楷体'; font-size: 100px;#默认大小是16 Font-weight:bold;#自重 bold加粗 Color:red;rgb(255,255,255) rgba(255,255,255,0.3) 0.3是色彩透明度 } <span class="c2"> 小泽玛利亚 </span>
文字对齐方式 文字装饰
.c3{ text-align: left; #center,right,left line-height: 50px; #行高 } <!--字体对齐--> <div class="c3"> 从前车马很慢,书信很远,一生只够爱一人 </div>
.c4 a{
text-decoration: line-through; #使用中划线
/*text-decoration: none;*/ #去掉a标签默认的下划线
}
<!--文字装饰-->
<div class="c4">
<a href="">德玛西亚</a>
</div>
首行缩进
text-indent:32px;缩进两个字符
背景属性
.c1{
900px;
height: 900px;
/*background-color: green;*/ #背景颜色
/*background-image: url("gdg.png");*/#图片路径
/*background-repeat: no-repeat;*/#不进行多图拉伸
/*background-position: center top;*/ #把图片给居中
background:green url("gdg.png") no-repeat 500px 200px; #写一起效果 第一个200是左边 第二个是往下
background-attachment: fixed; #下拉的时候不会替换
border: 1px solid red; #边框
}
边框
.c1{ /* 200*200是正方形 */ 200px; height: 200px; border-left: 10px dashed green;#虚线左半圈绿色 border-right: 10px dashed red;#右半圈绿色 border-bottom: 10px dashed yellow;#下黄色 border-top: 10px solid purple; #实线 紫色 border-radius: 50%; #50%拉 <div class="c1"> <img src="xyjy.png" alt=""> </div>
.c1 img{
/*按照父级标签的宽度来展示,并且进行等比缩放*/
max- 100%;
}
/*溢出的部分隐藏*/
overflow: hidden;
<div class="c1">
<img src="xyjy.png" alt="">
</div>
.c1{ 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid black; } .c2{ background-color: red; /*display: none;*/ #隐藏标签 /*visibility: hidden;*/#隐藏标签,但是保留标签所占位置 } .c3{ background-color: blue; } .c3,.c4{ #挨着c3 display: inline-block; #将块级标签或者内敛标签,改成块级标签和内敛标签的 } 还有2个不常用 Display:block;将内敛标签改为块级标签 Display:inline;将块级标签改为内敛标签 #################### <div class="c1"> </div> <div class="c1 c2"> </div> <div class="c1 c3"> #注意这里的class c1的样式也有c3的样式 类似继承 我是c3标签 </div> <div class="c1 c4"> 我是c4标签 </div>
盒子模型

1(盒子型的属性)
内容的宽度
height:内容的宽度
margin:外边距,盒子边框到附近最近盒子的距离
border:边距,就是指定的盒子的宽度
padding:内边距,边框到内容的距离
content:内容
###常用 body{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } #####演示效果######## <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>哈哈哈哈</title> <style> .box{ width: 200px; height: 200px; padding: 50px; /* padding 分上 右 下 左 10px 20px 30px 50px*/ background-color: red; border: 1px solid yellow; margin: 30px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">哈哈哈哈哈哈我是曹宝宝</div> </body> </html>
#############总结##########
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 0;
/*外边距*/
padding: 0;
/*内边距*/
}
.c1,.c2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.c3{
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.c2{
float: right;
/*把c2放右边*/
}
.c1{
float: left;
}
/*c3默认会盖过c1 c2 设置伪类选择器,设立给他加空白 设置成block 让他占位子 清除浮动*/
.cc:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.cc:before{
/*清除浮动的标识 可不写*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cc">
<div class="c1"></div>
<div class="c2"></div>
</div>
<div class="c3" >
</div>
</body>
</html>
#############################如果不加浮动c3黄色会上去 变成一行#############################################

定位
relative(相对定位)
absolute(绝对定位)
#div1{ position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: blueviolet; margin-left: 100px; }
这个位置两个div都能占
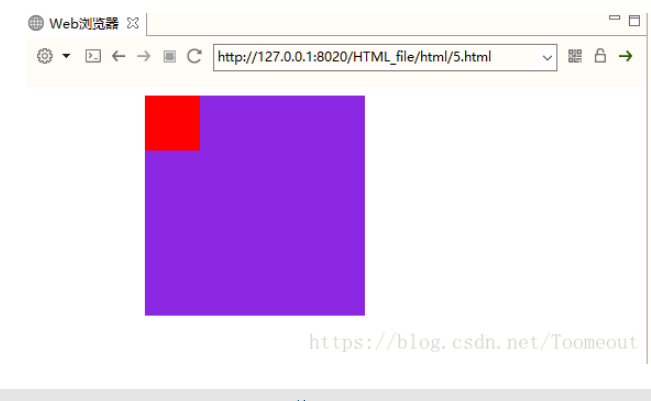
fixed(固定)不管页面怎么动,都在整个屏幕的某个位置
相对路径
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body { border: 1px solid green; } div { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: red; /*margin-top: 50px;*/ /*如果想让红色方块下移50px,我们首先想到的是使用margin-top 50px*/ /*打开代码注释的部分,刷新页面。会发现,body被撑开了。这不是我们想要的,这个时候,需要用到相对定位。*/ /*它不会撑开body*/ /*相对定位,相对自己原来的位置,跟父级没有任何关系*/ position: relative; /*移动50px*/ top: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="wrap"> </div> </body> </html>

老家留坑
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .box1{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } .box2{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; /*老家留坑*/ position: relative; left: 100px; } .box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"> </div> <div class="box2"> </div> <div class="box3"> </div> </body> </html>
相对路径:让搜索框和提交按钮在一条水平线显示
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .where{ font-size: 30px; } .search{ width: 100px; height: 40px; position: relative; top: -4px; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <form action="" method="post"> <input type="text" class="where"> <input type="submit" class="search" value="搜索"> </form> </div> </body> </html>
绝对路径 制作导航栏 不会随着鼠标的拉取而变化
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style> *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul{ list-style: none; } .nav{ width: 960px; overflow: hidden; /*margin: 0px auto;*/ background-color: purple; border-radius: 5px; position: fixed; left: 50%; margin-left: -480px; } .nav ul li{ float: left; width: 160px; height: 40px; line-height: 40px; text-align: center; } .nav ul li a{ width: 160px; height: 40px; display: block; color: white; font-size: 14px; text-decoration: none; } .nav ul li a:hover{ background: yellow; color: green; text-decoration: underline; } .wrap{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #666; } </style> </head> <body style="height: 3000px"> <div class="nav"> <ul> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> <li> <a href="#">网站导航</a> </li> </ul> </div> <div class="wrap"></div> </body> </html>
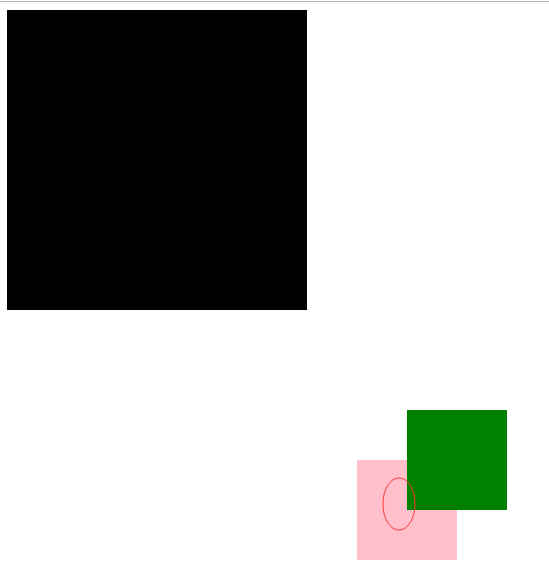
z-index
- z-index 值表示谁压着谁,数值大的压盖住数值小的,
- 只有定位了的元素,才能有z-index,也就是说,不管相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位,都可以使用z-index,而浮动元素不能使用z-index
- z-index值没有单位,就是一个正整数,默认的z-index值为0如果大家都没有z-index值,或者z-index值一样,那么谁写在HTML后面,谁在上面压着别人,定位了元素,永远压住没有定位的元素。
- 从父现象:父亲怂了,儿子再牛逼也没用
只要又定位的盒子,一定大于标准流的盒子
从父现象
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .lzy{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: black; position: absolute; z-index: 14; } .tl{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: yellow; position: absolute; z-index: 11; } .kimi{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; position: absolute; top: 400px; left: 400px; } .sd{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; position: absolute; top: 450px; left: 350px; z-index: 1000; /*优先级最高不是最前面*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="lzy"> <div class="kimi"></div> </div> <div class="tl"> <div class="sd"></div> </div> </body> </html>