脑筋急转弯:

答案一:
经理生成个随机数num,a员工加上随机数再告诉员工b,依次类推,最会得到个值val ,
就可以求出平均值:
avg = (val -num)/3
答案二:
设计个程序,让每个员工都输入自己的工资,然后求和平均即可。
链表概述:

预备知识:链表基础:
基础(c语言版)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 struct ListNode { 3 int val; 4 struct ListNode* next; 5 }; 6 7 int main() { 8 struct ListNode node1; 9 struct ListNode node2; 10 struct ListNode node3; 11 struct ListNode node4; 12 struct ListNode node5; 13 14 node1.val = 10; 15 node2.val = 20; 16 node3.val = 30; 17 node4.val = 40; 18 node5.val = 50; 19 20 node1.next = &node2; 21 node2.next = &node3; 22 node3.next = &node4; 23 node4.next = &node5; 24 node5.next = NULL; 25 26 struct ListNode *pCurrent = &node1; 27 while (pCurrent != NULL) { 28 printf("%d ", pCurrent->val); 29 pCurrent = pCurrent->next; 30 } 31 return 0; 32 } 33 /* 34 10 35 20 36 30 37 40 38 50 39 40 41 */
基础(c++版)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 struct ListNode { 3 int val; 4 struct ListNode * next; 5 }; 6 7 int main(){ 8 9 ListNode node1; 10 ListNode node2; 11 ListNode node3; 12 ListNode node4; 13 ListNode node5; 14 15 node1.val = 10; 16 node2.val = 20; 17 node3.val = 30; 18 node4.val = 40; 19 node5.val = 50; 20 21 node1.next = &node2; 22 node2.next = &node3; 23 node3.next = &node4; 24 node4.next = &node5; 25 node5.next = NULL; 26 27 ListNode * pCurrent = &node1; 28 while(pCurrent != NULL){ 29 printf("%d ",pCurrent->val); 30 pCurrent = pCurrent->next ; 31 } 32 return 0; 33 }
二者的主要区别是:c++ 可以没有 struct !

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 //链表相关的基础 5 struct ListNode { 6 int val; 7 struct ListNode * next; 8 }; 9 10 struct ListNode * ListInit(){ 11 struct ListNode * head =(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 12 head->val = 0; 13 head->next = NULL; 14 15 return head; 16 } 17 void printList(struct ListNode * head){ 18 while(head != NULL){ 19 printf("Val: %d ",head->val,head->next); 20 head = head->next; 21 } 22 } 23 void addOneNode(struct ListNode * head,int val){ 24 struct ListNode * newNode =(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 25 newNode->val = val; 26 newNode->next = NULL; 27 28 //遍历链表到 尾部 29 struct ListNode * temp = head; 30 while(temp->next !=NULL){ 31 temp = temp->next; 32 } 33 temp->next = newNode; 34 } 35 36 int main(){ 37 38 struct ListNode * head = ListInit(); //head存数据(默认存的值为0) 39 head->val = 1; //这里将默认的head.val =0 变为1 40 for(int i =2;i<10;++i){ 41 addOneNode(head,i); 42 } 43 printList(head); 44 return 0; 45 }
例1-a:链表逆序-a (leetcode 编号 206)

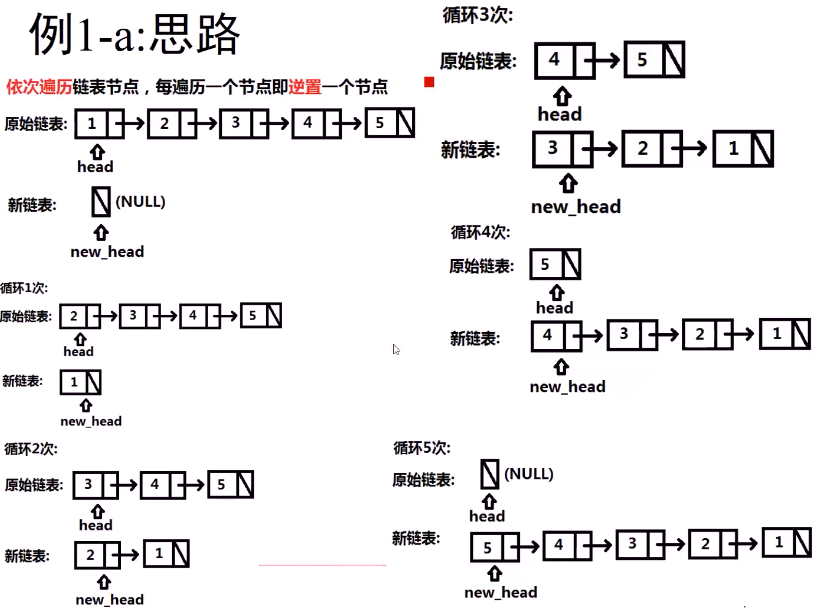
注:不允许申请额外的空间。
自己的代码:(缺点是:当head 为空的时候不能通过, 而且最后一个还要在循环外另外写一下!!! 优点是:它没有在循环中重复声明pNext变量)

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 //链表相关的基础 5 struct ListNode { 6 int val; 7 struct ListNode * next; 8 }; 9 10 struct ListNode * ListInit(){ 11 struct ListNode * head =(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 12 head->val = 0; 13 head->next = NULL; 14 15 return head; 16 } 17 void printList(struct ListNode * head){ 18 while(head != NULL){ 19 printf("Val: %d ",head->val,head->next); 20 head = head->next; 21 } 22 } 23 void addOneNode(struct ListNode * head,int val){ 24 struct ListNode * newNode =(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 25 newNode->val = val; 26 newNode->next = NULL; 27 28 //遍历链表到 尾部 29 struct ListNode * temp = head; 30 while(temp->next !=NULL){ 31 temp = temp->next; 32 } 33 temp->next = newNode; 34 } 35 36 //链表逆序 (Leetcode 代码) 37 struct ListNode * reverseList(struct ListNode * head){ 38 struct ListNode * pPre = NULL; //保存前一个地址 39 struct ListNode * pNext = head->next; //保存下一个地址 40 while(pNext != NULL){ 41 head->next = pPre; //主 42 pPre = head; 43 44 head = pNext; //主 45 pNext = head->next; 46 } 47 head->next = pPre; //这个是因为最后一个连不上,所以最后要自己连上! 48 return head; 49 } 50 51 52 int main(){ 53 54 struct ListNode * head = ListInit(); //head存数据(默认存的值为0) 55 head->val = 1; //这里将默认的head.val =0 变为1 56 for(int i =2;i<10;++i){ 57 addOneNode(head,i); 58 } 59 printList(head); 60 head = reverseList(head); 61 printList(head); 62 63 return 0; 64 }
下面是老师的代码:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { 4 ListNode * newHead =NULL; 5 while(head){ 6 ListNode *temp = head->next; 7 head->next =newHead; 8 newHead = head; 9 10 head = temp; 11 } 12 return newHead; 13 14 } 15 };
例1-b:链表逆序-b (leetcode 编号 92)
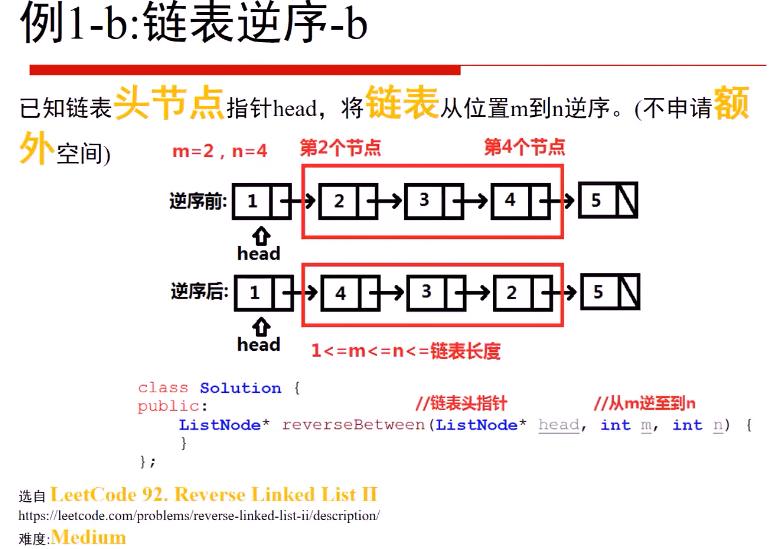
重要的四个结点:

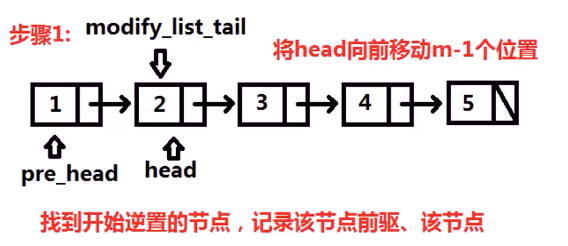
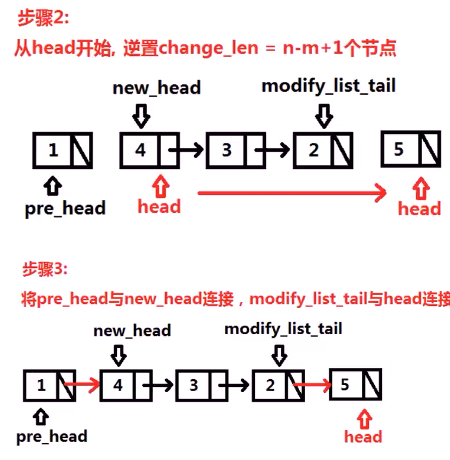

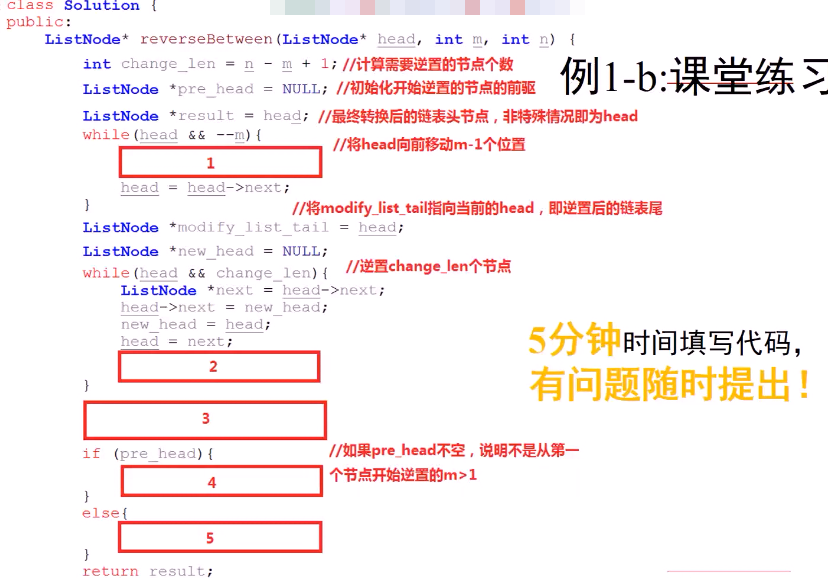

个人的思路:

1 ListNode * reverseBetween(ListNode * head,int m,int n){ 2 if(head ==NULL || m==n) return head; 3 int flag = 0; 4 if(m==1) flag = 1; 5 ListNode* pCur = head; 6 for(int i =0;i<m-2;++i){ 7 pCur = pCur->next; 8 }//将pCur 遍历到 m前一个节点 9 10 ListNode* pBackWard = pCur; //记录 11 ListNode* pM = pCur->next; //记录 12 //开始逆序 13 pCur = pM; 14 if(flag) pCur = pBackWard; //特殊情景时修正下 15 ListNode * pPre = NULL; 16 for(int i =0;i<n-m;++i){ 17 ListNode * pNext = pCur->next;//本次 18 pCur->next = pPre;//主 19 pPre = pCur; //下次 20 pCur = pNext; //主 21 } 22 if(!flag){ 23 pBackWard->next = pCur; 24 ListNode * temp = pCur->next; 25 pCur->next = pPre; 26 pM->next = temp; 27 }else{ 28 head = pCur; 29 ListNode * temp = pCur->next; 30 pBackWard->next = temp; 31 head->next = pPre; 32 } 33 return head; 34 }
下面是老师的代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 struct ListNode{ 3 int val; 4 struct ListNode *next; 5 }; 6 7 class Solution { 8 public: 9 ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { 10 ListNode * pre_head = NULL; 11 ListNode * result = head; //最终返回的头节点 12 // 向前移动m-1 个位置 ,pre_head 和 head 一起移动 13 for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; ++i) { 14 pre_head = head; 15 head = head->next; 16 } 17 18 ListNode * modified_list_tail =head; 19 ListNode * new_head = NULL; //新的逆序链表的头 20 int change_node_num = n-m+1; 21 while(head &&change_node_num){ 22 ListNode * temp = head->next; 23 head->next = new_head; 24 new_head = head; 25 head = temp; 26 27 change_node_num--; 28 } 29 modified_list_tail->next = head; 30 31 if(pre_head){ 32 pre_head->next = new_head; 33 } 34 else{ //如果是从第一个开始就逆序的话, 特殊情况! 35 result = new_head; 36 } 37 return result; 38 } 39 };
例2:求两个链表的交点(No.160):
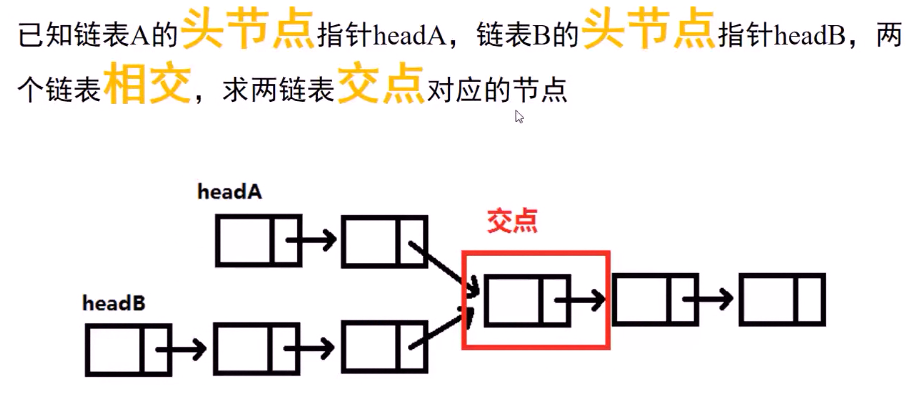
例2题目要求:

注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
方法一:
必备知识(STL set的使用):
使用set 求交集。

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <set> 5 6 int main(){ 7 8 set<int> test_set; 9 const int A_LEN = 7; 10 const int B_LEN = 8; 11 12 int a[A_LEN] = {5,1,4,8,10,1,3}; 13 int b[B_LEN] ={2,7,6,3,1,6,0,1}; 14 15 for (int i = 0; i < A_LEN; ++i) { 16 test_set.insert(a[i]); //将数组a 的元素插入到 set 中 17 } 18 for (int i = 0; i < B_LEN; ++i) { 19 if(test_set.find(b[i]) != test_set.end()){ 20 printf("b[%d] = %d in array A ",i,b[i]); 21 } 22 } 23 return 0; 24 }
方法一思路:使用set 求交集:
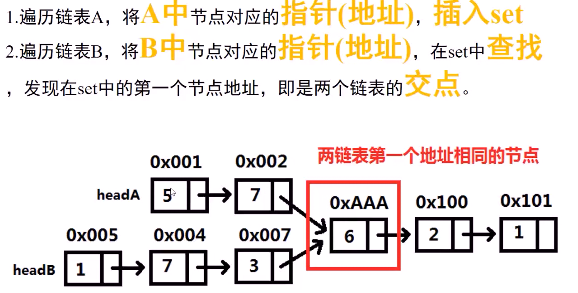

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <set> 5 struct ListNode{ 6 int val; 7 ListNode * next; 8 ListNode (int x): val(x) ,next(NULL){ 9 //构造函数 10 } 11 }; 12 13 class Solution{ 14 public: 15 ListNode * getIntersectionNode(ListNode * headA,ListNode *headB){ 16 set<ListNode *> node_set; 17 while(headA){ 18 node_set.insert(headA); //将 headA 加入到 set 中 19 headA = headA->next; 20 } 21 while(headB){ 22 if(node_set.find(headB) != node_set.end()){ 23 return headB; //在node_set 找到 headB 此时返回 24 } 25 headB = headB->next; 26 } 27 return NULL; 28 } 29 };
但是,此时并不是最优的!
因为用到了集合,此时的时间复杂度是 nlog(n) , 空间复杂度是O(n)
比较慢!!!
方法二:
思路2 :空间复杂度O(1):
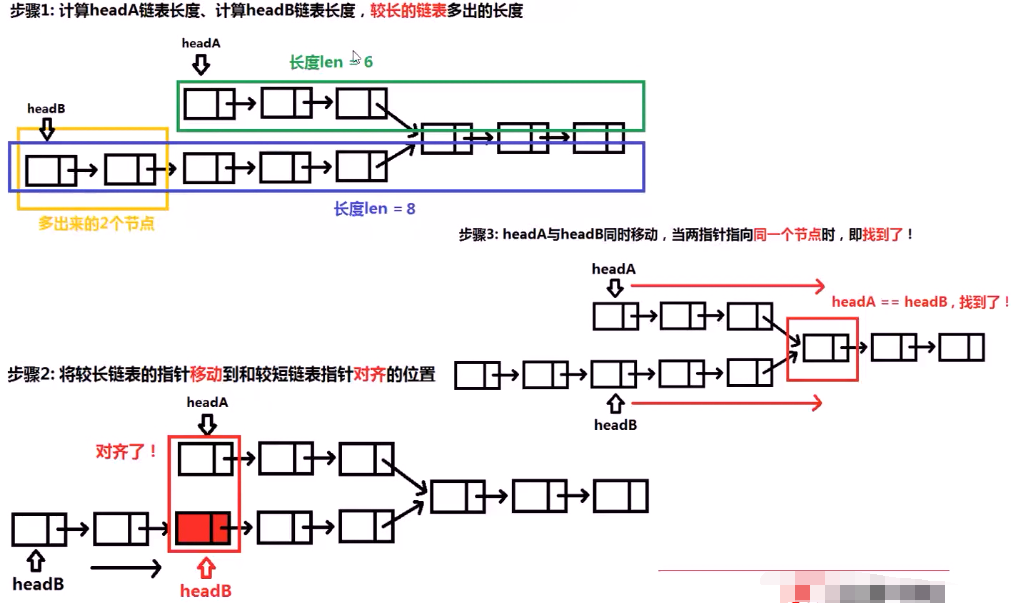
此时,我们最多遍历一个链表的长度,时间复杂度是O(n) 因为没有申请其他额外的空间,所以 空间复杂度为 O(1)

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct ListNode{ 5 int val; 6 ListNode * next; 7 ListNode (int x): val(x) ,next(NULL){ 8 //构造函数 9 } 10 }; 11 int get_list_length(ListNode * head){ 12 int len =0; 13 while(head){ 14 len ++; 15 head = head->next; 16 } 17 return len; 18 } 19 ListNode * forward_long_list(int long_len ,int short_len,ListNode *head){ 20 int delta = long_len - short_len; 21 for (int i = 0; i < delta; ++i) { 22 head = head->next; 23 } 24 return head; 25 } 26 27 class Solution{ 28 public: 29 ListNode * getIntersectionNode(ListNode * headA,ListNode *headB){ 30 int list_A_len = get_list_length(headA); 31 int list_B_len = get_list_length(headB); 32 33 if(list_A_len > list_B_len){ //如果 A 的长度比 B的长 34 headA = forward_long_list(list_A_len,list_B_len,headA); 35 }else{ 36 headB = forward_long_list(list_B_len,list_A_len,headB); 37 } 38 39 // 一起向前走,如果headA == headB 即为交点 40 while(headA && headB){ 41 if(headA == headB){ 42 return headA; 43 } 44 headA = headA->next; 45 headB = headB->next; 46 } 47 return NULL; 48 } 49 };
它就很快了!!!牛逼。
例2:链表求环(No.142 (No.141)):

思路1 :使用STL set 求环起始节点:
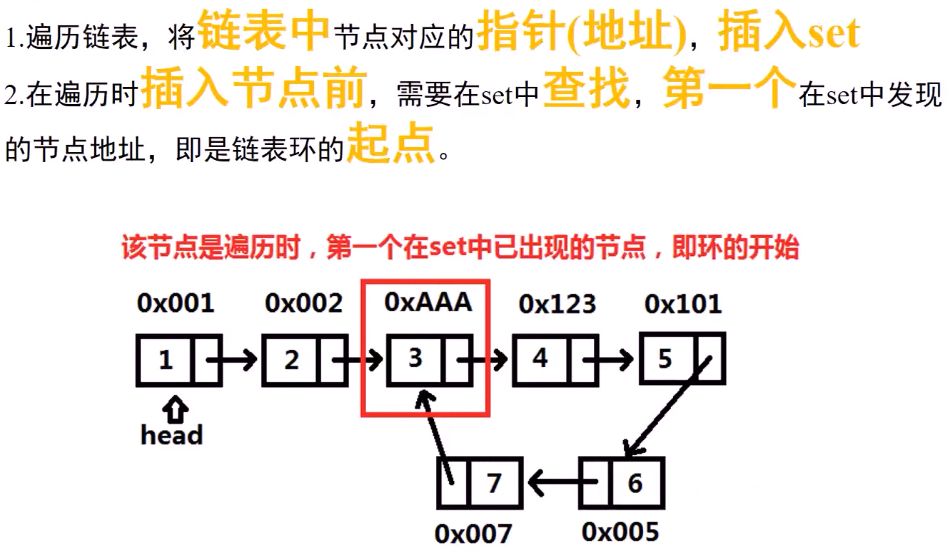

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <set> 5 struct ListNode{ 6 int val; 7 ListNode * next; 8 ListNode (int x): val(x) ,next(NULL){ 9 //构造函数 10 } 11 }; 12 13 class Solution{ 14 public: 15 ListNode * detectCycle(ListNode *head){ 16 set <ListNode *> node_set; 17 while (head){ //遍历链表 18 if(node_set.find(head) != node_set.end()){ //此时在set 中找到了 head 19 return head; 20 } 21 node_set.insert(head); 22 head = head->next; 23 } 24 return NULL; 25 } 26 };
缺点:太慢了!!!
思路2 :快慢指针赛跑:
它的思想和体育课上的跑步是一样的,赛道是环形的这样跑的快的人才有可能超过跑的慢的人!
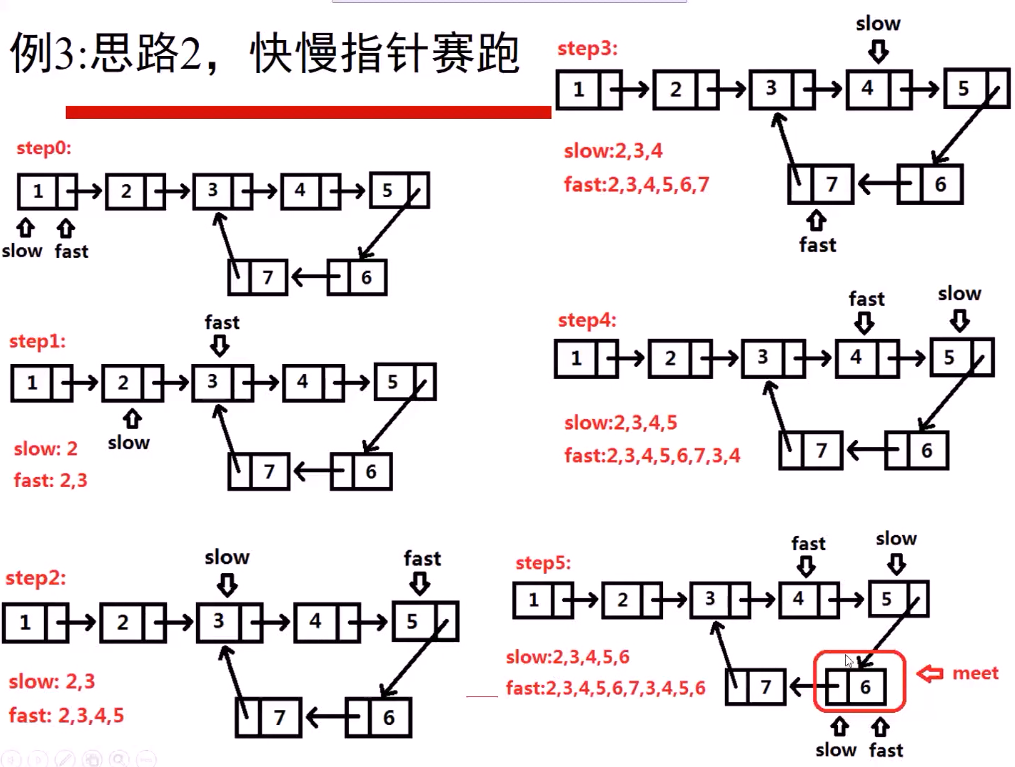
上图它可以确定有没有环,但是,它可能不是环的起始位置,
下面是如何求环的起始位置:
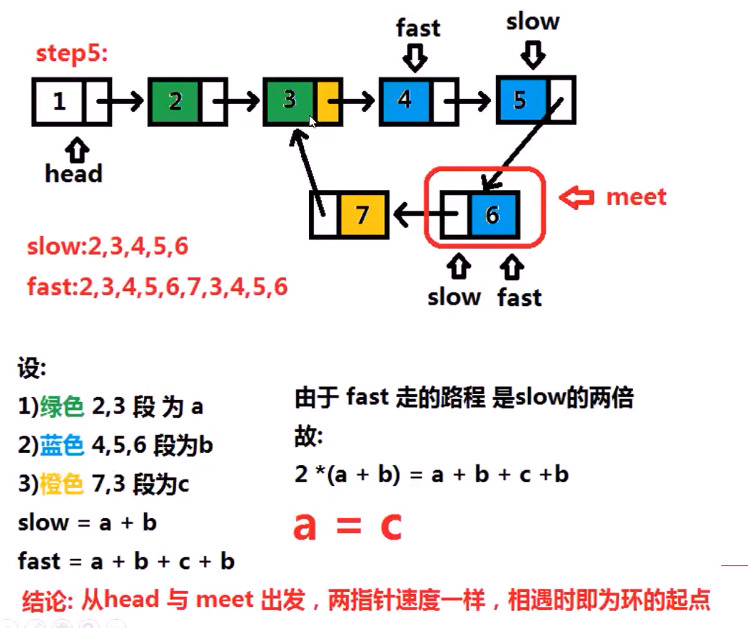

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <set> 5 struct ListNode{ 6 int val; 7 ListNode * next; 8 ListNode (int x): val(x) ,next(NULL){ 9 //构造函数 10 } 11 }; 12 13 class Solution{ 14 public: 15 ListNode * detectCycle(ListNode *head){ 16 ListNode *fast = head; //快指针 17 ListNode *slow = head; //慢指针 18 19 ListNode *meet = NULL ;//相遇的指针 20 while (fast){ 21 slow = slow->next; //slow 和 fast 各走一步 22 fast = fast->next; 23 if(!fast){ //如果fast 为空了 24 return NULL; 25 } 26 fast = fast->next; //fast 再走一步 27 if(fast == slow){ 28 meet = fast; // 相遇了 29 break; 30 } 31 } 32 if(meet == NULL){ 33 return NULL; 34 } 35 while (head && meet){ 36 if(head == meet ){ 37 return head; //此时为起始节点 38 } 39 head = head->next; 40 meet = meet->next; 41 } 42 return NULL; 43 } 44 };
leetcode No.141 的答案:
方法一:
使用STL 中的set

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { 4 set <ListNode *> node_set; 5 while (head){ //遍历链表 6 if(node_set.find(head) != node_set.end()){ //此时在set 中找到了 head 7 return true; 8 } 9 node_set.insert(head); 10 head = head->next; 11 } 12 return false; 13 } 14 };
方法二:

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { 4 ListNode *fast = head; //快指针 5 ListNode *slow = head; //慢指针 6 7 while (fast){ 8 slow = slow->next; //slow 和 fast 各走一步 9 fast = fast->next; 10 if(!fast){ //如果fast 为空了 11 return false; 12 } 13 fast = fast->next; //fast 再走一步 14 if(fast == slow){ 15 return true; 16 } 17 } 18 return false; 19 } 20 };
例4:链表划分 No.86

思路:巧用临时头结点:

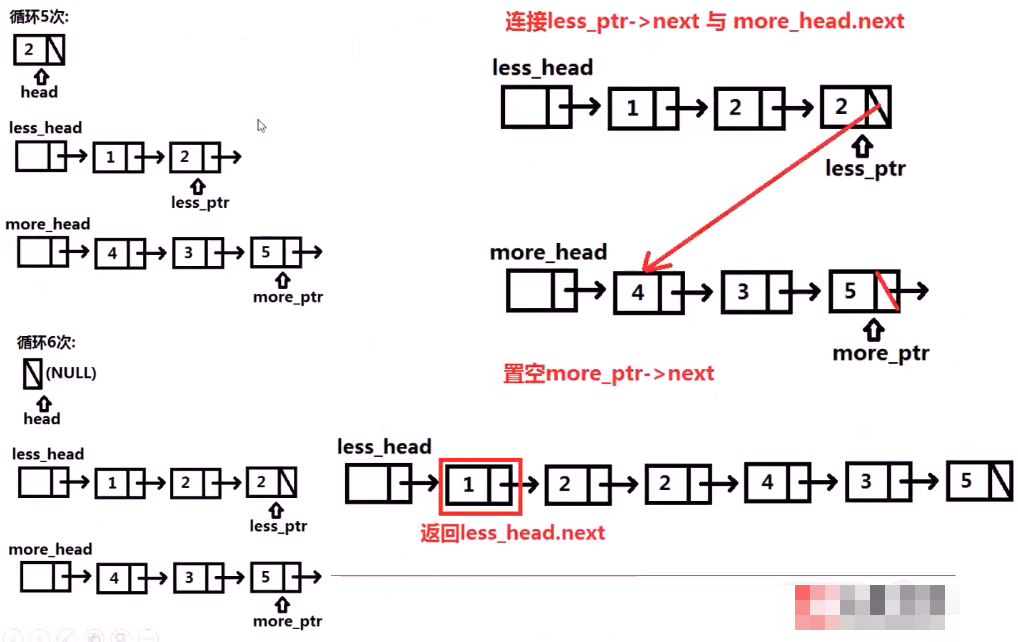

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct ListNode{ 5 int val; 6 ListNode * next; 7 ListNode (int x): val(x) ,next(NULL){ 8 //构造函数 9 } 10 }; 11 12 class Solution{ 13 public: 14 ListNode * partition(ListNode * head,int x){ 15 ListNode less_head(0); //设置两个临时头节点 16 ListNode more_head(0); 17 ListNode * less_ptr = &less_head; 18 ListNode * more_ptr = &more_head; 19 20 while(head){ 21 if(head->val <x){ 22 less_ptr->next = head; 23 less_ptr = head; 24 }else{ 25 more_ptr->next = head; 26 more_ptr = head; 27 } 28 29 head = head->next; 30 } 31 less_ptr->next = more_head.next; 32 more_ptr->next = NULL; 33 return less_head.next; 34 } 35 };
例5:复杂链表的深度拷贝 No.138



必备知识 (STL Map的使用):
构造如下的链表:


1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include <map> //STL map的头文件 5 6 struct RandomListNode{ 7 int label; 8 RandomListNode * next, * random; 9 RandomListNode(int x): label(x),next(NULL),random (NULL){}; 10 }; 11 12 13 int main(){ 14 map<RandomListNode *,int > node_map; //map的 key 是 节点地址, value 是 id号 15 RandomListNode a(5); 16 RandomListNode b(3); 17 RandomListNode c(6); 18 19 a.next = &b; 20 b.next = &c; 21 22 a.random = &c; 23 b.random = &a; 24 c.random = &c; 25 26 node_map[&a] = 1; 27 node_map[&b] = 2; 28 node_map[&c] = 3; 29 cout << "a.random id ="<<node_map[a.random]<<endl; 30 cout << "b.random id ="<<node_map[b.random]<<endl; 31 cout << "c.random id ="<<node_map[c.random]<<endl; 32 33 34 35 return 0; 36 } 37 /* 38 * 输出: 39 * a.random id =3 40 b.random id =1 41 c.random id =3 42 * */
思路及代码:
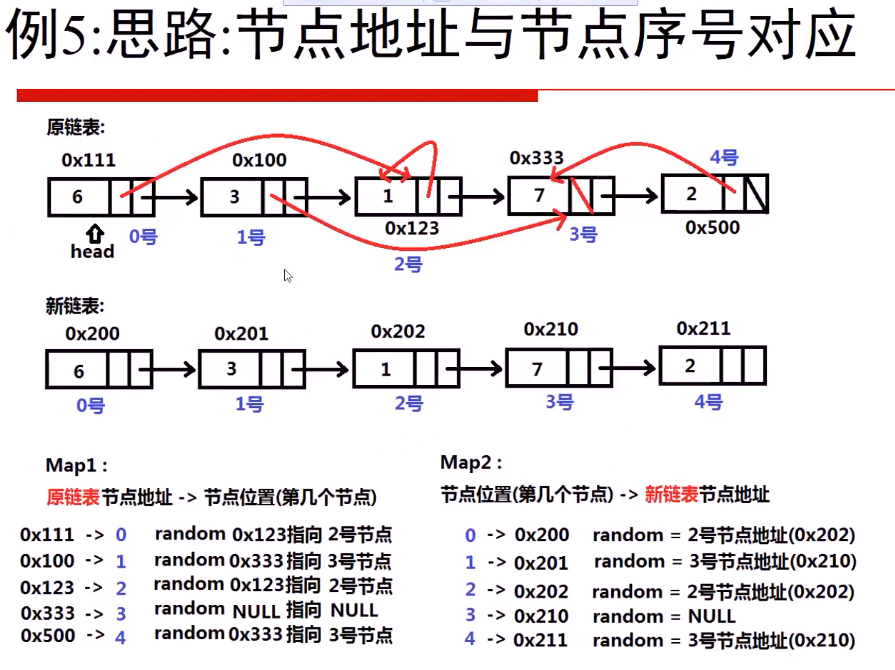
最重要的是 上面的这两个map , 第一个的key是节点地址 ,第二个的key 是id .
首先,遍历原链表,输入random 指针的值就知道,它指向的是哪个id ,
然后,在新链表中,知道要指向哪个id时,就可以得到对应的节点地址。

1 class Node { 2 public: 3 int val; 4 Node* next; 5 Node* random; 6 7 Node() {} 8 9 Node(int _val, Node* _next, Node* _random) { 10 val = _val; 11 next = _next; 12 random = _random; 13 } 14 }; 15 class Solution { 16 public: 17 Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { 18 if(!head) return head; //如果head 本身为空 直接返回 19 map<Node*,int> node_map; 20 vector <Node*> node_vec; //第二个map 本质是个数组 21 Node* ptr = head; 22 23 int i=0; 24 while(ptr){ 25 node_vec.push_back(new Node(ptr->val,NULL,NULL));//将新链表的节点 加入到 node_vec 构造成一个 map,id是下标。 26 node_map[ptr] = i; //构造原始链表的 node_map 27 ptr = ptr->next; 28 i++; 29 } 30 node_vec.push_back(0); //为了下面next 连接最后一个的时候,给最后一个赋空 31 ptr = head; 32 i =0; //再次遍历原始列表 ,连接新链表的next指针 和 random指针 33 while(ptr){ 34 node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1]; //连接新表的next 35 if(ptr->random) { //当random 指针不空的时候 36 int id = node_map[ptr->random]; 37 node_vec[i]->random = node_vec[id]; //连接新表的 random 38 } 39 ptr = ptr->next; 40 i++; 41 } 42 return node_vec[0]; 43 } 44 };

1 struct RandomListNode{ 2 int label; 3 RandomListNode * next, * random; 4 RandomListNode(int x): label(x),next(NULL),random (NULL){}; 5 }; 6 class Solution{ 7 public: 8 RandomListNode * copyRandomList(RandomListNode * head){ 9 map<RandomListNode *,int> node_map; 10 vector <RandomListNode * > node_vec; //第二个map 本质是个数组 11 RandomListNode *ptr = head; 12 13 int i=0; 14 while(ptr){ 15 node_vec.push_back(new RandomListNode(ptr->label));//将新链表的节点 加入到 node_vec 构造成一个 map,id是下标。 16 node_map[ptr] = i; //构造原始链表的 node_map 17 ptr = ptr->next; 18 i++; 19 } 20 node_vec.push_back(0); //为了下面next 连接最后一个的时候,给最后一个赋空 21 ptr = head; 22 i =0; //再次遍历原始列表 ,连接新链表的next指针 和 random指针 23 while(ptr){ 24 node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1]; //连接新表的next 25 if(ptr->random) { //当random 指针不空的时候 26 int id = node_map[ptr->random]; 27 node_vec[i]->random = node_vec[id]; //连接新表的 random 28 } 29 ptr = ptr->next; 30 i++; 31 } 32 return node_vec[0]; 33 } 34 };

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include <map> //STL map的头文件 5 #include <vector> 6 7 struct RandomListNode{ 8 int val; 9 RandomListNode * next, * random; 10 RandomListNode(int x): val(x),next(NULL),random (NULL){}; 11 }; 12 class Solution{ 13 public: 14 RandomListNode * copyRandomList(RandomListNode * head){ 15 map<RandomListNode *,int> node_map; 16 vector <RandomListNode * > node_vec; //第二个map 本质是个数组 17 RandomListNode *ptr = head; 18 19 int i=0; 20 while(ptr){ 21 node_vec.push_back(new RandomListNode(ptr->val));//将新链表的节点 加入到 node_vec 构造成一个 map,id是下标。 22 node_map[ptr] = i; //构造原始链表的 node_map 23 ptr = ptr->next; 24 i++; 25 } 26 node_vec.push_back(0); //为了下面next 连接最后一个的时候,给最后一个赋空 27 ptr = head; 28 i =0; //再次遍历原始列表 ,连接新链表的next指针 和 random指针 29 while(ptr){ 30 node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1]; //连接新表的next 31 if(ptr->random) { //当random 指针不空的时候 32 int id = node_map[ptr->random]; 33 node_vec[i]->random = node_vec[id]; //连接新表的 random 34 } 35 ptr = ptr->next; 36 i++; 37 } 38 return node_vec[0]; 39 } 40 }; 41 42 int main(){ 43 map<RandomListNode *,int > node_map; //map的 key 是 节点地址, value 是 id号 44 RandomListNode a(5); 45 RandomListNode b(3); 46 RandomListNode c(6); 47 48 a.next = &b; 49 b.next = &c; 50 51 a.random = &c; 52 b.random = &a; 53 c.random = &c; 54 55 node_map[&a] = 1; 56 node_map[&b] = 2; 57 node_map[&c] = 3; 58 cout << "a.random id ="<<node_map[a.random]<<endl; 59 cout << "b.random id ="<<node_map[b.random]<<endl; 60 cout << "c.random id ="<<node_map[c.random]<<endl; 61 62 Solution * solution = new Solution(); 63 RandomListNode * res = solution->copyRandomList(&a); 64 65 while(res){ 66 cout<<"val = "<<res->val; 67 if(res->random){ 68 cout<<" random地址中的val = "<<res->random->val<<endl; 69 }else{ 70 cout<<" random地址中的val = NULL"<<endl; 71 } 72 res = res->next; 73 } 74 return 0; 75 }
例6-a:排序链表的合并 No.21
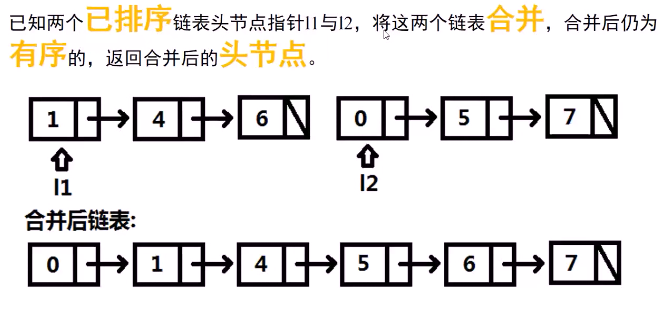
思路及代码:


1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 /** 4 * Definition for singly-linked list. 5 * struct ListNode { 6 * int val; 7 * ListNode *next; 8 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 9 * }; 10 */ 11 struct ListNode { 12 int val; 13 ListNode *next; 14 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 15 }; 16 17 class Solution { 18 public: 19 ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { 20 ListNode temp_head(0); 21 ListNode *pre = &temp_head; 22 23 while (l1 && l2) { //l1 和 l2 都不为空的时候遍历 24 if (l1->val < l2->val) { 25 pre->next = l1; //pre 指向 l1当前的节点 26 l1 = l1->next; 27 } else { 28 pre->next = l2; 29 l2 = l2->next; 30 } 31 pre = pre->next; //将新的链表的pre 向前移动 32 } 33 34 //如果 l1 有剩余 35 if(l1){ 36 pre->next = l1; 37 } 38 //如果l2 有剩余 39 if(l2){ 40 pre->next = l2; 41 } 42 return temp_head.next; 43 } 44 };
例6-b:排序链表的合并 (多个)No.23
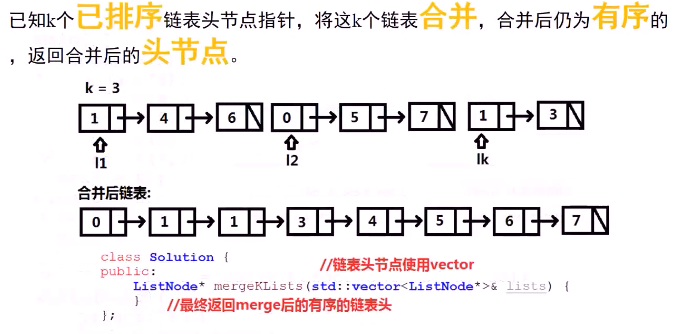
思路及代码:
方案一:
直接暴力!

但是,这样是不行的,因为它的时间复杂度O(k^2 *n)太高了!是无法在LeetCode 上通过的 。
下面看方案二:
方案二:
排序后相连

vector 排序的时间复杂度最优是 nlog(n)
方案二的时间复杂度是 O(kn *log(kn)) , 它和方案一比 当n 比较大时 方案二更好.....
这里我们排序使用STL 中的sort() 算法!
简单的例子(排序算法):

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 struct ListNode { 7 int val; 8 ListNode *next; 9 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 10 }; 11 12 bool cmp(const ListNode * a,const ListNode * b){ 13 return a->val < b->val; 14 } 15 int main(){ 16 ListNode a(3); 17 ListNode b(4); 18 ListNode c(0); 19 ListNode d(1); 20 21 vector <ListNode *> v; 22 v.push_back(&a); 23 v.push_back(&b); 24 v.push_back(&c); 25 v.push_back(&d); 26 27 //调用std::sort 算法 28 sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp); 29 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) { 30 cout << v[i]->val; 31 } 32 return 0; 33 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 7 struct ListNode { 8 int val; 9 ListNode *next; 10 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 11 }; 12 13 bool cmp(const ListNode * a,const ListNode * b){ 14 return a->val < b->val; 15 } 16 class Solution { 17 public: 18 ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { 19 vector <ListNode *> node_vec; 20 for (int i = 0; i < lists.size(); ++i) { 21 ListNode * head = lists[i]; 22 while (head){ 23 node_vec.push_back(head); 24 head = head->next; 25 } 26 } 27 if (node_vec.size() == 0){ 28 return NULL; 29 } 30 sort(node_vec.begin(),node_vec.end(),cmp); //根据节点数值进行排序 31 for (int i = 0; i < node_vec.size() -1; ++i) { 32 node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i + 1]; //将排序好的节点首尾相连 33 } 34 node_vec[node_vec.size()-1] ->next = NULL; 35 return node_vec[0]; 36 } 37 };
方案三:
分治!!!!!

这里的log 都是以2为底的对数 。。。

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 7 struct ListNode { 8 int val; 9 ListNode *next; 10 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 11 }; 12 bool cmp(const ListNode *a,const ListNode *b){ 13 return a->val < b->val; 14 } 15 16 ListNode * mergeTwoLists(ListNode *l1,ListNode *l2){ 17 if(l1 == NULL &&l2 ==NULL){ 18 return NULL; 19 } 20 if(l1 == NULL){ 21 return l2; 22 } 23 if(l2 == NULL){ 24 return l1; 25 } 26 vector <ListNode *> node_vec; 27 while(l1){ 28 node_vec.push_back(l1); 29 l1 = l1->next; 30 } 31 node_vec[node_vec.size() -1]->next =l2; //将两个链 连接起来 32 while(l2){ 33 node_vec.push_back(l2); 34 l2 = l2->next; 35 } 36 sort(node_vec.begin(),node_vec.end(),cmp); 37 //将排序好的节点 首尾 相连 38 for (int i = 0; i < node_vec.size() -1; ++i) { 39 node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1]; 40 } 41 node_vec[node_vec.size()-1]->next = NULL; 42 return node_vec[0]; //vector 只是个容器,它不负责将里面的东西相连 43 } 44 45 46 class Solution { 47 public: 48 ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { 49 if(lists.size() == 0){ 50 return NULL; 51 } 52 if(lists.size() ==1){ 53 return lists[0]; 54 } 55 if(lists.size() == 2 ){ //如果只有两个链表 56 return mergeTwoLists(lists[0],lists[1]); 57 } 58 int mid = lists.size()/2; 59 60 vector <ListNode *> sub1_lists; 61 vector <ListNode *> sub2_lists; //拆分lists 为两个子lists 62 63 for (int i = 0; i < mid; ++i) { 64 sub1_lists.push_back(lists[i]); 65 } 66 for (int i = mid; i < lists.size(); ++i) { 67 sub2_lists.push_back(lists[i]); 68 } 69 ListNode * l1 = mergeKLists(sub1_lists); //递归调用 70 ListNode * l2 = mergeKLists(sub2_lists); 71 72 return mergeTwoLists(l1,l2); //分治 73 } 74 }; 75 76 int main() { 77 78 ListNode a(1); 79 ListNode b(10); 80 ListNode c(9); 81 ListNode d(7); 82 ListNode e(92); 83 ListNode f(5); 84 ListNode g(24); 85 ListNode h(16); 86 87 a.next = &b; 88 b.next = &c; 89 90 d.next = &e; 91 e.next = &f; 92 93 g.next = &h; 94 95 Solution solve; 96 97 vector<ListNode *> lists; 98 lists.push_back(&a); 99 lists.push_back(&d); 100 lists.push_back(&g); 101 102 ListNode *head = solve.mergeKLists(lists); 103 // ListNode * head = mergeTwoLists(lists[0],lists[1]); 104 while (head) { 105 cout << head->val << endl; 106 head = head->next; 107 } 108 return 0; 109 }
但是提交之后,发现还不如方案二!!!。
