作者QQ:1095737364 QQ群:123300273 欢迎加入!
1.线程池介绍
JDK5.0以上: java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor
构造函数签名:
public ThreadPoolExecutor( int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler );
参数介绍:
corePoolSize 核心线程数,指保留的线程池大小(不超过maximumPoolSize值时,线程池中最多有corePoolSize 个线程工作)。
maximumPoolSize 指的是线程池的最大大小(线程池中最大有corePoolSize 个线程可运行)。
keepAliveTime 指的是空闲线程结束的超时时间(当一个线程不工作时,过keepAliveTime 长时间将停止该线程)。
unit 是一个枚举,表示 keepAliveTime 的单位(有NANOSECONDS, MICROSECONDS, MILLISECONDS, SECONDS, MINUTES, HOURS, DAYS,7个可选值)。
workQueue 表示存放任务的队列(存放需要被线程池执行的线程队列)。
handler 拒绝策略(添加任务失败后如何处理该任务).
2.运行策略
1、线程池刚创建时,里面没有一个线程。任务队列是作为参数传进来的。不过,就算队列里面有任务,线程池也不会马上执行它们。
2、当调用 execute() 方法添加一个任务时,线程池会做如下判断:
a. 如果正在运行的线程数量小于 corePoolSize,那么马上创建线程运行这个任务;
b. 如果正在运行的线程数量大于或等于 corePoolSize,那么将这个任务放入队列。
c. 如果这时候队列满了,而且正在运行的线程数量小于 maximumPoolSize,那么还是要创建线程运行这个任务;
d. 如果队列满了,而且正在运行的线程数量大于或等于 maximumPoolSize,那么线程池会抛出异常,告诉调用者“我不能再接受任务了”。
3、当一个线程完成任务时,它会从队列中取下一个任务来执行。
4、当一个线程无事可做,超过一定的时间(keepAliveTime)时,线程池会判断,如果当前运行 的线程数大于 corePoolSize,那么这个线程就被停掉。所以线程池的所有任务完成后,它最终会收缩到 corePoolSize 的大小。
这个过程说明,并不是先加入任务就一定会先执行。假设队列大小为 4,corePoolSize为2,maximumPoolSize为6,那么当加入15个任务时,执行的顺序类似这样:首先执行任务 1、2,然后任务3~6被放入队列。这时候队列满了,任务7、8、9、10 会被马上执行,而任务 11~15 则会抛出异常。最终顺序是:1、2、7、8、9、10、3、4、5、6。当然这个过程是针对指定大小的ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>来说,如果是LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>,因为该队列无大小限制,所以不存在上述问题。
3.测试示例
(1)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用1:
package threadQueueTest; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * User: 杨永生 * Date: 15:47 2017/8/8 * Email: kevin@hiibook.com */ public class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable { public void run() { synchronized(this) { try{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(3000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(); ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest(),"TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); } executor.shutdown(); } }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->5
线程队列大小为-->6
线程队列大小为-->7
线程队列大小为-->8
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
说明:可见,线程队列最大为8,共执行了10个线线程。因为是从线程池里运行的线程,所以虽然将线程的名称设为"TestThread".concat(""+i),但输出后还是变成了pool-1-thread-x。
(2)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用2:
package threadQueueTest; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * User: 杨永生 * Date: 15:55 2017/8/8 * Email: kevin@hiibook.com */ public class ThreadPoolTest2 implements Runnable { public void run() { synchronized(this) { try{ System.out.println("线程名称:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(3000); //休眠是为了让该线程不至于执行完毕后从线程池里释放 }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4); //固定为4的线程队列 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest2(), "TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); } executor.shutdown(); } }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
线程名称:pool-1-thread-5
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
说明: 可见,总共10个线程,因为核心线程数为2,2个线程被立即运行,线程队列大小为4,所以4个线程被加入队列,最大线程数为6,还能运行6-2=4个,其10个线程的其余4个线程又立即运行了。
(3)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用3(测试异常):
如果将我们要运行的线程数10改为11,则由于最大线程数6+线程队列大小4=10<11,则根据线程池工作原则,最后一个线程将被拒绝策略拒绝,将示例二的main方法改为如下
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4); //固定为4的线程队列 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest2(), "TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); } executor.shutdown(); }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task Thread[TestThread10,5,main] rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@21588809[Running, pool size = 6, active threads = 6, queued tasks = 4, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2047)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:823)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1369)
at threadQueueTest.ThreadPoolTest2.main(ThreadPoolTest2.java:27)
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
线程名称:pool-1-thread-5
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
说明:很明显,抛RejectedExecutionException异常了,被拒绝策略拒绝了,这就说明线程超出了线程池的总容量(线程队列大小+最大线程数)。
对于 java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue 类有有三种方法将线程添加到线程队列里面,然而如何区别三种方法的不同呢,其实在队列未满的情况下结果相同,都是将线程添加到线程队列里面,区分就在于当线程队列已经满的时候,此时
public boolean add(E e) 方法将抛出IllegalStateException异常,说明队列已满。
public boolean offer(E e) 方法则不会抛异常,只会返回boolean值,告诉你添加成功与否,队列已满,当然返回false。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException 方法则一直阻塞(即等待,直到线程池中有线程运行完毕,可以加入队列为止)。
(4)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用3(测试add(E e)异常):
将示例二的main方法改为如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4); //固定为4的线程队列 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest4(), "TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); if (threadSize==4){ queue.add(new Runnable() { //队列已满,抛异常 @Override public void run(){ System.out.println("我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!"); } }); } } executor.shutdown(); }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98)
at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312)
at threadQueueTest.ThreadPoolTest4.main(ThreadPoolTest4.java:33)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:147)
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
(5)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用3(测试 offer(E e)异常):
将示例二的main方法改为如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4); //固定为4的线程队列 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest5(), "TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); if (threadSize==4){ final boolean flag = queue.offer(new Runnable() { @Override public void run(){ System.out.println("我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!"); } }); System.out.println("添加新线程标志为-->"+flag); } } executor.shutdown(); }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
添加新线程标志为-->false
线程队列大小为-->4
添加新线程标志为-->false
线程队列大小为-->4
添加新线程标志为-->false
线程队列大小为-->4
添加新线程标志为-->false
线程队列大小为-->4
添加新线程标志为-->false
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
线程名称:pool-1-thread-5
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-6
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
(6)LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>队列使用3(测试put(E e)异常):
将示例二的main方法改为如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4); //固定为4的线程队列 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 6, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executor.execute(new Thread(new ThreadPoolTest6(), "TestThread".concat(""+i))); int threadSize = queue.size(); System.out.println("线程队列大小为-->"+threadSize); if (threadSize==4){ queue.put(new Runnable() { @Override public void run(){ System.out.println("我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!"); } }); } } executor.shutdown(); }
结果:
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->0
线程队列大小为-->1
线程队列大小为-->2
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-1
线程名称:pool-1-thread-3
线程队列大小为-->3
线程队列大小为-->4
线程名称:pool-1-thread-5
我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!
我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!
我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!
线程名称:pool-1-thread-2
我是新线程,看看能不能搭个车加进去!
说明:很明显,尝试了四次才加进去,前面三次尝试添加,但由于线程sleep(3000),所以没有执行完,线程队列一直处于满的状态,直到某个线程执行完,队列有空位,新线程才加进去,没空位之前一直阻塞(即等待),我能加进去为止。
4.总结:
那么线程池的排除策略是什么样呢,一般按如下规律执行:
A. 如果运行的线程少于 corePoolSize,则 Executor 始终首选添加新的线程,而不进行排队。
B. 如果运行的线程等于或多于 corePoolSize,则 Executor 始终首选将请求加入队列,而不添加新的线程。
C. 如果无法将请求加入队列,则创建新的线程,除非创建此线程超出 maximumPoolSize,在这种情况下,任务将被拒绝。
总结:
1. 线程池可立即运行的最大线程数 即maximumPoolSize 参数。
2. 线程池能包含的最大线程数 = 可立即运行的最大线程数 + 线程队列大小 (一部分立即运行,一部分装队列里等待)
3. 核心线程数可理解为建议值,即建议使用的线程数,或者依据CPU核数
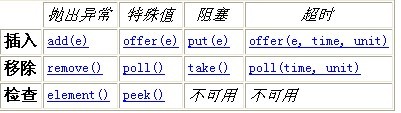
4. add,offer,put三种添加线程到队列的方法只在队列满的时候有区别,add为抛异常,offer返回boolean值,put直到添加成功为止。
5.同理remove,poll, take三种移除队列中线程的方法只在队列为空的时候有区别, remove为抛异常,poll为返回boolean值, take等待直到有线程可以被移除。
看看下面这张图就清楚了:
版权声明: 本文有 ```...裥簞點 发表于 bloghome博客
转载声明: 可自由转载、引用,但需要属名作者且注明文章出处。