liympanda, one of Ikki’s friend, likes playing games with Ikki. Today after minesweeping with Ikki and winning so many times, he is tired of such easy games and wants to play another game with Ikki.
liympanda has a magic circle and he puts it on a plane, there are n points on its boundary in circular border: 0, 1, 2, …, n − 1. Evil panda claims that he is connecting m pairs of points. To connect two points, liympanda either places the link entirely inside the circle or entirely outside the circle. Now liympanda tells Ikki no two links touch inside/outside the circle, except on the boundary. He wants Ikki to figure out whether this is possible…
Despaired at the minesweeping game just played, Ikki is totally at a loss, so he decides to write a program to help him.
Input
The input contains exactly one test case.
In the test case there will be a line consisting of of two integers: n and m (n ≤ 1,000, m ≤ 500). The following m lines each contain two integers ai and bi, which denote the endpoints of the ith wire. Every point will have at most one link.
Output
Output a line, either “panda is telling the truth...” or “the evil panda is lying again”.
Sample Input
4 2 0 1 3 2
Sample Output
panda is telling the truth...
题目大意 圆上有n个点,从左至右依次编号为0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1。给出m对点的编号,连接这m对点(连线只能全在圆外或者圆内),问是否可以使得这m条连线不相交。
首先看一下可能会相交的情况:
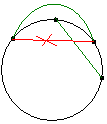
即存在两对点l1和r1,l2和r2,且满足 。
。
我们将每条连线拆成2个点,(2 * i - 1)和2 * i,表示在圆内还是在圆外。于是这道题就转化成了2-sat问题。Tarjan完了缩点,再判断是否存在每条连线对应的两个点在同一强连通分量内,如果有,则无解,否则有解。
Code
1 /** 2 * poj 3 * Problem#3207 4 * Accepted 5 * Time:32ms 6 * Memory:8604k 7 */ 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <cstdio> 10 #include <ctime> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <cctype> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include <cstdlib> 15 #include <fstream> 16 #include <sstream> 17 #include <algorithm> 18 #include <map> 19 #include <set> 20 #include <stack> 21 #include <queue> 22 #include <vector> 23 #include <stack> 24 #ifndef WIN32 25 #define Auto "%lld" 26 #else 27 #define Auto "%I64d" 28 #endif 29 using namespace std; 30 typedef bool boolean; 31 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 32 const double eps = 1e-6; 33 const int binary_limit = 128; 34 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 35 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 36 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 37 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 38 template<typename T> 39 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 40 char x; 41 int aFlag = 1; 42 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -1); 43 if(x == -1) { 44 ungetc(x, stdin); 45 return false; 46 } 47 if(x == '-'){ 48 x = getchar(); 49 aFlag = -1; 50 } 51 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 52 ungetc(x, stdin); 53 u *= aFlag; 54 return true; 55 } 56 57 ///map template starts 58 typedef class Edge{ 59 public: 60 int end; 61 int next; 62 Edge(const int end = 0, const int next = 0):end(end), next(next){} 63 }Edge; 64 65 typedef class MapManager{ 66 public: 67 int ce; 68 int *h; 69 Edge *edge; 70 MapManager(){} 71 MapManager(int points, int limit):ce(0){ 72 h = new int[(const int)(points + 1)]; 73 edge = new Edge[(const int)(limit + 1)]; 74 memset(h, 0, sizeof(int) * (points + 1)); 75 } 76 inline void addEdge(int from, int end){ 77 edge[++ce] = Edge(end, h[from]); 78 h[from] = ce; 79 } 80 inline void addDoubleEdge(int from, int end){ 81 addEdge(from, end); 82 addEdge(end, from); 83 } 84 Edge& operator [] (int pos) { 85 return edge[pos]; 86 } 87 }MapManager; 88 #define m_begin(g, i) (g).h[(i)] 89 ///map template ends 90 91 int n, m; 92 MapManager g; 93 int *ls, *rs; 94 95 inline void init() { 96 readInteger(n); 97 readInteger(m); 98 ls = new int[(m + 1)]; 99 rs = new int[(m + 1)]; 100 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 101 readInteger(ls[i]); 102 readInteger(rs[i]); 103 if(ls[i] > rs[i]) 104 swap(ls[i], rs[i]); 105 } 106 } 107 108 inline void init_map() { 109 g = MapManager(2 * m + 3, 2 * n * m); 110 for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { 111 for(int j = i + 1; j <= m; j++) { 112 if(ls[i] <= ls[j] && rs[i] >= ls[j] && rs[i] <= rs[j]) { 113 g.addDoubleEdge(2 * i - 1, 2 * j); 114 g.addDoubleEdge(2 * j - 1, 2 * i); 115 } 116 } 117 } 118 } 119 120 int cnt = 0; 121 int* visitID; 122 int* exitID; 123 boolean* visited; 124 boolean* instack; 125 stack<int> s; 126 int* belong; 127 inline void init_tarjan() { 128 int an = 2 * m + 3; 129 visitID = new int[(an)]; 130 exitID = new int[(an)]; 131 visited = new boolean[(an)]; 132 instack = new boolean[(an)]; 133 belong = new int[(an)]; 134 memset(visited, false, sizeof(boolean) * an); 135 memset(instack, false, sizeof(boolean) * an); 136 } 137 138 void tarjan(int node) { 139 visitID[node] = exitID[node] = cnt++; 140 visited[node] = instack[node] = true; 141 s.push(node); 142 143 for(int i = m_begin(g, node); i; i = g[i].next) { 144 int& e = g[i].end; 145 if(!visited[e]) { 146 tarjan(e); 147 smin(exitID[node], exitID[e]); 148 } else if(instack[e]) { 149 smin(exitID[node], visitID[e]); 150 } 151 } 152 153 if(visitID[node] == exitID[node]) { 154 int now = -1; 155 while(now != node) { 156 now = s.top(); 157 s.pop(); 158 instack[now] = false; 159 belong[now] = node; 160 } 161 } 162 } 163 164 inline void solve() { 165 for(int i = 1; i < (m << 1); i += 2) 166 if(belong[i] == belong[i + 1]) { 167 puts("the evil panda is lying again"); 168 return; 169 } 170 puts("panda is telling the truth..."); 171 } 172 173 int main() { 174 init(); 175 init_map(); 176 init_tarjan(); 177 for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * m; i++) 178 if(!visited[i]) 179 tarjan(i); 180 solve(); 181 return 0; 182 }