题目
Sasha has an array of integers a1, a2, ..., an. You have to perform m queries. There might be queries of two types:
- 1 l r x — increase all integers on the segment from l to r by values x;
- 2 l r — find
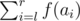 , where f(x) is the x-th Fibonacci number. As this number may be large, you only have to find it modulo 109 + 7.
, where f(x) is the x-th Fibonacci number. As this number may be large, you only have to find it modulo 109 + 7.
In this problem we define Fibonacci numbers as follows: f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(x) = f(x - 1) + f(x - 2) for all x > 2.
Sasha is a very talented boy and he managed to perform all queries in five seconds. Will you be able to write the program that performs as well as Sasha?
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000) — the number of elements in the array and the number of queries respectively.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Then follow m lines with queries descriptions. Each of them contains integers tpi, li, ri and may be xi (1 ≤ tpi ≤ 2, 1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n, 1 ≤ xi ≤ 109). Here tpi = 1 corresponds to the queries of the first type and tpi corresponds to the queries of the second type.
It's guaranteed that the input will contains at least one query of the second type.
For each query of the second type print the answer modulo 109 + 7.
题目大意
给你一个长度为n的数列an,有两种操作
1、将L到R的ai加上X
2、询问L到R之间,f(aL)+f(aL+1)+……+f(aR)的和
f是斐波那契函数
分析
我们可以将斐波那契数转化成它所对应的矩阵,对于每一次加x就是给原来矩阵乘上斐波那契矩阵的x次方。将为赋值的矩阵全部初始化为单位矩阵,然后进行朴素的线段树为何两节点之和即可。
代码
#pragma G++ optimize (2)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
#include<ctime>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define rri register int
const int mod=1e9+7;
struct mat {
int g[5][5];
};
mat d[440000],one,per;
mat add[440000];
inline mat operator * (const mat a,const mat b){
mat c;
c.g[1][1]=c.g[1][2]=c.g[2][1]=c.g[2][2]=0;
for(rri i=1;i<=2;++i)
for(rri k=1;k<=2;++k)
for(rri j=1;j<=2;++j)
c.g[i][j]=(c.g[i][j]+(long long)a.g[i][k]*b.g[k][j]%mod)%mod;
return c;
}
inline mat operator + (const mat a,const mat b){
mat c;
for(rri i=1;i<=2;++i)
for(rri j=1;j<=2;++j)
c.g[i][j]=(a.g[i][j]+b.g[i][j])%mod;
return c;
}
inline mat pw(mat a,int p){
mat res=a;
p-=1;
while(p){
if(p&1)res=res*a;
a=a*a;
p>>=1;
}
return res;
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char s=getchar();
while(s<'0'||s>'9'){if(s=='-')f=-1;s=getchar();}
while(s>='0'&&s<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(s-'0');s=getchar();}
return f*x;
}
inline void build(int le,int ri,int pl,mat k,int wh){
add[wh]=per;
if(le==ri){
d[wh]=k;
return;
}
int mid=(le+ri)>>1;
if(mid>=pl)build(le,mid,pl,k,wh<<1);
else build(mid+1,ri,pl,k,wh<<1|1);
d[wh]=d[wh<<1]+d[wh<<1|1];
}
inline void pd(int wh){
if(add[wh].g[1][1]!=1||add[wh].g[2][2]!=1||
add[wh].g[1][2]!=0||add[wh].g[2][1]!=0){
add[wh<<1]=add[wh<<1]*add[wh];
add[wh<<1|1]=add[wh<<1|1]*add[wh];
d[wh<<1]=d[wh<<1]*add[wh];
d[wh<<1|1]=d[wh<<1|1]*add[wh];
add[wh]=per;
}
}
inline void update(int le,int ri,int x,int y,mat k,int wh){
if(le>=x&&ri<=y){
add[wh]=add[wh]*k;
d[wh]=d[wh]*k;
return;
}
int mid=(le+ri)>>1;
pd(wh);
if(mid>=x)update(le,mid,x,y,k,wh<<1);
if(mid<y)update(mid+1,ri,x,y,k,wh<<1|1);
d[wh]=d[wh<<1]+d[wh<<1|1];
}
inline int q(int le,int ri,int x,int y,int wh){
if(le>=x&&ri<=y)return d[wh].g[1][2]%mod;
int mid=(le+ri)>>1,ans=0;
pd(wh);
if(mid>=x)ans=(ans+q(le,mid,x,y,wh<<1))%mod;
if(mid<y)ans=(ans+q(mid+1,ri,x,y,wh<<1|1))%mod;
d[wh]=d[wh<<1]+d[wh<<1|1];
return ans%mod;
}
int main()
{ int n,m,x,l,r,k;
one.g[1][1]=0,one.g[1][2]=one.g[2][1]=one.g[2][2]=1;
per.g[1][1]=per.g[2][2]=1,per.g[1][2]=per.g[2][1]=0;
n=read(),m=read();
for(rri i=1;i<=n;++i){
x=read();
build(1,n,i,pw(one,x),1);
}
for(rri i=1;i<=m;++i){
k=read();
if(k==1){
l=read(),r=read(),x=read();
update(1,n,l,r,pw(one,x),1);
}else {
l=read(),r=read();
printf("%d
",q(1,n,l,r,1)%mod);
}
}
return 0;
}