Windy has N balls of distinct weights from 1 unit to N units. Now he tries to label them with 1 to N in such a way that:
- No two balls share the same label.
- The labeling satisfies several constrains like "The ball labeled with a is lighter than the one labeled with b".
Can you help windy to find a solution?
Input
The first line of input is the number of test case. The first line of each test case contains two integers, N (1 ≤ N ≤ 200) and M (0 ≤ M ≤ 40,000). The next M line each contain two integers a and b indicating the ball labeled with a must be lighter than the one labeled with b. (1 ≤ a, b ≤ N) There is a blank line before each test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the balls' weights from label 1 to labelN. If several solutions exist, you should output the one with the smallest weight for label 1, then with the smallest weight for label 2, then with the smallest weight for label 3 and so on... If no solution exists, output -1 instead.
Sample Input
5 4 0 4 1 1 1 4 2 1 2 2 1 4 1 2 1 4 1 3 2
Sample Output
1 2 3 4 -1 -1 2 1 3 4 1 3 2 4
题目大意 找出原图的一个拓扑序,使得1尽量靠前,2尽量靠前....(注意输出的是第i个球的重量是第几小)。无解输出-1.
我学长给出了一个正确性很显然的做法
正向建图,把当前集合中的点中最小点找出来,然后再暴力统计有多少个点指向它,那么这些点一定在它之前,就可以将原DAG分成两部分递归处理。时间复杂度O(n(n + m))
Code
还有个做法是反向建图,然后用大根堆去跑拓扑排序,最后输出的时候reverse一遍。虽然n变成了log2n,但是似乎正确性不是那么的显然。
如果解释的话可以这么想,正向建图,跑小根堆先把小的取走,保证了在大的尽量在后面,但是无法保证小的尽量在前面,比如说下面这个建出来的DAG。
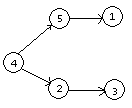 这真是一个优美的反例。
这真是一个优美的反例。
而反向建图跑大根堆,可以保证大的先被取走,自然小的就留在后面,reverse后,小的就跑到前面去了。
下面给出一个并不太严谨的证明(有问题一定要指出来)
假定存在一个更优的答案,那么第一处不相同的地方一定满足这个算法跑出来的值比这个答案大,因为前面的都相同,又因为都是1 ~ n的一个排列,那么意味着一定存在某个位置,这个答案比这个算法跑出来的值大。这意味着答案取出了比拓扑序某个时候,入度为0的点的最大值还大的数,这显然是不可能的。所以不存在更有的答案,所以这个答案就是最优的答案。
Code
1 /** 2 * poj 3 * Problem#3687 4 * Accepted 5 * Time:32ms 6 * Memory:1116k 7 */ 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <cstdio> 10 #include <ctime> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <cctype> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include <cstdlib> 15 #include <fstream> 16 #include <sstream> 17 #include <algorithm> 18 #include <map> 19 #include <set> 20 #include <stack> 21 #include <queue> 22 #include <vector> 23 #include <stack> 24 #ifndef WIN32 25 #define Auto "%lld" 26 #else 27 #define Auto "%I64d" 28 #endif 29 using namespace std; 30 typedef bool boolean; 31 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 32 const double eps = 1e-6; 33 const int binary_limit = 128; 34 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 35 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 36 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 37 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 38 template<typename T> 39 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 40 char x; 41 int aFlag = 1; 42 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -1); 43 if(x == -1) { 44 ungetc(x, stdin); 45 return false; 46 } 47 if(x == '-'){ 48 x = getchar(); 49 aFlag = -1; 50 } 51 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 52 ungetc(x, stdin); 53 u *= aFlag; 54 return true; 55 } 56 57 ///map template starts 58 typedef class Edge{ 59 public: 60 int end; 61 int next; 62 Edge(const int end = 0, const int next = -1):end(end), next(next){} 63 }Edge; 64 65 typedef class MapManager{ 66 public: 67 int ce; 68 int *h; 69 vector<Edge> edge; 70 MapManager(){} 71 MapManager(int points):ce(0){ 72 h = new int[(const int)(points + 1)]; 73 memset(h, -1, sizeof(int) * (points + 1)); 74 } 75 inline void addEdge(int from, int end){ 76 edge.push_back(Edge(end, h[from])); 77 h[from] = ce++; 78 } 79 inline void addDoubleEdge(int from, int end){ 80 addEdge(from, end); 81 addEdge(end, from); 82 } 83 Edge& operator [] (int pos) { 84 return edge[pos]; 85 } 86 inline void clear() { 87 edge.clear(); 88 delete[] h; 89 } 90 }MapManager; 91 #define m_begin(g, i) (g).h[(i)] 92 #define m_endpos -1 93 ///map template ends 94 95 int n, m; 96 MapManager g; 97 int* dag; 98 int* dep; 99 100 inline boolean init() { 101 if(!readInteger(n)) return false; 102 readInteger(m); 103 g = MapManager(n); 104 dag = new int[(n + 1)]; 105 dep = new int[(n + 1)]; 106 memset(dag, 0, sizeof(int) * (n + 1)); 107 for(int i = 1, a, b; i <= m; i++) { 108 readInteger(a); 109 readInteger(b); 110 g.addEdge(b, a); 111 dag[a]++; 112 } 113 return true; 114 } 115 116 priority_queue<int> que; 117 inline void topu() { 118 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 119 if(!dag[i]) { 120 que.push(i); 121 } 122 int cnt = 0; 123 while(!que.empty()) { 124 int e = que.top(); 125 dep[e] = cnt++; 126 que.pop(); 127 for(int i = m_begin(g, e); i != m_endpos; i = g[i].next) { 128 int& eu = g[i].end; 129 dag[eu]--; 130 if(!dag[eu]) 131 que.push(eu); 132 } 133 } 134 } 135 136 inline void solve() { 137 topu(); 138 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 139 if(dag[i]) { 140 puts("-1"); 141 return; 142 } 143 } 144 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 145 printf("%d ", n - dep[i]); 146 putchar(' '); 147 } 148 149 inline void clear() { 150 g.clear(); 151 delete[] dep; 152 delete[] dag; 153 } 154 155 int T; 156 int main() { 157 readInteger(T); 158 while(T--) { 159 init(); 160 solve(); 161 clear(); 162 } 163 return 0; 164 }