At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
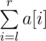 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 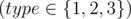 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
题目大意 维护一个数列,有3种操作,分别是区间求和,区间取模和单点修改。
显然线段树(请不要问我为什么。。。学长的Tag打在那儿的)
区间求和和单点修改都是线段树的拿手好戏,但是对于区间取模似乎不是那么好做。考虑可以区间批量更新sum吗?显然不行。
但是考虑到这里只有单点修改,而且对一个大于模数的数取模,它的值至多为它原来的值的一半。
所以区间记录一个最大值剪枝,每次区间取模先判断是否有必要进行递归取模,如果有,就暴力递归下去,在底层修改。
Code
1 /** 2 * Codeforces 3 * Problem#438D 4 * Accepted 5 * Time: 436ms 6 * Memory: 8740k 7 */ 8 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 9 #ifndef WIN32 10 #define Auto "%lld" 11 #else 12 #define Auto "%I64d" 13 #endif 14 using namespace std; 15 16 typedef class SegTreeNode { 17 public: 18 int maxv; 19 long long sum; 20 SegTreeNode *l, *r; 21 22 SegTreeNode():maxv(0), sum(0), l(NULL), r(NULL) { } 23 24 inline void pushUp() { 25 maxv = max(l->maxv, r->maxv); 26 sum = l->sum + r->sum; 27 } 28 }SegTreeNode; 29 30 typedef class SegTree { 31 public: 32 SegTreeNode* root; 33 34 SegTree():root(NULL) { } 35 SegTree(int n, int* a) { 36 build(root, 1, n, a); 37 } 38 39 void build(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int* a) { 40 node = new SegTreeNode(); 41 if(l == r) { 42 node->sum = node->maxv = a[l]; 43 return; 44 } 45 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 46 build(node->l, l, mid, a); 47 build(node->r, mid + 1, r, a); 48 node->pushUp(); 49 } 50 51 void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int idx, int val) { 52 if(l == r) { 53 node->maxv = node->sum = val; 54 return; 55 } 56 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 57 if(idx <= mid) update(node->l, l, mid, idx, val); 58 else update(node->r, mid + 1, r, idx, val); 59 node->pushUp(); 60 } 61 62 void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int moder) { 63 if(l == r) { 64 node->maxv = (node->sum %= moder); 65 return; 66 } 67 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 68 if(qr <= mid && node->l->maxv >= moder) update(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr, moder); 69 else if(ql > mid && node->r->maxv >= moder) update(node->r, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, moder); 70 else if(qr > mid && ql <= mid) { 71 if(node->l->maxv >= moder) 72 update(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid, moder); 73 if(node->r->maxv >= moder) 74 update(node->r, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, qr, moder); 75 } 76 node->pushUp(); 77 } 78 79 long long query(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) { 80 if(l == ql && r == qr) { 81 return node->sum; 82 } 83 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 84 if(qr <= mid) return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr); 85 if(ql > mid) return query(node->r, mid + 1, r, ql, qr); 86 return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid) + query(node->r, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, qr); 87 } 88 }SegTree; 89 90 int n, m; 91 int* arr; 92 SegTree st; 93 inline void init() { 94 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); 95 arr = new int[(n + 1)]; 96 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 97 scanf("%d", arr + i); 98 st = SegTree(n, arr); 99 } 100 101 inline void solve() { 102 int opt, a, b, c; 103 while(m--) { 104 scanf("%d%d%d", &opt, &a, &b); 105 if(opt == 1) { 106 printf(Auto" ", st.query(st.root, 1, n, a, b)); 107 } else if(opt == 2) { 108 scanf("%d", &c); 109 st.update(st.root, 1, n, a, b, c); 110 } else { 111 st.update(st.root, 1, n, a, b); 112 } 113 } 114 } 115 116 int main() { 117 init(); 118 solve(); 119 return 0; 120 }