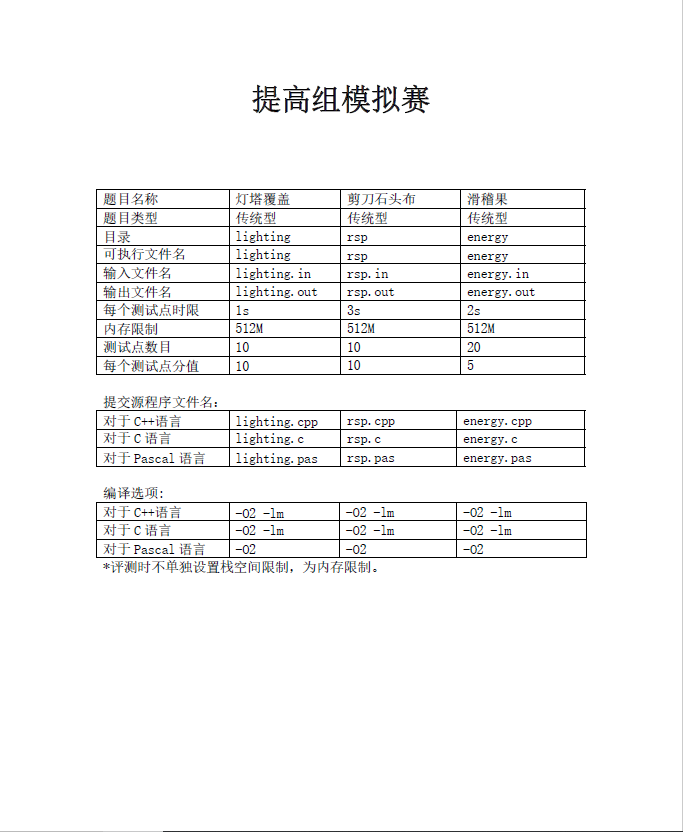
题面:






题解:
T1:
算法1:
枚举每个灯塔的方向,并分别判断是否有解。时间复杂度O(K*4^K)。
预计得分:50-70分
算法2:
不难发现,当k≥4的时候一定有解,将最靠左的两个下面的朝右上、上面的朝右下。最右边的两个做同样的处理。不难发现这样一定可以覆盖整个场地。
与算法1结合后可以期望获得100分
# include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace Base{
# define mr make_pair
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, INF = 0x7fffffff;
const ll infll = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll, INFll = 0x7fffffffffffffffll;
template<typename T> void read(T &x){
x = 0; int fh = 1; double num = 1.0; char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)){ if (ch == '-') fh = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (isdigit(ch)){ x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
if (ch == '.'){
ch = getchar();
while (isdigit(ch)){num /= 10; x = x + num * (ch - '0'); ch = getchar();}
}
x = x * fh;
}
template<typename T> void chmax(T &x, T y){x = x < y ? y : x;}
template<typename T> void chmin(T &x, T y){x = x > y ? y : x;}
}
using namespace Base;
const int K = 110;
struct Point{
int x, y;
}p[K], t[K], a[K], b[K];
int k, n, mu[K], flag;
void check(){
int lim = (1 << k);
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < lim; i++){
int num = 0;
int ax = 0, ay = 0, bx = n - 1, by = n - 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if ((i & (1 << (j - 1))) != 0){
num++;
ax = max(a[j].x, ax);
ay = max(a[j].y, ay);
bx = min(b[j].x, bx);
by = min(b[j].y, by);
}
if (ax <= bx && ay <= by)
sum = sum + mu[num] * 1ll * (bx - ax) * (by - ay);
}
if (sum == 1ll * (n - 1) * (n - 1)) flag = true;
}
void dfs(int x){
if (x > k){
check();
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
a[x].x = min(p[x].x, t[i].x);
a[x].y = min(p[x].y, t[i].y);
b[x].x = max(p[x].x, t[i].x);
b[x].y = max(p[x].y, t[i].y);
dfs(x + 1);
}
}
int main(){
freopen("lighting.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("lighting.out", "w", stdout);
mu[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < K; i++) mu[i] = mu[i - 1] * (-1);
int op; read(op);
while (op--){
read(k); read(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
read(p[i].x), read(p[i].y);
flag = false;
if (k > 4) {
printf("yes
");
continue;
}
t[0].x = 0, t[0].y = 0;
t[1].x = n - 1, t[1].y = 0;
t[2].x = 0, t[2].y = n - 1;
t[3].x = n - 1, t[3].y = n - 1;
dfs(1);
if (flag == true)
printf("yes
");
else printf("no
");
}
return 0;
}
T2:
算法0:
对于如何还原串中的一段,可以用类似线段树查询的方式做,时间复杂度O(N+R-L)。
算法1:
枚举每个玩家的出拳方法。时间复杂度O(3^(2^N)*(2^N))。
预计得分:20分
算法2:
不难发现,当我们确定最后的获胜者后,我们可以倒推出每一轮比赛的情况。同时我们可以正着推出每一层每个出拳方式的字典序大小关系。所以,当我们确定了最后的情况。我们可以花O(2^N)的时间还原出初始情况。
预计得分:40分
算法3:
其实我们不用还原出整个过程,只要知道底层每种出拳方式有多少个即可。用高精度计算即可。
预计得分:70分(其实取模就可以过了)
算法4:
再次观察后,我们发现。在一层中,每种出拳方式的数量的差不大于1。当我们有差和层数时,我们可以O(1)判断一个状态是否合法。
预计得分:100分
# include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace Base{
# define mr make_pair
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, INF = 0x7fffffff;
const ll infll = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll, INFll = 0x7fffffffffffffffll;
template<typename T> void read(T &x){
x = 0; int fh = 1; double num = 1.0; char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)){ if (ch == '-') fh = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (isdigit(ch)){ x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
if (ch == '.'){
ch = getchar();
while (isdigit(ch)){num /= 10; x = x + num * (ch - '0'); ch = getchar();}
}
x = x * fh;
}
template<typename T> void chmax(T &x, T y){x = x < y ? y : x;}
template<typename T> void chmin(T &x, T y){x = x > y ? y : x;}
}
using namespace Base;
const int N = 300010, P = 998244353;
struct INT{
int n[N], len;
void GetFromSt(char *st){
len = strlen(st);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) n[i] = st[len - i - 1] - '0';
}
}num[4], tmp;
bool operator >=(INT &x, INT &y){
if (x.len > y.len) return true;
if (x.len < y.len) return false;
for (int i = x.len - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (x.n[i] > y.n[i]) return true;
if (x.n[i] < y.n[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
INT operator -(INT a, INT &b){
for (int i = 0; i < a.len; i++)
a.n[i] -= b.n[i];
for (int i = 0; i < a.len; i++)
if (a.n[i] < 0) a.n[i] += 10, a.n[i + 1] -= 1;
while (a.len > 0 && a.n[a.len - 1] == 0) a.len--;
return a;
}
int n, op;
const int to[] = {-1, 0, 2, 1, 4, 5, 3, -1};
ll h[N][3], mul[N];
int rk[N][3], tnp[3];
char st[N], mp[3], l[N], r[N];
void error(){
printf("-1
");
exit(0);
}
void solve(int id, int now, int tag){
if (id == 0){
printf("%c", mp[now]);
return;
}
int nowl = now, nowr = (now + 1) % 3;
if (rk[id - 1][nowl] > rk[id - 1][nowr]) std::swap(nowl, nowr);
if ((tag & 1) != 0){
if (r[id] == '0' && (tag & 2) == 0)
solve(id - 1, nowl, 1);
else solve(id - 1, nowl, 3);
}
else {
if (l[id] == '0'){
if (r[id] == '0' && (tag & 2) == 0)
solve(id - 1, nowl, 0);
else solve(id - 1, nowl, 2);
}
}
if ((tag & 2) != 0){
if (l[id] == '1' && (tag & 1) == 0)
solve(id - 1, nowr, 2);
else solve(id - 1, nowr, 3);
}
else {
if (r[id] == '1'){
if (l[id] == '1' && (tag & 1) == 0)
solve(id - 1, nowr, 0);
else solve(id - 1, nowr, 1);
}
}
}
int main(){
freopen("rsp.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("rsp.out", "w", stdout);
read(n); read(op);
scanf("
%s", st); num[1].GetFromSt(st);
scanf("
%s", st); num[2].GetFromSt(st);
scanf("
%s", st); num[0].GetFromSt(st);
num[3] = num[0]; tmp.len = 1; tmp.n[0] = 2;
if (num[3] >= num[1]) num[3] = num[1];
if (num[3] >= num[2]) num[3] = num[2];
num[0] = num[0] - num[3]; if (num[0] >= tmp) error();
num[1] = num[1] - num[3]; if (num[1] >= tmp) error();
num[2] = num[2] - num[3]; if (num[2] >= tmp) error();
int tag = (num[0].n[0]) + (num[1].n[0] << 1) + (num[2].n[0] << 2);
tag = to[tag];
tag = ((tag - n) % 6 + 6) % 6;
tag = tag / 2;
rk[0][0] = 0, rk[0][1] = 1, rk[0][2] = 2;
h[0][0] = 'P', h[0][1] = 'R', h[0][2] = 'S'; mul[0] = 233;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
mul[i] = mul[i - 1] * mul[i - 1] % P;
rk[i][0] = std::min(rk[i - 1][0], rk[i - 1][1]) * 3 + std::max(rk[i - 1][0], rk[i - 1][1]);
rk[i][1] = std::min(rk[i - 1][1], rk[i - 1][2]) * 3 + std::max(rk[i - 1][1], rk[i - 1][2]);
rk[i][2] = std::min(rk[i - 1][2], rk[i - 1][0]) * 3 + std::max(rk[i - 1][2], rk[i - 1][0]);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) tnp[j] = (rk[i][j] > rk[i][0]) + (rk[i][j] > rk[i][1]) + (rk[i][j] > rk[i][2]);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
rk[i][j] = tnp[j];
if (rk[i - 1][j] < rk[i - 1][(j + 1) % 3])
h[i][j] = (h[i - 1][j] + h[i - 1][(j + 1) % 3] * mul[i - 1]) % P;
else h[i][j] = (h[i - 1][(j + 1) % 3] + h[i - 1][j] * mul[i - 1]) % P;
}
}
if (op != 2) printf("%lld
", h[n][tag]);
if (op == 1) exit(0);
scanf("
%s", l + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++) std::swap(l[i], l[n - i + 1]);
scanf("
%s", r + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++) std::swap(r[i], r[n - i + 1]);
mp[0] = 'P', mp[1] = 'R', mp[2] = 'S';
solve(n, tag, 0);
printf("
");
return 0;
}
T3:
算法1:
k=1时随便做做,预计得分0-10
算法2:
n≤1000, k≤4,dp统计答案,复杂度O(nvk),
预计得分10。
以下所有多项式的均为卷积(不会啊qaq)。
算法3:
考虑生成函数,以Vi为下标,数量为系数建立多项式f1,那么f1f1就是选两个的方案数。但是这样会有重复,(a,b)与(b,a)会算2次,同时会把(a,a)算进来,那么我们建立多项式f2表示一个物品取两次。那么当k=2时,ans=(f1f1-f2)/2;
预计额外得分20
算法4:
考虑算法3的拓展,记多项式f3为一个物品取三次,那么根据容斥原理,k=3时ans=(f1f1f1-3f2f1+2f3)/6,f2f1表示其中有两个或以上的物品相同,那么在f1f1f1中,一个f2f1会出现三次,即(a,a,b),(a,b,a),(b,a,a),f2f1中也会有f3出现,所以要减去三个f3,但是f1f1f1中本身还有一个f3所以还要减去一个。
预计额外得分30
算分5:
考虑进一步拓展,形式无非就f1f1f1f1,f2f2,f3f1,f2f1f1,f4这几种情况,剩下的问题就是配容斥系数,因为k只有4容斥系数可以手算出来。最终答案是:
Ans=(f1f1f1f1+8f3f1+3f2f2-6f2f1f1-6f4)/24
预计额外得分40
将算法1,3,4,5拼在一起即可得到满分,时间复杂度O(V log V)
# include <bits/stdc++.h>
# define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int T = 100001, N = 600001;
ll ans[N];
int read(){
int tmp=0, fh=1; char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if (ch=='-') fh=-1; ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){tmp=tmp*10+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}
return tmp*fh;
}
namespace Transform{
const int P = 998244353, G = 3;
int power(int x, int y){
int i = x; x = 1;
while (y > 0){
if (y % 2 == 1) x = 1ll * i * x % P;
i = 1ll * i * i % P;
y /= 2;
}
return x;
}
void NTT(int *a, int l, int tag){
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < l; i++){
if (i > j) swap(a[i], a[j]);
for (int k = (l >> 1); (j ^= k) < k; k >>= 1);
}
for (int i = 1; i < l; i <<= 1){
int wn = power(G, (P - 1) / (i * 2));
if (tag == -1) wn = power(wn, P - 2);
for (int j = 0; j < l; j += i + i){
int w = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++, w = 1ll * w * wn % P){
int x = a[k + j], y = 1ll * w * a[k + j + i] % P;
a[k + j] = (x + y) % P, a[k + j + i] = (x - y + P) % P;
}
}
}
if (tag == -1){
int in = power(l, P - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) a[i] = 1ll * a[i] * in % P;
}
}
}
using namespace Transform;
int num1[N], num2[N], num3[N], num4[N], now1[N], now2[N], now3[N], now4[N], len, nn, n, m, k;
void print(){
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
sum = sum ^ (1ll * ans[i] * i % P);
printf("%d
", sum);
}
int main(){
freopen("energy.in","r",stdin);
freopen("energy.out","w",stdout);
int inv2 = power(2, P - 2), inv6 = power(6, P - 2), inv24 = power(24, P - 2);
n = read(), k = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) num1[read()]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) num2[i * 2]= num1[i], num3[i * 3] = num1[i], num4[i * 4] = num1[i];
len = T * 4 + 1;
nn = 1; while (nn < len) nn <<= 1;
if (k == 1){
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) ans[i] = num1[i];
print();
return 0;
}
if (k == 2){
NTT(num1, nn, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now1[i] = 1ll * num1[i] * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now1, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) ans[i] = 1ll * (now1[i] - num2[i] + P) * inv2 % P;
print();
return 0;
}
if (k == 3){
NTT(num1, nn, 1); NTT(num2, nn, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now2[i] = 1ll * num2[i] * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now2, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now1[i] = 1ll * num1[i] * num1[i] % P * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now1, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) ans[i] = (1ll * (now1[i] - 3ll * now2[i] + 2ll * num3[i]) % P * inv6 % P + P) % P;
print();
return 0;
}
if (k == 4){
NTT(num1, nn, 1); NTT(num2, nn, 1); NTT(num3, nn, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now1[i] = 1ll * num1[i] * num1[i] % P * num1[i] % P * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now1, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now2[i] = 1ll * num3[i] * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now2, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now3[i] = 1ll * num2[i] * num2[i] % P;
NTT(now3, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) now4[i] = 1ll * num2[i] * num1[i] % P * num1[i] % P;
NTT(now4, nn, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) ans[i] = (1ll * (now1[i] + 8ll * now2[i] + 3ll * now3[i] - 6ll * now4[i] - 6ll *num4[i]) * inv24 % P + P) % P;
print();
return 0;
}
return 0;
}