复习及今日计划:
复习:




今日计划:

改变函数中this的指向:
apply 和call 方法的使用:


下面通过 apply 和 call 改变this 的指向。
将要改变的对象 放在第一个参数位置,就可以使得函数对象中的this 变为该对象。
apply 和 call 的区别:
如果函数对象中有参数,apply 是以一个数组传入的。
而call 是以不定参数(...)传入的。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 //改变函数对象 中this 的指向 8 function f1(name, age) { 9 console.log("Name:"+name+ " Age :"+age+" 此时的this "+ this); 10 } 11 f1("tom",18); 12 var obj = { 13 sex:"男" 14 }; 15 //使用apply /call 调用f1 函数 16 //f1 是个对象 17 // f1.apply(null,["tom",18]); //和 f1("tom",18); 没区别 18 // f1.call(null,"tom",18); //和 f1("tom",18); 没区别 19 20 f1.apply(obj,["tom",18]); //此时 f1中的this 就变为 了 obj 21 f1.call(obj,"tom",18); //此时 f1中的this 就变为 了 obj 22 23 </script> 24 </head> 25 <body> 26 27 28 </body> 29 </html>
对于方法也是如此,和函数完全一致。
总结:
使用时机:
我们想使用一个函数,但是希望它里面的this 是我们想用的对象。就可以使用它了!将我们想用的对象传入即可。
补充:
上述两个方法实际是在函数 的 构造函数(Function)的 原型中。
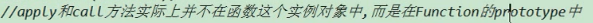

bind() 方法的使用:


使用时机:
和apply()/call() 一样。
我们想使用一个函数,但是希望它里面的this 是我们想用的对象。就可以使用它了!将我们想用的对象传入即可。
只不过一个是直接调用 该函数,而.bind() 将函数中的this替换为我们想用的对象之后,会返回一个该函数对象。
bind() 的应用:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 //函数对象 中this 的指向 8 function ShowRandom() { 9 //1-10 的随机数 10 this.num = parseInt(Math.random()*10 +1); 11 } 12 //添加原型方法 --- show1, show2 方法 13 ShowRandom.prototype.show1 = function () { 14 setInterval(function () { 15 this.show2(); 16 }.bind(this),100); //原本function(){} 匿名函数中的this 指向是 window ,但是通过bind 复制 产生了一个新的函数,而且里面的this变为了我们想要的this(实例对象) 17 }; 18 //上述代码也可如下:(推荐使用!) 注意bind() 的返回值 是个函数 19 /* 20 ShowRandom.prototype.show1 = function () { 21 // setInterval(this.show2,100); //这肯定是不可以。因为此时this 是window . 22 //我们想在想用 this.show2这个函数,而且想让它里面的this为 实例对象this 23 //如下即可。 24 setInterval(this.show2.bind(this),100); 25 }; 26 */ 27 28 ShowRandom.prototype.show2 = function () { 29 console.log(this.num); 30 }; 31 32 var showRandom = new ShowRandom(); 33 showRandom.show1(); 34 35 36 37 38 </script> 39 </head> 40 <body> 41 42 43 </body> 44 </html>
函数中的几个成员变量:


高阶函数:
函数作为参数:


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 //定时器 8 function Wrapper(fn){ 9 setInterval(function () { 10 console.log("这里是定时器!"); 11 fn(); 12 },1000); //1s 执行一次 指定的函数 。 13 } 14 Wrapper(function () { 15 console.log("Hello World!"); 16 }); 17 </script> 18 </head> 19 <body> 20 21 22 </body> 23 </html>
上面用到了包装。
函数作为返回值:
略。。。
如何获取一个数据的数据类型:
三种方式!!!
我们之前 想要知道一个数据的数据类型:
有以下两种方式:
1,通过typeof 获取
2,通过instanceof 来判断

下面看第三种:使用.call 借用 Object的一个方法: Object.prototype.toString() 方法。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 8 var ret = Object.prototype.toString(); //[object Object] 此时.toString()中的this是Object的实例对象。所以它的类型是Object 9 console.log(ret); 10 11 var arr = [1,2,3]; 12 //现在 ,我们想用下 Object.prototype.toString()的方法,希望它里面的this不是Object的实例对象,而是我们arr对象。 13 //于是尝试如下: 14 var ret2 = Object.prototype.toString.call(arr); 15 console.log(ret2); //[object Array] 于是,我们就可以知道,只要是用Object.prototype.toString()的方法,并且将这个方法中的this改为相应的对象,就可以得到这个对象的类型。 16 17 //再例如: 18 var str = "Hello World"; 19 console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(str)); //[object String] 20 21 22 23 </script> 24 </head> 25 <body> 26 27 28 </body> 29 </html>
只要将toString()中的this改为相应的对象,就能得到 该对象的数据类型了。
注:该方法的返回值是个string ! 即返回的结果 “ [object String] ” 是string类型的。
排序:

可以通过给它传入一个 函数 来解决。(即函数做为参数 )

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 var arr = [1,3,7,5,2,1,45,2,0,1]; 8 arr.sort(function (a, b) { 9 if(a>b) 10 return 1; 11 else if(a ==b) 12 return 0; 13 else 14 return -1; 15 }); 16 console.log(arr); 17 18 19 </script> 20 </head> 21 <body> 22 23 24 </body> 25 </html>
可是上面是数字间的排序,如果变为字符串呢?

字符串之所以可以比较是因为 ASCII 值。
可是如果是对象,对象之间是不能直接进行比较的。我可以通过对象的某个属性排序。
案例:排序 + 函数作为返回值 的应用:
现在有三个人,我们分别按照他们的姓名,年龄,身高进行排序。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 8 //现在有 三个人 9 function Person(name, age, height) { 10 this.name = name; 11 this.age = age; 12 this.height = height; 13 } 14 var p1 = new Person("eom",18,160); 15 var p2 = new Person("tgon",48,150); 16 var p3 = new Person("alex",28,175); 17 18 var arr = [p1,p2,p3]; 19 20 // 遍历输出 21 function printArr() { 22 for (var i =0;i<arr.length;i++){ 23 console.log("Name: "+arr[i].name+" Age: "+arr[i].age+" Height: "+arr[i].height); 24 } 25 } 26 printArr(); 27 28 //1,现在按照 "人的名字" 进行排序输出 29 console.log("------------------"); 30 arr.sort(function (obj1,obj2) { 31 if(obj1.name > obj2.name) 32 return 1; 33 else if(obj1.name == obj2.name) 34 return 0; 35 else 36 return -1; 37 }); 38 printArr(); 39 40 41 //2,现在按照 "人的年龄" 进行排序输出 42 console.log("------------------"); 43 arr.sort(function (obj1,obj2) { 44 if(obj1.age > obj2.age) 45 return 1; 46 else if(obj1.age == obj2.age) 47 return 0; 48 else 49 return -1; 50 }); 51 printArr(); 52 53 //3,现在按照 "人的身高" 进行排序输出 54 console.log("------------------"); 55 arr.sort(function (obj1,obj2) { 56 if(obj1.height > obj2.height) 57 return 1; 58 else if(obj1.height == obj2.height) 59 return 0; 60 else 61 return -1; 62 }); 63 printArr(); 64 65 </script> 66 </head> 67 <body> 68 69 70 </body> 71 </html>
但是,上述代码的冗余性太高了。
下面利用 函数作为返回值来解决。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 8 //现在有 三个人 9 function Person(name, age, height) { 10 this.name = name; 11 this.age = age; 12 this.height = height; 13 } 14 var p1 = new Person("eom",18,160); 15 var p2 = new Person("tgon",48,150); 16 var p3 = new Person("alex",28,175); 17 18 var arr = [p1,p2,p3]; 19 20 // 遍历输出 21 function printArr() { 22 for (var i =0;i<arr.length;i++){ 23 console.log("Name: "+arr[i].name+" Age: "+arr[i].age+" Height: "+arr[i].height); 24 } 25 } 26 printArr(); 27 28 //1,现在按照 "人的名字" 进行排序输出 29 console.log("------------------"); 30 function solution(attr){ 31 return function (obj1,obj2) { 32 if(obj1[attr] > obj2[attr]) 33 return 1; 34 else if(obj1[attr] == obj2[attr]) 35 return 0; 36 else 37 return -1; 38 } 39 } 40 arr.sort(solution("name")); 41 printArr(); 42 43 //2,现在按照 "人的年龄" 进行排序输出 44 console.log("------------------"); 45 arr.sort(solution("age")); 46 printArr(); 47 48 //3,现在按照 "人的身高" 进行排序输出 49 console.log("------------------"); 50 arr.sort(solution("height")); 51 printArr(); 52 </script> 53 </head> 54 <body> 55 56 57 </body> 58 </html>
可见,输出没变,代码少了很多。
作用域_作用域链_预解析:
作用域:

所以,下面代码是可以输出的。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 while (true){ 8 var num = 0; 9 break; 10 } 11 console.log(num); //输出是 0 12 13 </script> 14 </head> 15 <body> 16 17 18 </body> 19 </html>
但是,在函数内部的 是不能输出的。(函数内 是局部作用域!)如下代码:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 function f(){ 8 var num = 0; 9 } 10 console.log(num); //输出是 报错 num is not defined! 11 12 </script> 13 </head> 14 <body> 15 16 17 </body> 18 </html>
作用域链:


预解析:


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 1变量声明 的提升 8 console.log(num); //此时的输出为 undefined ! 9 var num = 100; 10 11 // 2函数声明 的提升 12 func(); 13 function func() { 14 console.log("我是个函数"); 15 } 16 17 func1(); //此时,就没有 函数声明 的提升 而是变量的声明提前。 func1是 undefined! func1不是个函数 18 var func1 = function () { 19 console.log("我也是函数"); 20 } 21 </script> 22 </head> 23 <body> 24 25 26 </body> 27 </html>
闭包:


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 1,函数模式的闭包 :在一个函数中有一个函数 ,内层函数可以访问外层函数作用域中的变量 。 8 function f1() { 9 var num = 0; 10 function f2() { 11 console.log(num); 12 } 13 f2(); 14 } 15 f1(); 16 17 // 2,对象模式的闭包 :在一个函数中有个对象。对象可以访问外层函数作用域中的变量 。 18 function f3() { 19 var num = 10; 20 var obj = { 21 age:num 22 }; 23 console.log(obj.age); 24 } 25 f3(); 26 27 28 29 30 </script> 31 </head> 32 <body> 33 34 35 </body> 36 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 1,函数模式 闭包 8 function f1() { 9 var num =10; 10 return function () { 11 console.log("Hello World"); 12 return num; 13 } 14 } 15 16 var ret1 = f1(); 17 var ret2 = ret1(); 18 console.log(ret2); 19 20 // 2 对象模式闭包 21 function f2() { 22 var num = 20; 23 return { 24 age:num 25 } 26 } 27 var obj = f2(); 28 console.log(obj.age); 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 </script> 38 </head> 39 <body> 40 41 42 </body> 43 </html>
之所以,闭包,就是将数据封存起来,起到了缓存的目的。
闭包小案例:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 1 8 function f1() { 9 var num = 10; 10 num ++; 11 return num; 12 } 13 console.log(f1()); //11 14 console.log(f1()); //11 15 console.log(f1()); //11 16 17 // 2 18 function f2() { 19 var num = 10; 20 return function () { 21 num ++; 22 return num; 23 } 24 } 25 var ret = f2(); 26 console.log(ret()); //11 27 console.log(ret()); //12 28 console.log(ret()); //13 //原因是 ret 对象中 缓存的num 每次都不会再重新赋值 10 啦! 29 30 31 </script> 32 </head> 33 <body> 34 35 36 </body> 37 </html>
可以看出,闭包有缓存的功能。
以后需要缓存一个变量的话,可以在闭包中返回!
如下:

通过闭包产生相同的随机数:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <script> 7 // 1 8 function showRandom() { 9 var num = parseInt(Math.random()*10 + 1); 10 return num; 11 } 12 console.log(showRandom()); 13 console.log(showRandom()); 14 console.log(showRandom()); //随机数产生代码,执行了三次。 15 16 // 2那么如何产生三个相同的 随机数值呢? 17 function showRandom2() { 18 var num = parseInt(Math.random()*10 +1); 19 return function () { 20 return num; 21 } 22 } 23 var ret = showRandom2(); 24 console.log(ret()); 25 console.log(ret()); 26 console.log(ret()); //虽然调用了 三次,其实真正产生随机数只是执行了一次。 27 28 29 30 31 32 </script> 33 </head> 34 <body> 35 36 37 </body> 38 </html>

闭包分析:
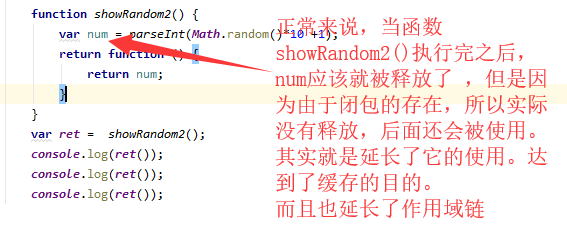
闭包的优点:缓存了数据。
闭包的缺点:导致不能及时的释放变量的内存空间。
闭包案例:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 <style> 7 ul{ 8 list-style-type: none; 9 } 10 li{ 11 float: left; 12 margin-left: 10px; 13 } 14 img{ 15 width: 200px; 16 /*height: 180px;*/ 17 } 18 input { 19 margin-left: 30%; 20 } 21 22 </style> 23 </head> 24 <body> 25 <ul> 26 <li><img src="images/slidepic1.jpg" alt=""><br><input type="button" value="赞(1)"></li> 27 <li><img src="images/slidepic2.jpg" alt=""><br><input type="button" value="赞(1)"></li> 28 <li><img src="images/slidepic3.jpg" alt=""><br><input type="button" value="赞(1)"></li> 29 <li><img src="images/slidepic4.jpg" alt=""><br><input type="button" value="赞(1)"></li> 30 </ul> 31 <script> 32 //获取所有的按钮 通过 tagName 33 function getByTagName(tagName) { 34 return document.getElementsByTagName(tagName); 35 } 36 /* 1 37 var btnObjs = getByTagName("input"); 38 for (var i =0;i<btnObjs.length;i++ ){ 39 btnObjs[i].onclick = function () { 40 var num = parseInt(this.value.slice(2)); //[2,) 41 this.value = "赞("+(++num)+")"; 42 }; 43 } 44 45 */ 46 47 48 //2 使用闭包完成上述功能, 闭包缓冲数据。多次使用! 推荐使用 49 function getValue() { 50 var num = 1; 51 return function () { 52 this.value = "赞("+(++num)+")"; 53 } 54 } 55 // 56 var btnObjs = getByTagName("input"); 57 for (var i =0;i<btnObjs.length;i++ ){ 58 btnObjs[i].onclick = getValue(); 59 } 60 61 62 </script> 63 64 65 66 67 </body> 68 </html>
沙箱:
利用自调用函数来 形成 沙箱。


沙箱小案例:

以后的代码可以直接都放到沙箱中,这样 代码之间就很少会有冲突了。
例如:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <input type="button" value="点我" id="btn"> 9 <script> 10 //点击按钮 弹出对话框 11 (function(){ 12 document.getElementById("btn").onclick = function () { 13 alert("我出来了"); 14 } 15 })(); 16 </script> 17 </body> 18 </html>
递归:

递归案例:求1-n的和:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <script> 9 10 function getSum(n) { 11 if( n == 1){ 12 return 1; 13 } 14 return n + getSum(n-1); 15 } 16 var res = getSum(100); 17 console.log(res); //5050 18 19 </script> 20 </body> 21 </html>
递归案例:求一个数字各个位数上的和:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <script> 9 10 function getSum(n) { 11 // if(Math.floor(n /10) == 0){ 12 if(n < 10){ //也可以这样,都一样。 13 return n; 14 } 15 return n %10 + getSum(Math.floor(n/10)); 16 } 17 console.log(getSum(73636)); //25 18 19 </script> 20 </body> 21 </html>
递归案例:求斐波那契数列 的第n项的值:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <script> 9 10 function getFib(n) { 11 if(n == 1 || n ==2){ 12 return 1; 13 } 14 return getFib(n-1) + getFib(n-2); 15 } 16 console.log(getFib(10)); //第十项的值为:55 17 // 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 ! 18 19 </script> 20 </body> 21 </html>

