IO概述:

File:

File 类的出现:
File 类 在java.io 中!

这个类 是平台无关的。它既可以用于 UNIX 系统,也可以用Windows

一些相关的名词:
文件:file
目录:directory
路径:path
File 类静态的成员变量:
第一类 路径分隔符:
static String pathSeparator
它是与系统路径有关的分隔符,例如环境变量的配置中,我们必须要以分号 结束。就是它!
为了方便将其表示成了 String!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 public class Test { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //File 类的静态成员变量 8 String ret = File.pathSeparator; 9 System.out.println(ret); //输出是个 分号; 它表示的是一个路径 的结束! 10 //还有它只是在windows 平台是这样的结果。Linux 上输出的是 : 冒号 ! 11 12 } 13 }
static char pathSeparatorChar
它返回的是个char ,不过,我们一般喜欢返回值是字符串,所以就用上面的了。不过上面的源码其实就是等于char + "" 变为的字符串!
查看源码:

第二类 名称分隔符:
它指的是路径里 的每个层级的 分隔符。
在Win中是 ,在 Linux上 是 /

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 public class Test { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //File 类的静态成员变量 8 String ret = File.separator; 9 System.out.println(ret); //输出是个 它表示的是一个层级目录的结束 10 //windows 上是 Linux 上是/ 11 12 } 13 }
总结:在做与系统无关的时候,可能会用到上面这两个静态变量!
File 类的 构造方法:
三种重载方式:

1,第一种 File(String pathname)
传递的pathname ,既可以写到文件夹,也可以到一个具体的文件。
然后将路径封装成 File类型对象。

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.nio.file.Files; 5 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 // File file = new File("d:\test"); 10 // File file = new File("d:\Test"); 11 File file = new File("d:\TEST");//Win平台不区分大小写,Linux就区分了! 12 System.out.println(file); 13 /* 14 * 输出 15 * d: est 16 * */ 17 18 // 也可以直接写到具体的文件 19 File file1 = new File("d:\test\a.txt"); 20 System.out.println(file1); //还有他们的输出不是 地址,说明File 重写了.toString() 21 22 23 24 25 } 26 }
注:Win平台不区分大小写,Linux区分! 不过最好一致!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.nio.file.Files; 5 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 File file = new File("d:\test02"); //此路径不存在 10 System.out.println(file); //它照样有输出,也不报错。 d: est02 11 //这说明 构造器是不作判断的。它只是将路径变为 File的对象! 12 13 // File 中 有可以判断路径是否存在的方法 .exists() 14 boolean ret = file.exists(); 15 System.out.println(ret); //false 16 } 17 }
2,第二种 File(String parent,String child)
Create a new File instance from a parent pathname string and a child pathname string!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.nio.file.Files; 5 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 File file = new File("d:","test"); 9 System.out.println(file); 10 11 12 } 13 }
它相对于第一种构造函数来说,它更灵活。既可以 单独控制 父路径,也可以单独控制子路径!
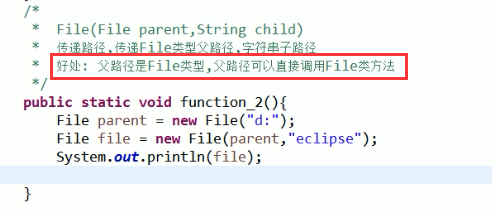
3,第三种 File(File parent ,String child)
它是将一个已经初始化好了的File 对象,再给它加上个子路径!
File 类的 创建文件 -- .createNewFile() :
它只能创建文件,不能创建文件夹。如果已经存在文件,返回false !
它的创建的具体文件路径在 File的构造方法中给出!
注意:它要声明可能存在的IO 异常! throws IOExceptions

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 public class Test { 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 7 // File file = new File("d:\b.txt"); 8 File file = new File("d:\b"); //此时创建的也不会是文件夹,而是文件!!! 9 10 11 boolean ret = file.createNewFile(); 12 /* 13 * 该函数只能创建文件,不能创建文件夹! 14 * 而且,如果文件已经存在则返回false 15 * */ 16 System.out.println(ret); 17 18 19 } 20 }
File 类的 创建文件夹 --- .mkdir() 和 .mkdirs() :
.mkdir 只能创建 单层文件夹,.mkdirs() 多级创建文件夹 ,二者都不能创建文件。
它的创建的具体文件夹 路径在 File的构造方法中给出!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 public class Test { 6 public static void main(String[] args){ 7 File file = new File("d:\aaa"); 8 9 boolean ret = file.mkdir(); 10 //创建 单层文件夹! 11 System.out.println(ret); 12 13 File file1 = new File("d:\test\a\b"); 14 //创建多级 文件夹! 15 boolean ret1 = file1.mkdirs(); 16 System.out.println(ret1); 17 18 19 } 20 }
一般使用.mkdirs() 就可以了,因为它既可以创建单层文件夹也可以创建多层文件夹!
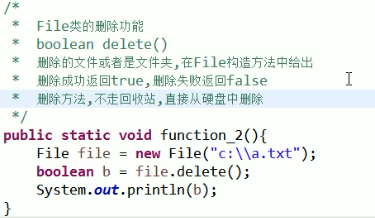
File 类的 删除文件 文件夹 .delete() :

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 4 public class Test { 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 File file = new File("D:\test\a\b"); 7 boolean ret = file.delete(); 8 System.out.println(ret); //true 9 } 10 }
而且要十分注意到,删除是直接从硬盘中清除,不会走回收站!
File 类 的 getName() 获取 路径的最后部分:

File 类 的 length() 获取 文件的字节数:

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 4 public class Test { 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 File file = new File("D:\aa.txt"); 7 8 long res = file.length(); //获取该文件的字节数 9 System.out.println(res); //41736 10 11 File dir = new File("d:\images"); 12 long res1 = dir.length(); 13 System.out.println(res1); // 4096 文件夹的字节是4096 14 15 File file1 = new File("d:\不存在的文件.txt"); 16 long res2 = file1.length(); 17 System.out.println(res2); //0 不存在的文件的字节数为 0 18 19 20 21 } 22 }
File 类 获取绝对路径:
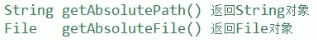
如果写的是个 相对路径,是相对于当前工程的 根目录。
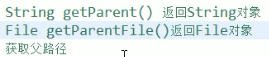
File 类 获取父路径:
File 类 判断功能:

它既可以判断是否存在文件,也可以判断是否存在文件夹!

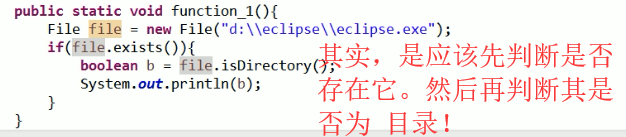
除了 isDirectory () 外,还有 isFile(); 二者用一个就好了!

File 类 .list() 遍历 文件夹功能(不递归):


推荐是用 返回值是 File 的,它的内容比较全!!!
File 类 递归遍历 文件夹的所有内容(递归):

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 4 public class Test { 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 File file = new File("D:\aaa"); 7 8 printAllDirs(file); 9 } 10 public static void printAllDirs(File file){ 11 System.out.println(file+" DIR"); //当前目录的路径!!! 12 13 //调用 listFiles() 对目录遍历 14 File [] arrs = file.listFiles(); 15 for (File f:arrs ){ 16 if(f.isDirectory()){ 17 printAllDirs(f); //1,递归链条 18 } 19 else { //2,终止条件 20 System.out.println(f); 21 System.out.println("=========="); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }
File 类 获取系统的所有根目录:

File 类 过滤器:
前面的listFiles() 里面没有参数!

将想要的过滤出来!

因为FileFilter接口没有 已经实现好的实现类,所以我们要自定义实现类!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 4 public class Test { 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 File file = new File("D:\aaa"); 7 8 File[] fileArrs = file.listFiles(new MyFilter()); 9 for (File f:fileArrs){ 10 System.out.println(f); 11 } 12 13 } 14 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileFilter; 5 6 public class MyFilter implements FileFilter { 7 public boolean accept(File pathname){ 8 return true; 9 } 10 }
文件过滤器 原理分析:

如果使用file.listFiles() 时候,使用了文件过滤器!
即给file.listFiles() 传入一个参数----MyFliter 对象。
这个对象会自动调用它的accept(File pathname) 方法。调用的时候会将构建file时候的路径中的文件 依次传入!!!
所以最终的所有文件路径都会传到 MyFliter中的accept() 方法中。
如果accept() 返回为 true,那么就将其加入到数组中,反之不加入。

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 4 public class Test { 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 File file = new File("D:\aaa"); 7 8 File[] fileArrs = file.listFiles(new MyFilter()); 9 for (File f:fileArrs){ 10 System.out.println(f); 11 } 12 13 } 14 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileFilter; 4 5 public class MyFilter implements FileFilter { 6 public boolean accept(File pathname){ 7 if(pathname.getName().endsWith(".txt")){ 8 return true; 9 }else { 10 return false; 11 } 12 } 13 }
这时就只能所有的.txt 文件才能显示出来了。
递归:
递归概念:
递归,指在当前方法内调用自己的这种现象

递归的分类:

递归的注意事项:

递归求和运算 求阶乘:


1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int res = getSum(100); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 } 8 public static int getSum(int n){ 9 if(n == 0) // 1终止条件 10 return 0; 11 /* 12 * 终止条件的 多种形式 13 if(n == 1) 14 return 1; 15 if(n ==2 ) 16 return 3; 17 if(n ==3 ) 18 return 6; 19 ... 20 * */ 21 22 else // 2递归链条 23 return n + getSum(n-1); 24 } 25 }
但是,递归的缺点是 太慢了,多次进栈!!!

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int res = getFactorial(3); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 } 8 public static int getFactorial(int n){ 9 if(n == 1) 10 return 1; 11 else 12 return n*getFactorial(n-1); 13 } 14 }
斐波那契数列:

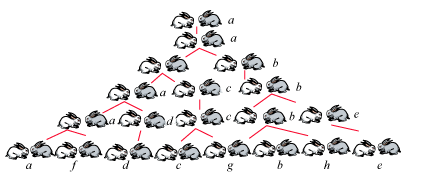
参考博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zkfopen/p/11245857.html

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 int res = getNum(12); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 } 8 public static int getNum(int month){ 9 if(month == 1 || month ==2){ 10 return 1; 11 } 12 else{ 13 return getNum(month -2) + getNum(month -1); 14 } 15 } 16 }
遍历目录下的 所有 .txt 文件:

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 File file = new File("d:\aaa"); 6 printFileUnderDir(file); 7 } 8 public static void printFileUnderDir(File dir){ 9 System.out.println(dir); 10 File [] files = dir.listFiles(new MyFilter()); //过滤出 txt 文件 ! 11 for (File f:files){ 12 if(f.isDirectory()){ 13 printFileUnderDir(f); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.println(f); 16 System.out.println("============"); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 22 23 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo01; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileFilter; 4 5 public class MyFilter implements FileFilter { 6 public boolean accept(File pathname){ 7 if(pathname.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".txt") || pathname.isDirectory()){ //toLowerCase 是先全部 转为小写 再判断 8 return true; 9 }else { 10 return false; 11 } 12 } 13 }
