异常:
异常的继承体系:

Throwable 在java.lang中。
Throwable 是所有错误或异常的超类,所以它下面有两个大的子类---Error错误类,---Exception异常类。(我们平时不会关心错误,而是关心异常类。)
Throwable(类) <--Exception (类)
<--Error (类)
Error 和 Exception 的区别:
什么是错误,什么是异常呢?
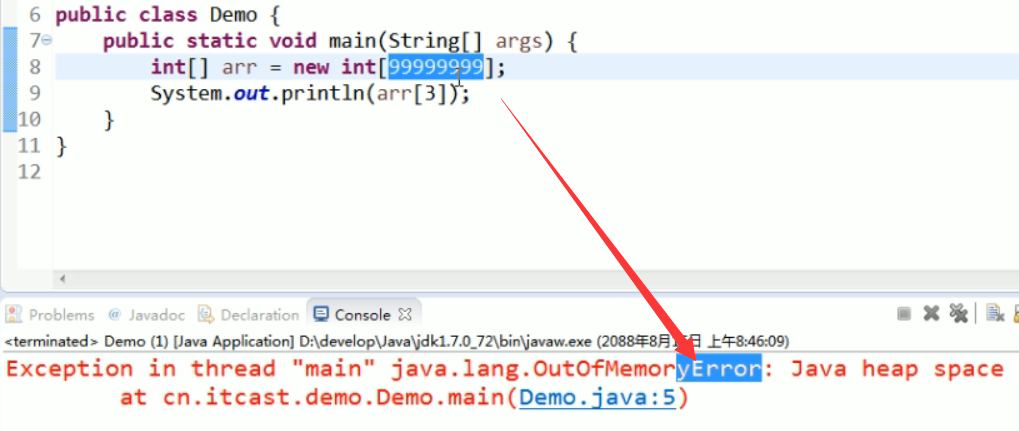
Error 一般都是大问题,例如,开辟的内存过大之类,这样的一般都要修改代码!
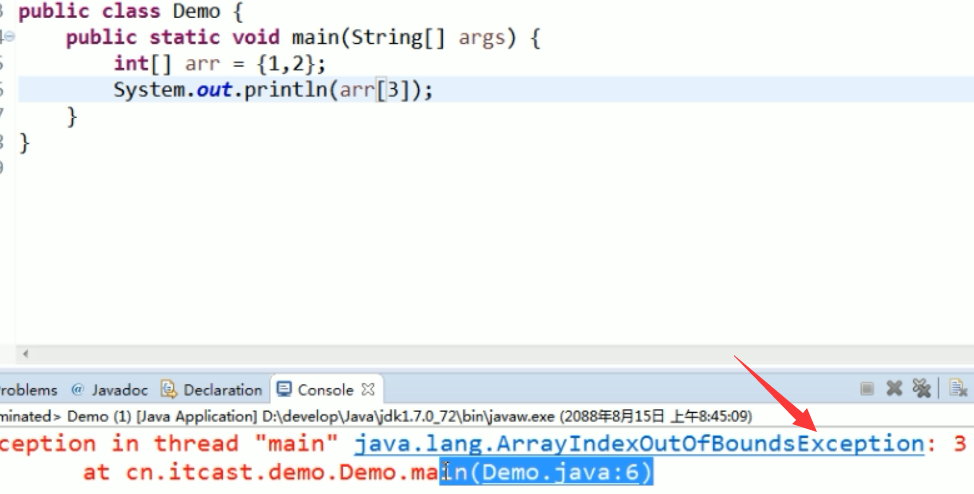
Exception 一般都是小问题,例如,数组越界之类的,这样的一般将异常处理掉就可以了。


错误在运行的时候才会发生。
Exception 异常,的解决方法是:将异常处理掉,就可以了。
Error 错误,的解决方法是: 修改程序。
所以,我们一般处理的也都是异常,如果是Error 就只能改代码了。
在Exception异常 下面还有个子类 --RuntimeException 类。
我们主要说 Exception 和 RuntimeException !
异常对象的产生原因 和 处理方式:

如果最终 main 到了 JVM 的话,
它又做了两件事:
1,将异常信息,以红色字体输出到控制台。
2,将程序停止结束。
如果在这个过程中,有人处理 这个异常的话,就不会出现抛到上一级的情况,那么代码也就可以继续执行了。
注: 当抛出到上一级的时候,剩余的程序都不会再执行了。
方法内部抛出异常的 关键字 throw :


抛出的对象,必须是Exception 或者 它的子类对象。

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int arr[] = {1,2,3}; 6 int a = getNum(arr); 7 System.out.println(a); 8 9 } 10 public static int getNum(int []arr){ 11 if(arr == null){ 12 throw new Exception("传递的数组不存在"); 13 } 14 if(arr.length == 0){ 15 throw new Exception("数组中为任何元素"); 16 } 17 int ret = arr[3]; 18 return ret; 19 } 20 21 22 }
此时的程序还是有bug 的。继续看下面:
声明异常的 关键字 throws :
上面的throw + 对象是用来抛出异常的。
这里的throws是用来写在方法的声明上的。声明此方法可能会出现异常。

当调用者调用一个可能出现异常的方法的时候,它就必须处理该异常,如果不处理就会编译失败!
例如:

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int arr[] = {1,2,3}; 6 int a = getNum(arr);//此时main 调用了可能出现异常的方法getNum,但是却没有处理该异常。于是就编译失败了! 7 System.out.println(a); 8 9 } 10 public static int getNum(int []arr) throws Exception{ 11 if(arr == null){ 12 throw new Exception("传递的数组不存在"); 13 } 14 if(arr.length == 0){ 15 throw new Exception("数组中为任何元素"); 16 } 17 int ret = arr[3]; 18 return ret; 19 } 20 21 22 }
注:Exception 类的异常必须要声明异常,但是RuntimeException及其子类不用声明异常
异常的处理方式 try -catch-finally :
之前,遇到异常都是一个字:往上抛,最后抛给了JVM,然后程序就终止了。
下面我们使用异常的另一个 处理方式 try -catch!
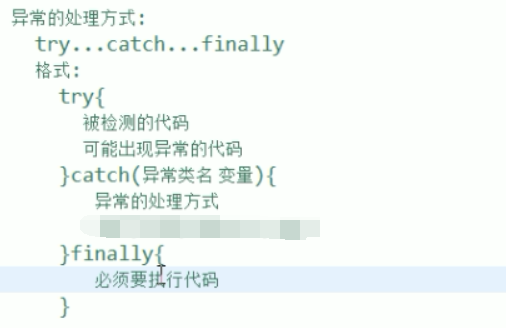
catch 中执行之后,就是处理了异常了,就不会往上面抛了。

注:finally 是一定会执行的。
异常的处理方式 多catch 捕获:
指的是调用的方法可能有多个 异常产生,这时可以用多个catch 。

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 // int arr[] = null; 6 int arr[] = new int[0]; 7 try { 8 int a = getNum(arr); 9 System.out.println(a); 10 }catch (NullPointerException e){ 11 System.out.println(e); 12 }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ 13 System.out.println(e); 14 } 15 } 16 public static int getNum(int []arr)throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException { 17 //因为传来的参数是 引用类型,因此肯定要判断是否为空 18 if(arr == null){ 19 throw new NullPointerException("数组不存在!"); 20 } 21 if(arr.length <=3){ 22 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组没有3索引"); 23 } 24 25 int ret = arr[3]; 26 return ret; 27 } 28 29 30 }
catch() 的顺序:
1,平级之间的异常( 例如NullPointerException 和 NoSuchElementExceptino 和 ArrayIndexOfBoundsException):

平级之间,书写是可以没有顺序的。
2,有继承关系的异常(NullPointerException 和 Exception):

平级之间,书写是有顺序的。
高级应该写在下面。
它的原因是多态调用。 如果将Exception写在上面的话,那么下面的异常就永远也起不到作用了!
关于 try-except-finally 中的finally :

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 try { 6 func(0); //产生异常 7 // func(1);//不产生异常! 8 }catch (Exception e){ 9 System.out.println(e); 10 }finally { 11 System.out.println("无论产生异常与否,我是一定会被执行的“"); 12 } 13 14 15 } 16 public static void func(int a) throws Exception{ 17 if( a == 0){ 18 throw new Exception("异常产生"); 19 } 20 } 21 22 }
finally 只有一种情况不执行,就是用代码将 JVM 停止:System.exit(0);

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 try { 6 // func(0); //产生异常 7 func(1);//不产生异常! 8 System.exit(0); 9 10 }catch (Exception e){ 11 System.out.println(e); 12 System.exit(0); 13 }finally { 14 System.out.println("无论产生异常与否,我是一定会被执行的“"); 15 } 16 17 18 } 19 public static void func(int a) throws Exception{ 20 if( a == 0){ 21 throw new Exception("异常产生"); 22 } 23 } 24 25 }
总结:一般finally 都是一定执行的,无论异常产生与否,除非你刻意不让它执行!
那么finally 的作用是什么呢?它可以释放资源! 后面IO流中会有涉及!
try-catch 和 throws 两种处理方式:
调用者调用一个可能产生异常的方法的时候,它必须要做出处理,
它有两种选择,
一是不管它,在自己函数声明的地方加上throws,这时,如果产生异常,异常会自动的抛给上一级,最后到JVM。
二是使用try-catch ,它会处理异常,然后继续执行程序。

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 5 func_P(); 6 } 7 public static void func_P() throws Exception{ 8 func(0); 9 } 10 public static void func(int a) throws Exception{ 11 if( a == 0){ 12 throw new Exception("异常产生"); 13 } 14 } 15 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 func_P(); 6 } 7 public static void func_P() { 8 try { 9 func(0); 10 }catch (Exception e){ 11 System.out.println(e); 12 } 13 } 14 public static void func(int a) throws Exception{ 15 if( a == 0){ 16 throw new Exception("异常产生"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
下面代码比上面好,下面代码不会终止程序,而上面代码会终止程序!
因此处理异常,我们应该使用try-catch !
注意:
对于可能会产生异常的方法,对于Exception 异常,方法自己 必须要声明该异常,但是对于RuntimeException 及其子类的异常,可以不声明!!!
异常 分类:
异常分为 编译时异常 和 运行时异常!!!
运行时异常 指的是 RuntimeException 类及其 子类 ,其他的基本都是编译时异常。
补:异常的继承关系:
Throwable(类) <--Exception (类) <- RuntimeException 类。
<--Error (类)
运行时异常是不需要进行 throws语句声明的!即我们前面说的----对于RuntimeException 及其子类,可以不进行throws声明。


调用也不需要对其处理,
具体代码如下:

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 func(0); //2 调用者也不需要进行处理 ! 6 } 7 public static void func(int a){ //1,这不需要写 throws声明语句! 8 if( a == 0){ 9 throw new RuntimeException("异常产生"); 10 } 11 } 12 }
那么,它这样设计的目的是什么呢?
是因为运行异常本身,就不能发生,这时候要做的是停止程序,修改源代码。
因为运行异常一旦发生,后面的代码在执行是没有意义的。
运行时异常就是让程序人员停下来改代码的。

它和其他的异常都不太一样!
运行时异常和 其他异常的区别:

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 try{ 6 func(0); 7 }catch (Exception e){ 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 } 11 public static int func(int a) throws Exception{ 12 if(a == 0){ 13 throw new Exception("异常!"); 14 } 15 return 0; 16 } 17 } 18 /* 19 * 一般异常 输出 20 java.lang.Exception: 异常! 21 at cn.zcb.demo05.Test.func(Test.java:13) 22 at cn.zcb.demo05.Test.main(Test.java:6) 23 24 Process finished with exit code 0 25 * */

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 func(0 ); //调用者不需要进行 try catch !!! 6 } 7 public static int func(int a) { 8 if(a == 0){ 9 throw new RuntimeException("异常!"); 10 } 11 return 0; 12 } 13 } 14 /* 15 * 运行时异常 输出 16 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 异常! 17 at cn.zcb.demo05.Test.func(Test.java:9) 18 at cn.zcb.demo05.Test.main(Test.java:5) 19 20 Process finished with exit code 1 21 * */
子类重写父类的方法 的异常问题:


总结:
一句话:父类抛了(声明)异常,子类可以抛(声明)但不能抛(声明)过头;父类没有(声明)抛,子类永远不能(声明)抛。
异常和错误 的超类 ---Throwable 类 的三个方法:
这三个方法都是和 “信息” 有关系,这个“信息” 是指的是 出现在输出框中的红色字!
String getMessage(); //对异常信息的简短描述
String toString(); 对异常信息的详细描述
void printStackTrace(); //将异常信息 追踪到标准的 错误流 ! 异常信息是最详细的(也是JVM默认的调用方法!)。

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 try { 6 func(0); 7 }catch (Exception e){ 8 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //简短异常信息 9 System.out.println(e.toString()); //异常信息 详细描述 !相对上面 有了具体哪个类 10 e.printStackTrace(); //异常信息,最详细! 11 } 12 13 } 14 public static void func(int a) throws Exception{ 15 if( a == 0){ 16 throw new Exception("异常产生"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
自定义异常:



1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int avg = getAvg(10,20,30,40); 6 System.out.println(avg); 7 8 } 9 /** 10 * 当计算成绩时候,如果传递是 负数,应该停止再计算了! 需要抛出异常! 11 * 但是,由于Java 中没有现成的 关于负数的异常,所以我们自定义异常! 12 */ 13 public static int getAvg(int ...score){ 14 int sum = 0; 15 for (int s:score){ 16 sum+= s; 17 } 18 return sum/score.length; 19 } 20 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int res = getAvg(10,20,30,40,-10); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 8 } 9 public static int getAvg(int...scores){ 10 int sum = 0; 11 for (int score:scores){ 12 if(score <0 ){ 13 throw new MyException("负数异常,成绩不能为负数!"); 14 } 15 sum += score; 16 } 17 return sum/scores.length; 18 } 19 }

package cn.zcb.demo05; //关于 负数的异常,它比较适合使用 RuntimeException 异常, //它只要是有 负数,我就直接把 你的程序给你停止(exit 码非0)了! public class MyException extends RuntimeException { //必须要 继承(继承Throwable 或其子类!),因为这样才会有可抛性! public MyException(){}; public MyException(String s){} }
此时的问题是 当异常产生时候,没有输出 我们new 时候的String。
上面也说了,我们这时候应该将这个参数传给super() ,传给上一级,它会一级一级的传,最后是在超类 Throwable中最终将这个字符串 输出到控制台!
代码最终如下:

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int res = getAvg(10,20,30,40,-10); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 8 } 9 public static int getAvg(int...scores){ 10 int sum = 0; 11 for (int score:scores){ 12 if(score <0 ){ 13 throw new MyException("负数异常,成绩不能为负数!"); 14 } 15 sum += score; 16 } 17 return sum/scores.length; 18 } 19 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 //关于 负数的异常,它比较适合使用 RuntimeException 异常, 4 //它只要是有 负数,我就直接把 你的程序给你停止(exit 码非0)了! 5 public class MyException extends RuntimeException { 6 //必须要 继承(继承Throwable 或其子类!),因为这样才会有可抛性! 7 public MyException(){ 8 super(); 9 } 10 public MyException(String s){ 11 super(s); 12 } 13 14 }
注:大部分的异常都是 RuntimeException 异常!
当然,也可以不自定义异常,如下代码:

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int res = getAvg(10,20,30,40,-10); 6 System.out.println(res); 7 8 } 9 public static int getAvg(int...scores){ 10 int sum = 0; 11 for (int score:scores){ 12 if(score <0 ){ 13 throw new RuntimeException("负数异常,成绩不能为负数!"); 14 } 15 sum += score; 16 } 17 return sum/scores.length; 18 } 19 }

