一、numpy库
numpy:科学计算包,支持N维数组运算、处理大型矩阵、成熟的广播函数库、矢量运算、线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成,并可与C++/Fortran语言无缝结合。树莓派Python v3默认安装已经包含了numpy。
另:scipy:scipy依赖于numpy,提供了更多的数学工具,包括矩阵运算、线性方程组求解、积分、优化、插值、信号处理、图像处理、统计等等。
1.扩展库numpy简介
导入模板:(交换式)
>>>import numpy as np
2.numpy库应用于数组
(1)简单数组的生成
>>>import numpy as np #把列表转化为数组 >>> np.array([0,1,2,3,4]) array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>>np.array((0,1,2,3,4)) # 元组转化为数组
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>>np.array(range(5)) # 把range对象转换成数组
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>>np.array([[1,2,3,4,],[5,6,7,8]]) #二维数组
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])
>>>np.arange(8) # 类似于内置函数range()
array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
>>>np.arange(1,10,1) #以步长为二的数组
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
>>> np.linspace(0, 10, 11) # 等差数组,包含11个数 array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.])
>>> np.linspace(0, 10, 11, endpoint=False) # 不包含终点 array([ 0. , 0.90909091, 1.81818182, 2.72727273, 3.63636364, 4.54545455, 5.45454545, 6.36363636, 7.27272727, 8.18181818, 9.09090909])
>>> np.logspace(0, 100, 10) # 对数数组 array([ 1.00000000e+000, 1.29154967e+011, 1.66810054e+022, 2.15443469e+033, 2.78255940e+044, 3.59381366e+055, 4.64158883e+066, 5.99484250e+077, 7.74263683e+088, 1.00000000e+100])
>>> np.logspace(1,6,5, base=2) # 对数数组,相当于2 ** np.linspace(1,6,5) array([ 2. , 4.75682846, 11.3137085 , 26.90868529, 64. ])
>>> np.zeros(3) # 全0一维数组 array([ 0., 0., 0.])
>>> np.ones(3) # 全1一维数组 array([ 1., 1., 1.])
(2)0,1数组、单位矩阵的生成
>>> np.zeros((3,3)) # 全0二维数组,3行3列 [[ 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0.]]
>>> np.zeros((3,1)) # 全0二维数组,3行1列 array([[ 0.], [ 0.], [ 0.]])
>>> np.zeros((1,3)) # 全0二维数组,1行3列 array([[ 0., 0., 0.]])
>>> np.ones((1,3)) # 全1二维数组 array([[ 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> np.ones((3,3)) # 全1二维数组 array([[ 1., 1., 1.], [ 1., 1., 1.], [ 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> np.identity(3) # 单位矩阵 array([[ 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 1., 0.], [ 0., 0., 1.]])
>>> np.identity(2) array([[ 1., 0.], [ 0., 1.]])
>>> np.empty((3,3)) # 空数组,只申请空间而不初始化,元素值是不确定的 array([[ 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0.]])
(3)数组与数值的简单运算
>>> x = np.array((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # 创建数组对象 >>> x array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) >>> x * 2 # 数组与数值相乘,返回新数组 array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10]) >>> x / 2 # 数组与数值相除 array([ 0.5, 1. , 1.5, 2. , 2.5]) >>> x // 2 # 数组与数值整除 array([0, 1, 1, 2, 2], dtype=int32) >>> x ** 3 # 幂运算 array([1, 8, 27, 64, 125], dtype=int32) >>> x + 2 # 数组与数值相加 array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) >>> x % 3 # 余数 array([1, 2, 0, 1, 2], dtype=int32)
>>> 2 ** x array([2, 4, 8, 16, 32], dtype=int32)
>>> 2 / x array([2. ,1. ,0.66666667, 0.5, 0.4])
>>> 63 // x array([63, 31, 21, 15, 12], dtype=int32)
(4)数组与数组之间的运算
>>> a = np.array((1, 2, 3)) >>> b = np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9])) >>> c = a * b # 数组与数组相乘 >>> c # a中的每个元素乘以b中的对应列元素 array([[ 1, 4, 9], [ 4, 10, 18], [ 7, 16, 27]]) >>> c / b # 数组之间的除法运算 array([[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 1., 2., 3.], [ 1., 2., 3.]]) >>> c / a array([[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6.], [ 7., 8., 9.]]) >>> a + a # 数组之间的加法运算 array([2, 4, 6]) >>> a * a # 数组之间的乘法运算 array([1, 4, 9]) >>> a - a # 数组之间的减法运算 array([0, 0, 0]) >>> a / a # 数组之间的除法运算 array([ 1., 1., 1.])
(5)数组的转置
>>> b = np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9])) >>> b array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> b.T # 转置 array([[1, 4, 7], [2, 5, 8], [3, 6, 9]]) >>> a = np.array((1, 2, 3, 4)) >>> a array([1, 2, 3, 4]) >>> a.T # 一维数组转置以后和原来是一样的 array([1, 2, 3, 4])
(6)点积/内积
>>> a = np.array((5, 6, 7)) >>> b = np.array((6, 6, 6)) >>> a.dot(b) # 向量内积 108 >>> np.dot(a,b) 108 >>> c = np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9])) # 二维数组 >>> c.dot(a) # 二维数组的每行与一维向量计算内积 array([ 38, 92, 146]) >>> a.dot(c) # 一维向量与二维向量的每列计算内积 array([78, 96, 114])
(7)数组元素访问
>>> b = np.array(([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9])) >>> b array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> b[0] # 第0行 array([1, 2, 3]) >>> b[0][0] # 第0行第0列的元素值 1 >>> b[0,2] # 第0行第2列的元素值 3 >>> b[[0,1]] # 第0行和第1行 array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) >>> b[[0,1], [1,2]] #第0行第1列的元素和第1行第2列的元素 array([2, 6])
3、numpy库应用于矩阵
(1)矩阵的简单运算
>>> a_list = [3, 5, 7] >>> a_mat = np.matrix(a_list) # 创建矩阵 >>> a_mat matrix([[3, 5, 7]]) >>> a_mat.T # 矩阵转置 matrix([[3], [5], [7]]) >>> a_mat.shape # 矩阵形状 (1, 3) >>> a_mat.size # 元素个数 3 >>> a_mat.mean() # 元素平均值 5.0 >>> a_mat.sum() # 所有元素之和 15 >>> a_mat.max() # 最大值 7 >>> a_mat.max(axis=1) # 横向最大值 matrix([[7]]) >>> a_mat.max(axis=0) # 纵向最大值 matrix([[3, 5, 7]]) ###------------------------------------------------------------### >>> b_mat = np.matrix((1, 2, 3)) # 创建矩阵 >>> b_mat matrix([[1, 2, 3]]) >>> a_mat * b_mat.T # 矩阵相乘 matrix([[34]]) ###------------------------------------------------------------### >>> c_mat = np.matrix([[1, 5, 3], [2, 9, 6]]) # 创建二维矩阵 >>> c_mat matrix([[1, 5, 3], [2, 9, 6]]) >>> c_mat.argsort(axis=0) # 纵向排序后的元素序号 matrix([[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1]], dtype=int64) >>> c_mat.argsort(axis=1) # 横向排序后的元素序号 matrix([[0, 2, 1], [0, 2, 1]], dtype=int64) >>> d_mat = np.matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> d_mat.diagonal() # 矩阵对角线元素 matrix([[1, 5, 9]])
(2)矩阵不同维度上的计算
>>> x = np.matrix(np.arange(0,10).reshape(2,5)) # 二维矩阵 >>> x matrix([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]) >>> x.sum() # 所有元素之和 45 >>> x.sum(axis=0) # 纵向求和 matrix([[ 5, 7, 9, 11, 13]]) >>> x.sum(axis=1) # 横向求和 matrix([[10], [35]]) >>> x.mean() # 平均值 4.5 >>> x.mean(axis=1) matrix([[ 2.], [ 7.]]) >>> x.mean(axis=0) matrix([[ 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5]]) >>> x.max() # 所有元素最大值 9 >>> x.max(axis=0) # 纵向最大值 matrix([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]) >>> x.max(axis=1) # 横向最大值 matrix([[4], [9]]) >>> weight = [0.3, 0.7] # 权重 >>> np.average(x, axis=0, weights=weight) matrix([[ 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5]]) ###——————————————-----------------------### >>> x = np.matrix(np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(3,3))) #建立矩阵 >>> x matrix([[3, 7, 4], [5, 1, 8], [2, 7, 0]]) >>> x.std() # 标准差 2.6851213274654606 >>> x.std(axis=1) # 横向标准差 matrix([[ 1.69967317], [ 2.86744176], [ 2.94392029]]) >>> x.std(axis=0) # 纵向标准差 matrix([[ 1.24721913, 2.82842712, 3.26598632]]) >>> x.var(axis=0) # 纵向方差 matrix([[ 1.55555556, 8. , 10.66666667]])
3、scipy简单应用
scipy在numpy的基础上增加了大量用于数学计算、科学计算以及工程计算的模块,包括线性代数、常微分方程数值求解、信号处理、图像处理、稀疏矩阵等等。
| 模块 | 说明 |
|
constants |
常数 |
| special |
特殊函数 |
| optimize | 数值优化算法,如最小二乘拟合(leastsq)、函数最小值(fmin系列)、非线性方程组求解(fsolve)等等 |
|
interpolate |
插值(interp1d、interp2d等等) |
|
integrate |
数值积分 |
| signal |
信号处理 |
| ndimage | 图像处理,包括滤波器模块filters、傅里叶变换模块fourier、图像插值模块interpolation、图像测量模块measurements、形态学图像处理模块morphology等等 |
| stats | 统计 |
|
misc |
提供了读取图像文件的方法和一些测试图像 |
|
io |
提供了读取Matlab和Fortran文件的方法 |
(1)scipy的special模块包含了大量函数库,包括基本数学函数、特殊函数以及numpy中的所有函数。
>>> from scipy import special as S >>> S.cbrt(8) # 立方根 2.0 >>> S.exp10(3) # 10**3 1000.0 >>> S.sindg(90) # 正弦函数,参数为角度 1.0 >>> S.round(3.1) # 四舍五入函数 3.0 >>> S.round(3.5) 4.0 >>> S.round(3.499) 3.0 >>> S.comb(5,3) # 从5个中任选3个的组合数 10.0 >>> S.perm(5,3) # 排列数 60.0 >>> S.gamma(4) # gamma函数 6.0 >>> S.beta(10, 200) # beta函数 2.839607777781333e-18 >>> S.sinc(0) # sinc函数 1.0 >>> S.sinc(1) 3.8981718325193755e-17
二、matplotlib库
- matplotlib模块依赖于numpy模块和tkinter模块,可以绘制多种形式的图形,包括线图、直方图、饼状图、散点图、误差线图等等。
- matplotlib是提供数据绘图功能的第三方库,其pyplot子库主要用于实现各种数据展示图形的绘制。
1、matplotlib.pyplot库概述
matplotlib.pyplot是matplotlib的子库,引用方法如下:
>>>import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(1)中文显示
>>>import matplotlib >>>matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='SimHei' >>>matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
拓展:字体
| 字体名称 | 字体英文表示 |
| 宋体 | SimSun |
| 黑体 | SimHei |
| 楷体 | KaiTi |
| 微软雅体 | Microsoft YaHei |
| 隶书 | LiSu |
| 仿宋 | FangSong |
| 幼圆 | YouYuan |
| 华文宋体 | STSong |
| 华文黑体 | STHeiti |
| 苹果丽中黑 | Apple LiGothic Medium |
(2)matplotlib.pyplot库解析
使用plt代替matplotlib.pyplot;plt子库提供了一批操作和绘图函数,每个函数代表对图像进行的一个操作,比如创建绘图区域,添加标注或者修改坐标轴等。这些函数采用pl.<b>()形式调用,其中<b>是具体函数名称。
plt库的绘图区域函数:
| 函数 | 描述 |
| plt.figure(figsize=None,facecolor=None) | 创建一个全局绘图区域 |
| plt.axes(rect,axisbg='w') | 创建一个坐标系风格的子绘图区域 |
| plt.subplot(nrows,ncols,plot_number) | 在全局绘图区域中创建一个子绘图区域 |
| plt.subplots_adjust() | 调整子绘图区域的布局 |
1.1//使用figure()函数创建一个全局绘图区域,figsize参数可以指定绘图区域的宽度和高度,单位为英寸
>>>plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
1.2// 绘图之前也可以不调用figure()函数创建全局区域
>>>plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
>>>plt.show()
1.3// subplot()用于在全局绘图区域内创建子绘图区域,其参数表示将全局绘图区域分成 nrows行和 ncols 列,并根据先行后列的计算方式在plot_number位置生成一个坐标系。(下面代码表示全局绘图区域被分割成3*2的网格,在第4个位置绘制了一个坐标系)
>>>plt.subplot(324)
>>>plt.show()
1.4// axes()默认创建一个subplot(111)坐标系,参数rec=[left,bottom,width,height]中4个变量的范围都为[0,1],表示坐标系与全局绘图区域的关系;axisbg指背景色,默认为white。
>>>plt.axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.7, 0.3 ],axisbg='y') >>>plt.show()
2、plt 子库提供了一组读取和显示相关的函数,用于在绘图区域中增加显示内容及读入数据
| 函数 | 描述 |
| plt.legend() | 在绘图区域中国放置绘图标签(也称图注) |
| plt.show() | 显示创建的绘图对象 |
| plt.matshow() | 在窗口显示数组矩阵 |
| plt.imshow() | 在axes上显示图像 |
| plt.imsave() | 保存数组为图像文件 |
| plt.imread() | 从图像文件中读取数组 |
3、plt 库的基本图表函数(共17个)
| 操作 | 描述 |
| plt.plot(x,y,label,width) | 根据x、y数组绘制直线、曲线 |
| plt.boxplot(date,notch,position) | 绘制一个箱型图(Box-plot) |
| plt.bar(left,height,width,bottom) | 绘制一个条形图 |
| plt.barh(bottom,width,height,left) | 绘制一个横向条形图 |
| plt.polar(theta,r) | 绘制一个极坐标图 |
| plt.pie(date,explode) | 绘制饼图 |
| plt.psd(x,NFFT=256,pad_to,Fs) | 绘制功率谱密度图 |
| plt.specgram(x,NFFT=256,pad_to,F) | 绘制谱图 |
| plt.cohere(x,y,NFFT=256,Fs) | 绘制X-Y的相关性函数 |
| plt.scatter() | 绘制散点图(x,y是长度相同的序列) |
| plt.step(x,y,where) | 绘制步阶图 |
| plt.hist(x,bins,normed) | 绘制直方图 |
| plt.contour(X,Y,Z,N) | 绘制等值线 |
| plt.vlines() | 绘制垂直线 |
| plt.stem(x,y,linefmt,markermt,basefmt) | 绘制曲线每个点到水平轴线的垂线 |
| plt.plot_date() | 绘制数据日期 |
| plt.plotfile() | 绘制数据后写入文件 |
另:plot()函数是用于绘制直线的最基础的函数,调用方式很灵活,x和y可以是numpy计算出的数组,并用关键字参数指定各种属性。其中,label表示设置标签并在图例(legend)中显示,color表示曲线的颜色,linewidth表示曲线的宽度。在字符串前后添加“$”符号,与latex中绘制公式差不多。
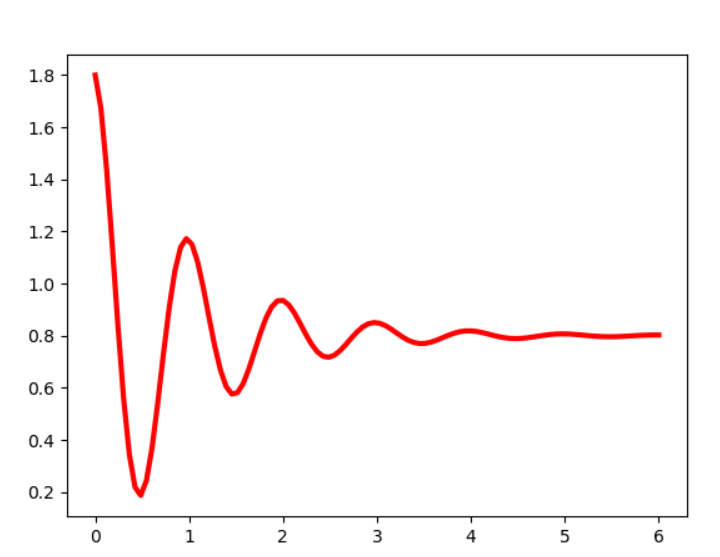
eg.绘制基本三角函数
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=np.linspace(0,6,100) y=np.cos(2*np.pi*x)*np.exp(-x)+0.8 plt.plot(x,y,'k',color='r',linewidth=3,linestyle='-') plt.show()
4.plt库的坐标轴设置函数
| 函数 | 描述 |
| plt.axis('V','off','equal','scaled',tight','image') | 获取设置轴属性的快捷方法 |
| plt.xlim(xmin,xmax) | 设置当前x轴取值范围 |
| plt.ylim(ymin,ymax) | 设置当前y轴取值范围 |
| plt.xscale() | 设置x轴缩放 |
| plt.yscale() | 设置y轴缩放 |
| plt.autoscale() | 自动缩放轴视图的数据 |
| plt.text(x,y,s,fontdic,withdash) | 为axes图轴添加注释 |
| plt.thetagrids(angles,labels,fmt,frac) | 设置极坐标网络theta的位置 |
| plt.grid(on/off) | 打开或者关闭坐标网络 |
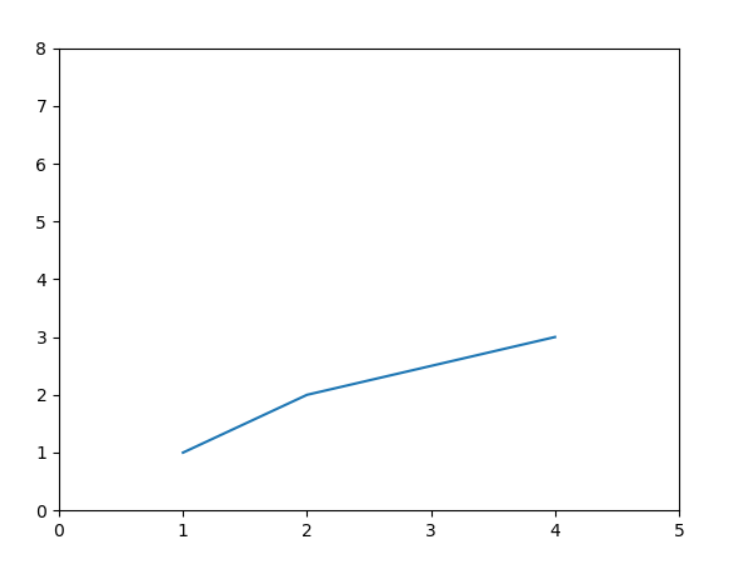
eg.(图如下:)
>>>import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>>plt.plot([1,2,4],[1,2,3]) >>>plt.axis() #获取当前坐标轴范围 (0.85, 4.15, 0.9, 3.1) >>>plt.axis([0,5,0,8]) #4个变量分别是[xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax] [0, 5, 0, 8] plt.show()
5.plt库的标签设置函数
| 函数 | 描述 |
| plt.figlegend(handles,label,loc) | 为全局绘图区域放置图注 |
| plt.legend() | 为当前坐标图放置图注 |
| plt.xlabel() | 设置当前x轴的标签 |
| plt.ylabel() | 设置当前y轴的标签 |
| plt.xticks(array,'a','b','c') | 设置当前x轴刻度位置的标签和值 |
| plt.yticks(array,'a','b','c') | 设置当前y轴刻度位置的标签和值 |
| plt.clabel(cs,v) | 为等值线图设置标签 |
| plt.get_figlabels() | 返回当前绘图区域的标签列表 |
| plt.figtext(x,y,s,fontdic) | 为全局绘图区域添加中心标题 |
| plt.title() | 设置标题 |
| plt.suptitle() | 为当前绘图区域添加中心标题 |
| plt.text(x,y,s,fontdic,withdash) | 为坐标轴添加注释 |
| plt.annotate(note,xy,xytext,xycoords,textcoords,arrowprops) | 用箭头在指定数据点创建一个注释或一段文本 |
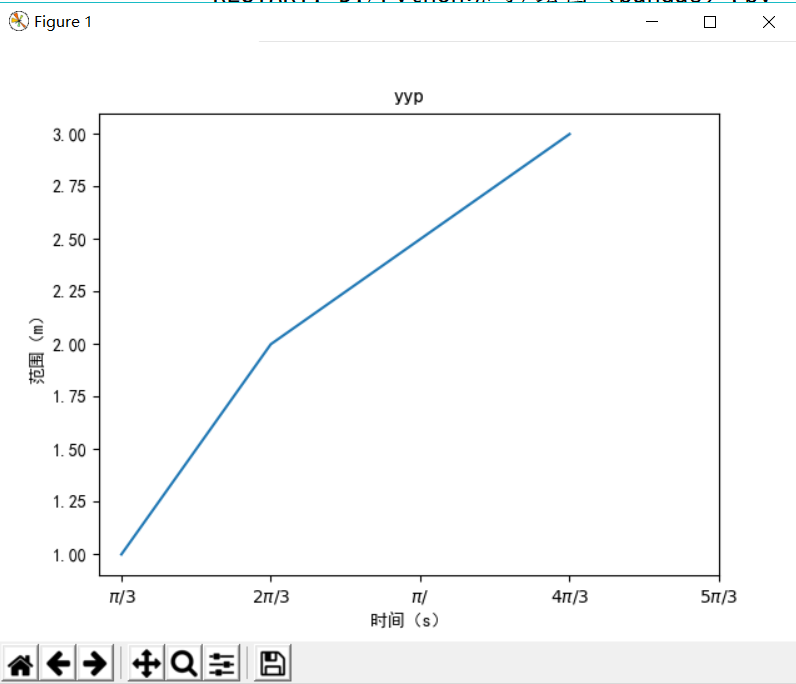
eg.带标签的坐标系
eg.带标签的坐标系
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='SimHei' matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] plt.plot([1,2,4],[1,2,3]) plt.title('yyp') #坐标系标题 plt.xlabel('时间(s)') plt.ylabel('范围(m)') plt.xticks([1,2,3,4,5],[r'$pi/3$',r'$2pi/3$',r'$pi/$',r'$4pi/3$',r'$5pi/3$',]) plt.show()
6.plt库提供了三个区域填充函数,对绘图区域填充颜色
| 函数 | 描述 |
| fill(x,y,color) | 填充多边形 |
| fill_between(x,y1,y2,where,color) | 填充两条曲线围成的多边形 |
| fill_betweenx(y,x1,x2,where,hold) | 填充两条水平线之间的区域 |
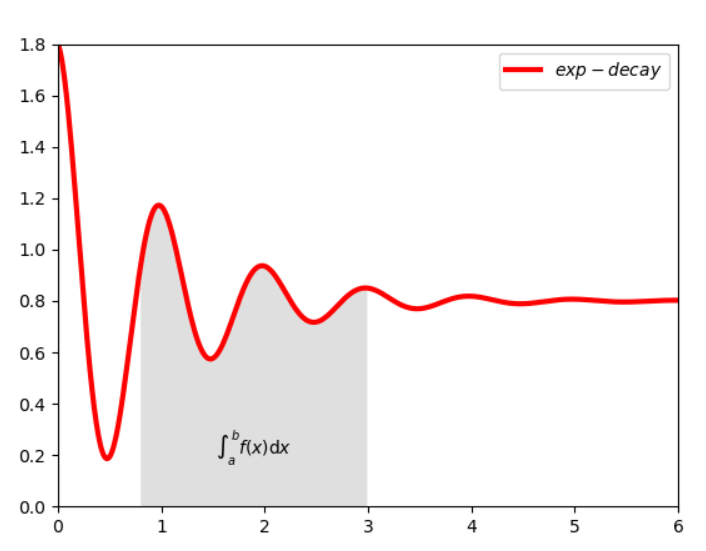
eg.带局部阴影的坐标系
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x=np.linspace(0,10,1000) y=np.cos(2*np.pi*x)*np.exp(-x)+0.8 plt.plot(x,y,'k',color='r',label="$exp-decay$",linewidth=3) plt.axis([0,6,0,1.8]) ix=(x>0.8)&(x<3) plt.fill_between(x,y,0,where=ix, facecolor='grey',alpha=0.25) plt.text(0.5*(0.8+3),0.2,r"$int_a^b f(x)mathrm{d}x$", horizontalalignment='center') plt.legend() plt.show()
如图所示:
三、多级雷达图绘制[numpy、matplotlib综合运用]
(1)
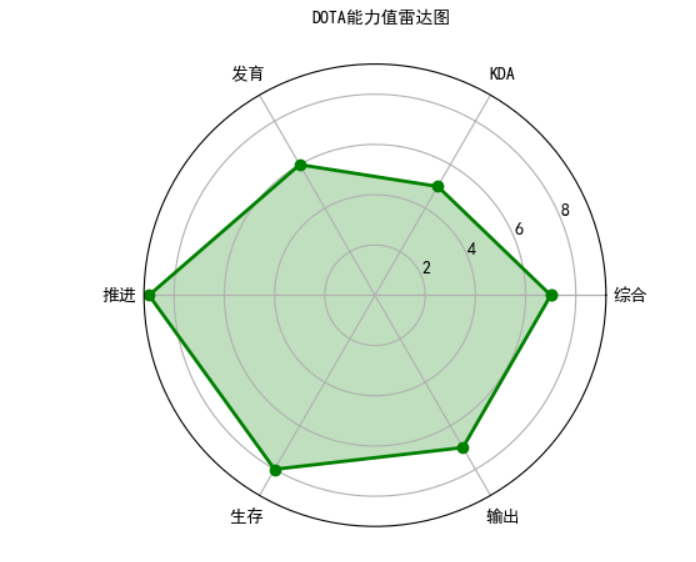
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='simHei' matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['simHei'] #显示中文 labels=np.array(['综合','KDA','发育','推进','生存','输出']) nAttr=6 date=np.array([7,5,6,9,8,7]) #数据值 angles=np.linspace(0,2*np.pi,nAttr,endpoint=False) #画出极坐标(角度) date=np.concatenate((date,[date[0]])) angles=np.concatenate((angles,[angles[0]])) fig=plt.figure(facecolor="white") #创建一个全局绘图区域,背景色为白色 plt.subplot(111,polar=True) #创建子绘图区域,1*1网格,在第1个位置绘图(极坐标), plt.plot(angles,date,'bo-',color='g',linewidth=2) plt.fill(angles,date,facecolor='g',alpha=0.25) #填充颜色 plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi,labels) #设置极坐标网络 theta 的位置 plt.figtext(0.52,0.95,'DOTA能力值雷达图',ha='center') #标签 plt.grid(True) # 显示背景的网格线 plt.savefig('dota_radar.JPG') #保存图片 plt.show()
图如下:
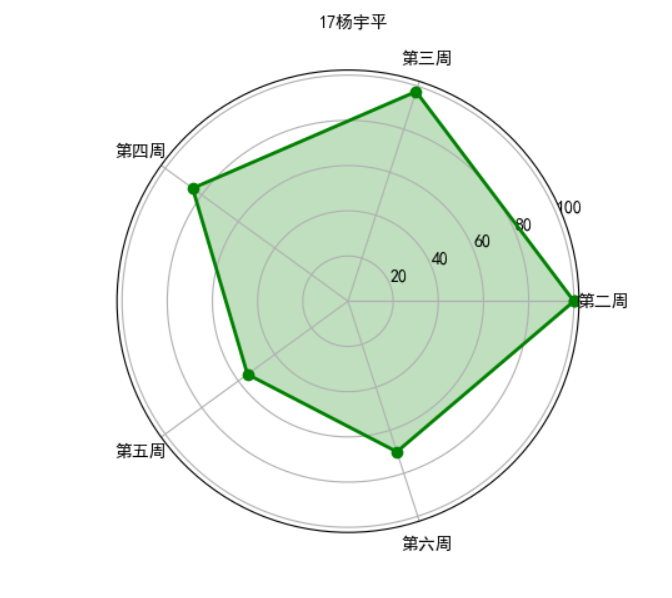
(2)【作业: 把python123作业的成绩,画出雷达图,写上学号。】
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='simHei' matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['simHei'] labels=np.array(['第二周','第三周','第四周','第五周','第六周']) nAttr=5 date=np.array([100,97.5,85,55,70])#数据值 angles=np.linspace(0,2*np.pi,nAttr,endpoint=False) date=np.concatenate((date,[date[0]])) angles=np.concatenate((angles,[angles[0]])) fig=plt.figure(facecolor="white") plt.subplot(111,polar=True) plt.plot(angles,date,'bo-',color='g',linewidth=2) plt.fill(angles,date,facecolor='g',alpha=0.25) plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi,labels) plt.figtext(0.52,0.95,'17杨宇平',ha='center') plt.grid(True) plt.savefig('grade.JPG') plt.show()
雷达图如图所示:
四、图像的手绘效果
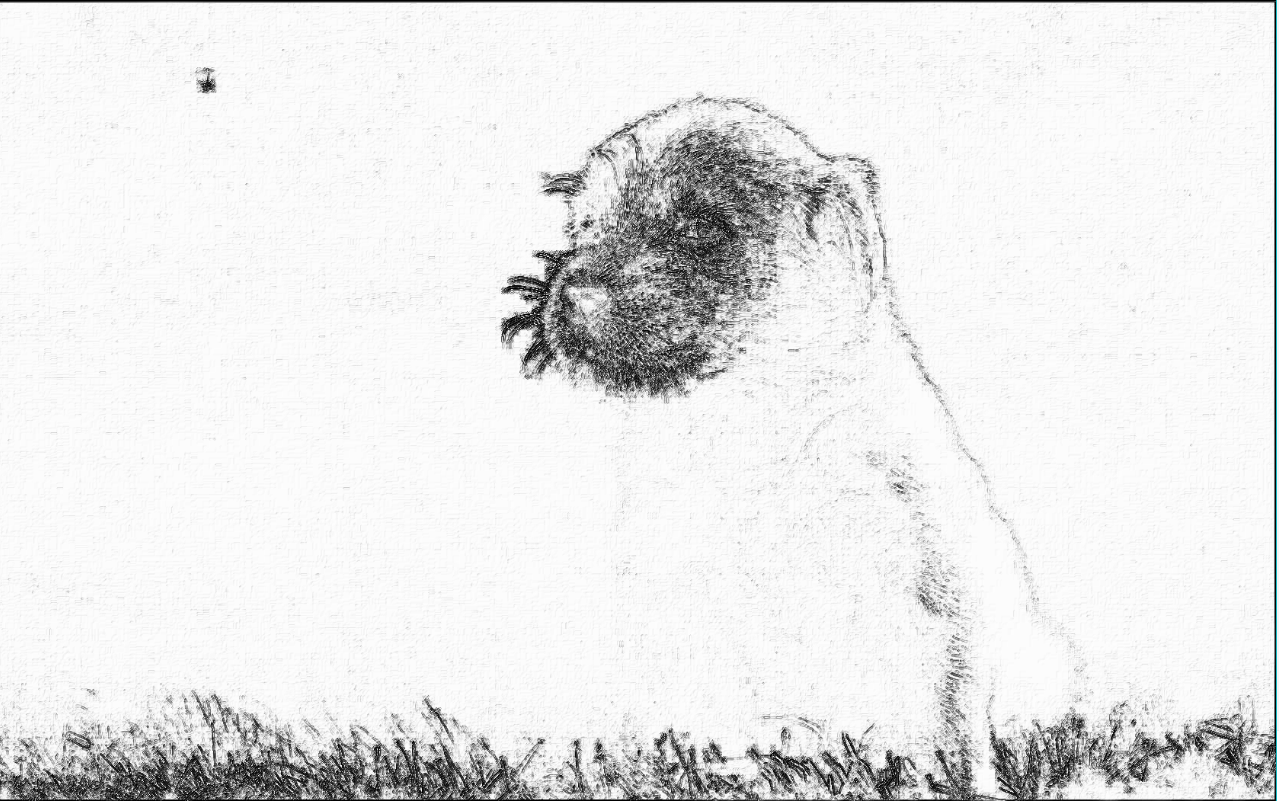
这是一个使用 numpy 和 PLT 库提取图像特征形成手绘效果的实例
from PIL import Image import numpy as np a = np.asarray(Image.open("D:/Python练习/小宠物.jpg").convert('L')).astype('float') depth = 10. # (0-100) grad = np.gradient(a) #取图像灰度的梯度值 grad_x, grad_y =grad #分别取横纵图像梯度值 grad_x = grad_x*depth/100. grad_y = grad_y*depth/100. A = np.sqrt(grad_x**2 + grad_y**2 + 1.) uni_x = grad_x/A uni_y = grad_y/A uni_z = 1./A vec_el = np.pi/2.2 # 光源的俯视角度,弧度值 vec_az = np.pi/4. # 光源的方位角度,弧度值 dx = np.cos(vec_el)*np.cos(vec_az) #光源对x 轴的影响 dy = np.cos(vec_el)*np.sin(vec_az) #光源对y 轴的影响 dz = np.sin(vec_el) #光源对z 轴的影响 b = 255*(dx*uni_x + dy*uni_y + dz*uni_z) #光源归一化 b = b.clip(0,255) im = Image.fromarray(b.astype('uint8')) #重构图像 im.show()

五、Python实现正态分布
绘制正态分布概率密度函数
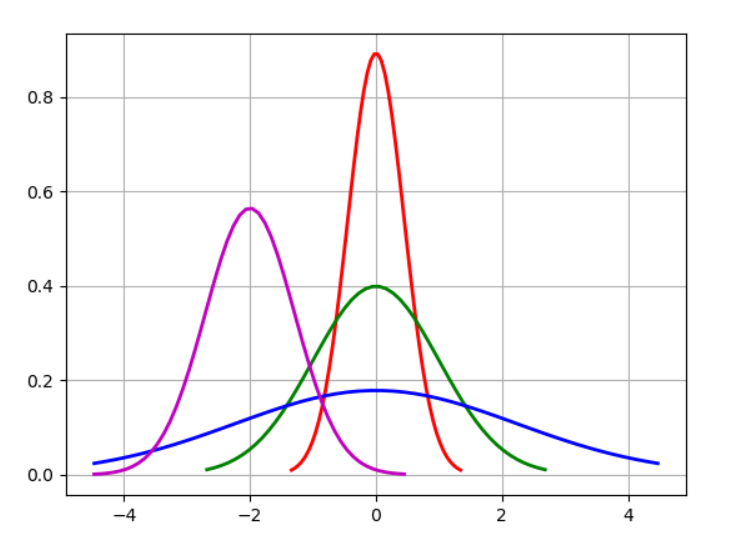
# Python实现正态分布 # 绘制正态分布概率密度函数 import math import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib u = 0 # 均值μ u01 = -2 sig = math.sqrt(0.2) # 标准差δ sig01 = math.sqrt(1) sig02 = math.sqrt(5) sig_u01 = math.sqrt(0.5) x = np.linspace(u - 3*sig, u + 3*sig, 50) x_01 = np.linspace(u - 6 * sig, u + 6 * sig, 50) x_02 = np.linspace(u - 10 * sig, u + 10 * sig, 50) x_u01 = np.linspace(u - 10 * sig, u + 1 * sig, 50) y_sig = np.exp(-(x - u) ** 2 /(2* sig **2))/(math.sqrt(2*math.pi)*sig) y_sig01 = np.exp(-(x_01 - u) ** 2 /(2* sig01 **2))/(math.sqrt(2*math.pi)*sig01) y_sig02 = np.exp(-(x_02 - u) ** 2 / (2 * sig02 ** 2)) / (math.sqrt(2 * math.pi) * sig02) y_sig_u01 = np.exp(-(x_u01 - u01) ** 2 / (2 * sig_u01 ** 2)) / (math.sqrt(2 * math.pi) * sig_u01) plt.plot(x, y_sig, "r-", linewidth=2) plt.plot(x_01, y_sig01, "g-", linewidth=2) plt.plot(x_02, y_sig02, "b-", linewidth=2) plt.plot(x_u01, y_sig_u01, "m-", linewidth=2) # plt.plot(x, y, 'r-', x, y, 'go', linewidth=2,markersize=8) plt.grid(True) plt.show()
图如下: